Sugar, a ubiquitous ingredient in our daily lives, often sparks curiosity about its nutritional value. One common question that arises is, "How many calories are in a cup of sugar?" This article aims to delve into the world of sugar, exploring its calorie content, its impact on our health, and offering insights into making informed dietary choices.
Understanding Sugar Calories
Sugar, scientifically known as sucrose, is a simple carbohydrate that provides a quick source of energy for our bodies. When we consume sugar, it is broken down into glucose and fructose, which are then absorbed into our bloodstream. The calorie content of sugar is a significant factor to consider when monitoring our daily intake.
Calorie Content in a Cup of Sugar

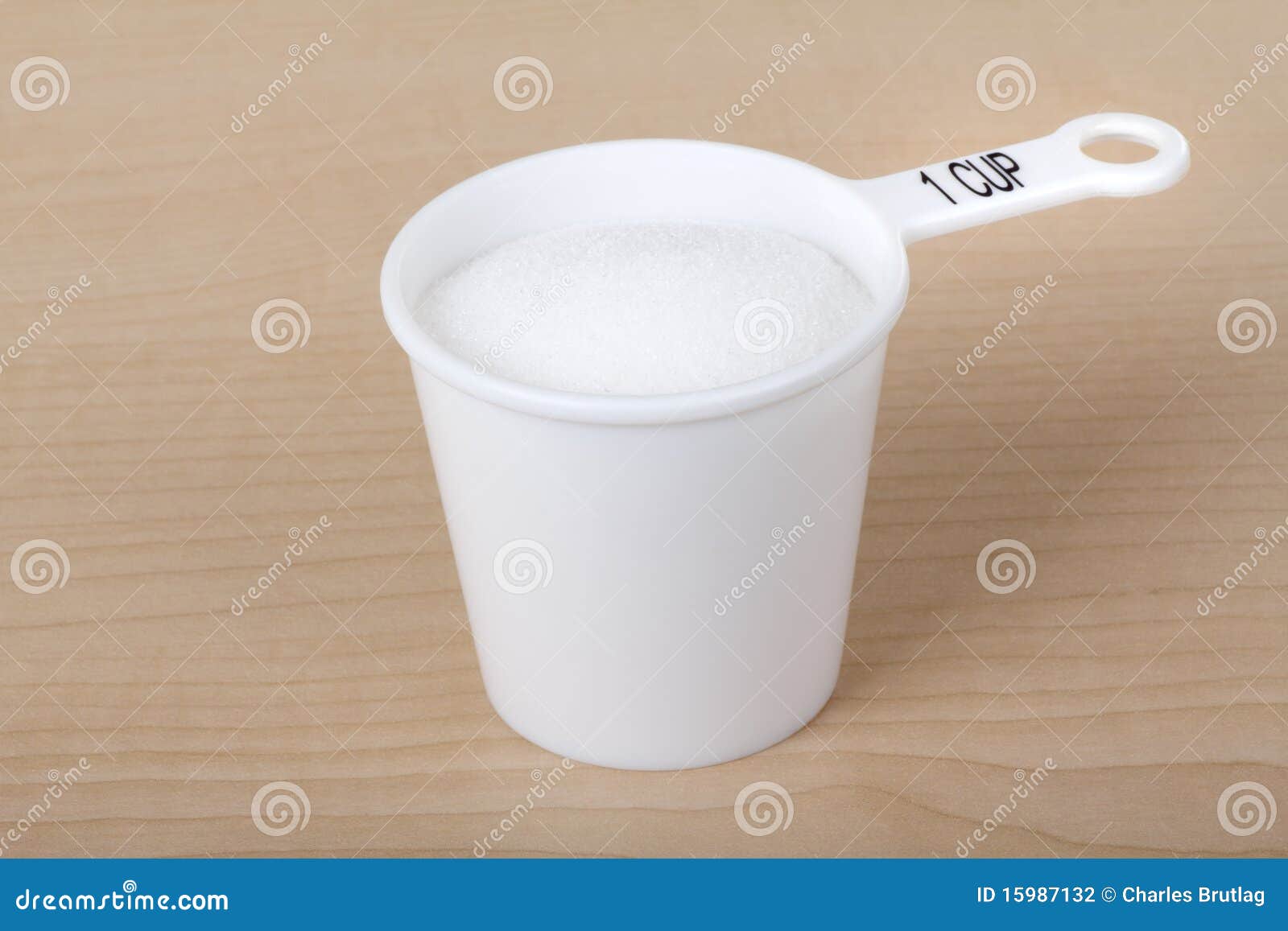
A standard cup of granulated sugar, which weighs approximately 200 grams, contains around 770 calories. This high calorie count is primarily due to sugar's chemical composition, which consists of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms.
It's important to note that this calorie count represents the energy potential of sugar, and not all of it may be utilized by our bodies. The digestion and absorption of sugar can vary depending on individual factors such as metabolism and overall diet.
Health Implications of Sugar Consumption

While sugar provides a rapid energy boost, excessive consumption can lead to various health concerns. Here are some key points to consider:
- Weight Gain: Sugar is often associated with weight gain due to its high calorie content. Consuming excessive sugar without balancing it with physical activity can lead to an energy imbalance, resulting in weight gain over time.
- Blood Sugar Spikes: Sugar is rapidly absorbed into the bloodstream, causing blood sugar levels to spike. This can lead to energy crashes and cravings for more sugar, creating a cycle of unhealthy eating habits.
- Dental Health: Sugar is a major contributor to dental issues such as tooth decay and cavities. The bacteria in our mouths feed on sugar, producing acids that erode tooth enamel.
- Chronic Diseases: Long-term excessive sugar consumption has been linked to an increased risk of chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and certain types of cancer.
Moderation and Alternative Sweeteners

Given the potential health risks associated with sugar, it is essential to practice moderation and explore alternative sweeteners. Here are some tips to consider:
- Reduce Added Sugars: Limit the consumption of processed foods and beverages that are high in added sugars. Instead, opt for whole foods and natural sweeteners like honey or maple syrup in moderation.
- Natural Sweeteners: Explore natural alternatives to sugar, such as stevia, erythritol, or monk fruit. These sweeteners provide a sweet taste without the excessive calories and potential health risks associated with sugar.
- Read Labels: When purchasing packaged foods, carefully read the ingredient list and nutrition facts. Look for hidden sources of sugar, such as high-fructose corn syrup, dextrose, or maltose.
- Mindful Eating: Pay attention to your sugar intake and be mindful of your body's signals. Avoid mindless snacking and opt for nutritious snacks that satisfy your sweet tooth without the negative health impacts.
Table: Comparison of Sugar and Alternative Sweeteners

| Sweetener | Calories per Cup (g) | Sweetness Level | Health Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sugar (Granulated) | 770 | Moderate | None |
| Honey | 1032 | High | Antibacterial properties |
| Maple Syrup | 964 | High | Rich in antioxidants |
| Stevia | 0 | High | Zero calories, suitable for diabetics |
| Erythritol | 0 | Moderate | Low calorie, tooth-friendly |
| Monk Fruit | 0 | High | Natural sweetener, suitable for diabetics |

The table above provides a comparison of different sweeteners based on their calorie content, sweetness level, and potential health benefits. It's important to note that while some alternative sweeteners offer health benefits, they should still be consumed in moderation.
Conclusion

Understanding the calorie content of sugar is crucial for making informed dietary choices. While sugar provides a quick energy boost, excessive consumption can lead to various health concerns. By practicing moderation and exploring alternative sweeteners, we can satisfy our sweet tooth while maintaining a balanced and healthy lifestyle. Remember, a balanced diet and mindful eating habits are key to overall well-being.
FAQ

Can I use sugar substitutes to reduce my calorie intake?

+
Yes, sugar substitutes like stevia, erythritol, or monk fruit can be excellent alternatives to reduce calorie intake while still satisfying your sweet cravings. These sweeteners are typically low-calorie or calorie-free, making them a healthier option.
Are there any natural ways to reduce my sugar cravings?

+
Absolutely! Some natural ways to reduce sugar cravings include incorporating more whole foods into your diet, such as fruits and vegetables. Additionally, staying hydrated and getting enough sleep can help regulate your body’s natural sugar cravings.
How can I incorporate alternative sweeteners into my baking?

+
Alternative sweeteners can be used in baking, but it’s important to note that their sweetness levels and baking properties may differ from sugar. Experiment with different ratios and adjust recipes accordingly. Honey and maple syrup are great natural sweeteners for baking, while stevia and erythritol can also be used with some adjustments.
Is it safe to consume sugar in moderation for people with diabetes?
+
For individuals with diabetes, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian to determine the appropriate level of sugar consumption. While some alternative sweeteners like stevia and monk fruit are suitable for diabetics, it’s crucial to monitor blood sugar levels and make informed dietary choices.
What are some tips for reducing added sugars in my diet?
+
Reducing added sugars in your diet can be achieved by limiting processed foods and beverages, reading labels to identify hidden sugars, and opting for whole foods and natural sweeteners in moderation. Additionally, incorporating more fiber-rich foods can help stabilize blood sugar levels and reduce sugar cravings.