Understanding Bradycardia and Its Connection to High Blood Pressure
Bradycardia, a condition characterized by a slow heart rate, has intrigued medical professionals and researchers for years. While a slow heart rate may seem counterintuitive when discussing cardiovascular health, it plays a significant role in understanding and managing various heart-related conditions, including high blood pressure. In this blog post, we will delve into the world of bradycardia, exploring its definition, causes, and most importantly, its intriguing link to high blood pressure. So, let’s get started on this informative journey!
What is Bradycardia?

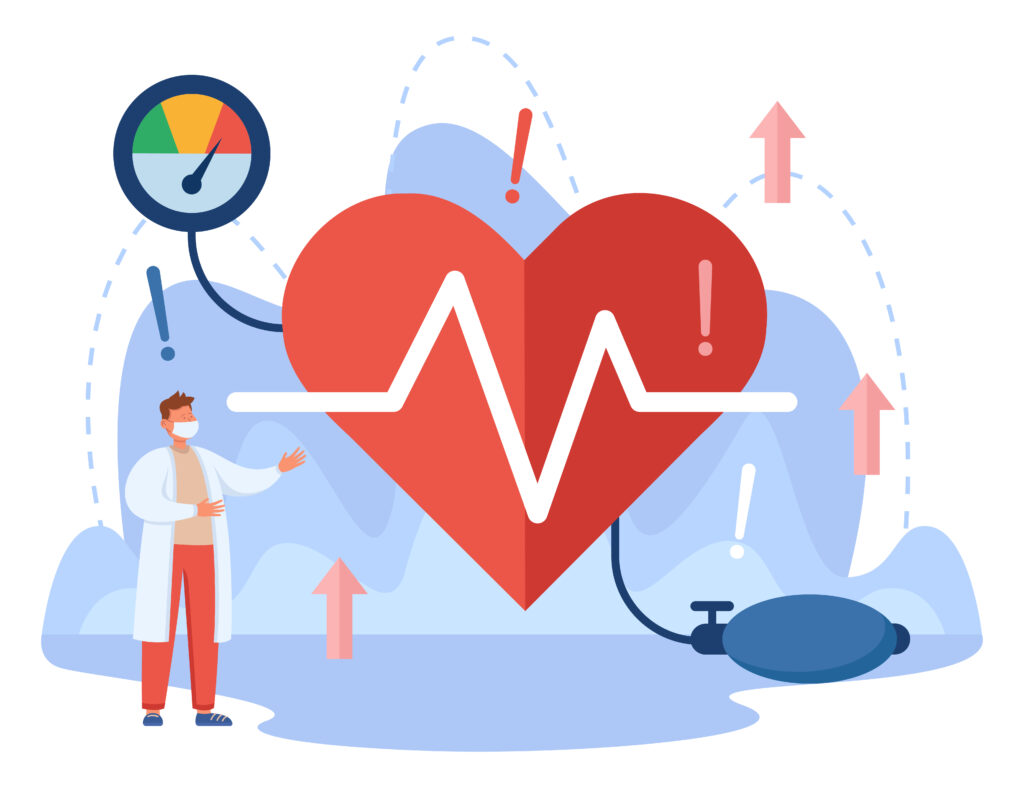
Bradycardia refers to a heart rate that is slower than the normal range, typically defined as a resting heart rate of fewer than 60 beats per minute (bpm). It is often associated with athletes and individuals who engage in regular physical activity, as their hearts become more efficient at pumping blood with each beat, resulting in a lower resting heart rate. However, bradycardia can also be a sign of an underlying medical condition or a side effect of certain medications.
Causes of Bradycardia

The causes of bradycardia can vary, and it is essential to identify the underlying factors to determine the appropriate treatment. Here are some common causes:
- Age-Related Changes: As we age, our heart rate tends to slow down naturally. This is a normal part of the aging process and is often not a cause for concern unless accompanied by other symptoms.
- Cardiac Conditions: Certain heart conditions, such as heart block or sinus node dysfunction, can disrupt the electrical signals that control the heart’s rhythm, leading to bradycardia.
- Medications: Some medications, including beta-blockers and certain anti-arrhythmic drugs, can slow down the heart rate as a side effect. It is crucial to discuss any medication-related concerns with your healthcare provider.
- Sleep Apnea: This sleep disorder, characterized by interrupted breathing during sleep, can cause a drop in oxygen levels, leading to bradycardia.
- Thyroid Disorders: An underactive thyroid gland (hypothyroidism) can result in a slower heart rate.
- Infections: Certain infections, such as endocarditis or myocarditis, can affect the heart’s electrical system and cause bradycardia.
The Link Between Bradycardia and High Blood Pressure
Now, let’s explore the intriguing connection between bradycardia and high blood pressure (hypertension). While it may seem paradoxical, bradycardia can, in some cases, be associated with high blood pressure. Here’s how:
- Compensatory Mechanism: When the heart rate slows down, the body’s natural response is to increase blood pressure to ensure adequate blood flow to vital organs. This compensatory mechanism can lead to elevated blood pressure readings.
- Atrial Fibrillation: Bradycardia can sometimes be a result of atrial fibrillation, a common heart rhythm disorder. Atrial fibrillation is often associated with high blood pressure, as it can cause the heart to pump less efficiently, leading to increased pressure in the arteries.
- Medication Side Effects: As mentioned earlier, certain medications used to treat high blood pressure, such as beta-blockers, can slow down the heart rate. While this may be a desired effect in some cases, it can also contribute to the development or exacerbation of bradycardia.
- Cardiovascular Risk Factors: Individuals with bradycardia often share similar cardiovascular risk factors with those who have high blood pressure. These risk factors include obesity, a sedentary lifestyle, smoking, and an unhealthy diet. Managing these risk factors is crucial for both conditions.
Diagnosis and Treatment

Diagnosing bradycardia typically involves a thorough medical evaluation, including a detailed medical history, physical examination, and various diagnostic tests. These tests may include an electrocardiogram (ECG) to assess the heart’s electrical activity and a Holter monitor to record the heart’s rhythm over an extended period.
The treatment approach for bradycardia depends on the underlying cause and the severity of symptoms. In some cases, no treatment may be necessary, especially if the bradycardia is mild and not causing any significant issues. However, if bradycardia is severe or associated with symptoms such as dizziness, fatigue, or fainting, the following treatment options may be considered:
- Medications: Certain medications can help regulate the heart’s rhythm and increase the heart rate.
- Pacemaker Implantation: In more severe cases, a pacemaker may be implanted to regulate the heart’s electrical signals and maintain a normal heart rate.
- Addressing Underlying Conditions: Treating the underlying cause, such as managing thyroid disorders or addressing sleep apnea, can help improve bradycardia.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management, can benefit both bradycardia and high blood pressure.
Preventive Measures

Preventing bradycardia and high blood pressure involves adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle. Here are some key preventive measures:
- Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to promote a healthy heart rate and maintain cardiovascular fitness.
- Healthy Diet: Follow a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limit the intake of processed foods, salt, and saturated fats.
- Weight Management: Maintain a healthy weight to reduce the risk of both bradycardia and high blood pressure.
- Stress Management: Practice stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
- Avoid Tobacco and Excessive Alcohol: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can negatively impact heart health. Quitting smoking and moderating alcohol intake are essential steps toward prevention.
- Regular Check-Ups: Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor your heart health and blood pressure. Early detection and management are crucial.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)

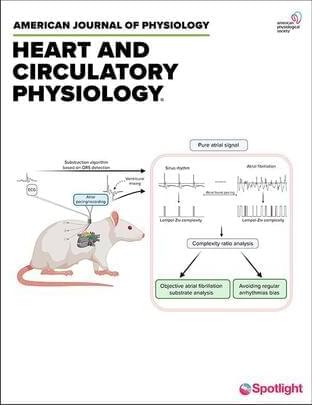
Can bradycardia be a sign of a serious heart condition?
+
Yes, bradycardia can sometimes be a symptom of an underlying heart condition, such as heart block or sinus node dysfunction. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Is it possible to have both bradycardia and high blood pressure simultaneously?

+
Yes, it is possible to have both conditions concurrently. As mentioned earlier, bradycardia can sometimes be linked to high blood pressure due to compensatory mechanisms or shared risk factors.
Can bradycardia be reversed or treated naturally?
+
In some cases, bradycardia can be managed through lifestyle changes and addressing underlying causes. However, severe cases may require medical intervention, such as medication or pacemaker implantation.
Are there any home remedies to improve bradycardia symptoms?

+
While home remedies may provide temporary relief, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment. Some lifestyle modifications, such as regular exercise and stress management, can help manage bradycardia symptoms.
Can bradycardia lead to other health complications?
+Bradycardia, if left untreated or poorly managed, can lead to complications such as fatigue, dizziness, fainting, and, in severe cases, cardiac arrest. It is crucial to seek medical advice if you experience any concerning symptoms.
Conclusion

In conclusion, bradycardia, a condition characterized by a slow heart rate, is intriguing due to its link to high blood pressure. While a slow heart rate may seem counterintuitive, it is essential to understand the underlying causes and the body’s compensatory mechanisms. By adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, managing risk factors, and seeking medical advice when needed, individuals can effectively manage both bradycardia and high blood pressure. Remember, early detection and prevention are key to maintaining a healthy cardiovascular system. Stay informed, stay active, and prioritize your heart health!