Your skin is your body's largest organ, serving as a protective barrier and a reflection of your overall health. However, it is not uncommon to experience various skin conditions throughout your life. Understanding these conditions is crucial for effective management and treatment. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore 12 common skin conditions, their characteristics, and the available treatment options.
Acne

Acne is a prevalent skin condition that affects people of all ages, often during puberty. It occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil and dead skin cells, leading to the formation of pimples, blackheads, and whiteheads. The severity of acne can range from mild to severe, causing emotional distress and scarring if left untreated.
Treatment Options for Acne
- Topical Treatments: Over-the-counter or prescription creams, gels, and lotions containing ingredients like benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, or retinoids can help unclog pores and reduce acne.
- Oral Medications: For moderate to severe acne, oral antibiotics or hormonal treatments may be prescribed to control bacteria and reduce inflammation.
- Chemical Peels: A chemical solution is applied to the skin to remove the top layer, promoting the growth of new, healthier skin.
- Laser and Light Therapies: These treatments use targeted light to reduce acne-causing bacteria and improve skin texture.
Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)

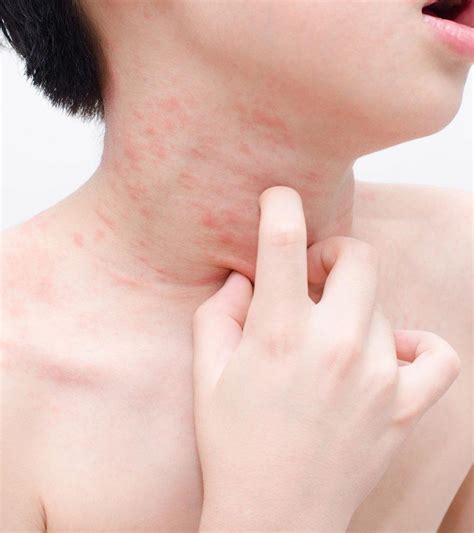
Eczema is a chronic skin condition characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. It often develops in early childhood and can persist into adulthood. Eczema flares can be triggered by various factors, including allergens, irritants, and stress.
Managing Eczema

- Moisturize Regularly: Applying a thick, fragrance-free moisturizer can help lock in moisture and soothe itchy skin.
- Avoid Irritants: Identify and avoid triggers such as harsh soaps, detergents, and certain fabrics that can irritate the skin.
- Wet Wrap Therapy: Soaking affected areas in lukewarm water and then applying a wet dressing can provide relief and reduce inflammation.
- Topical Corticosteroids: These medications can be prescribed to reduce inflammation and itching during eczema flares.
Psoriasis
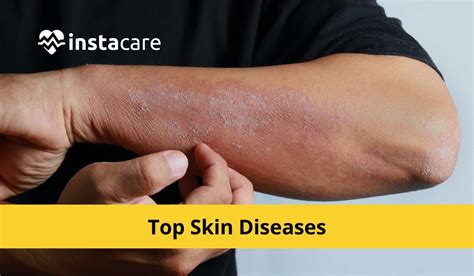
Psoriasis is an autoimmune skin condition that causes skin cells to multiply rapidly, leading to the formation of thick, scaly patches on the skin. It can affect any part of the body and is often associated with itching and pain.
Treatment Approaches for Psoriasis

- Topical Treatments: Creams and ointments containing corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, or retinoids can help reduce inflammation and slow down skin cell growth.
- Phototherapy: Exposing the skin to controlled amounts of natural or artificial light can help slow down skin cell turnover and reduce psoriasis symptoms.
- Systemic Medications: For more severe cases, oral or injectable medications may be prescribed to suppress the immune system and control psoriasis flares.
- Biologic Drugs: These targeted medications block specific immune system responses that contribute to psoriasis.
Rosacea

Rosacea is a chronic skin condition characterized by facial redness, visible blood vessels, and sometimes bumps or pimples. It primarily affects the central face, including the cheeks, nose, forehead, and chin. Rosacea can cause significant self-consciousness and impact an individual’s quality of life.
Managing Rosacea
- Trigger Identification: Rosacea flares can be triggered by various factors, such as sun exposure, spicy foods, alcohol, and stress. Identifying and avoiding triggers is crucial.
- Gentle Skincare: Using mild, fragrance-free skincare products and avoiding harsh ingredients can help prevent irritation and reduce flare-ups.
- Topical Treatments: Prescription creams or gels containing medications like metronidazole or azelaic acid can help reduce inflammation and redness.
- Oral Antibiotics: For more severe cases, oral antibiotics may be prescribed to control the underlying inflammation.
Hives (Urticaria)

Hives are itchy, raised welts that can appear on the skin and vary in size and shape. They are often a sign of an allergic reaction or an immune system response to certain triggers. Hives can be acute (lasting less than six weeks) or chronic (lasting longer than six weeks).
Treating Hives

- Avoid Triggers: Identifying and avoiding substances that trigger hives, such as certain foods, medications, or environmental factors, is essential.
- Antihistamines: Over-the-counter or prescription antihistamine medications can help relieve itching and reduce the severity of hives.
- Oral Corticosteroids: For severe or persistent hives, a short course of oral corticosteroids may be prescribed to control inflammation.
- Epinephrine Injection: In cases of anaphylaxis (a severe allergic reaction), an epinephrine auto-injector may be prescribed for emergency use.
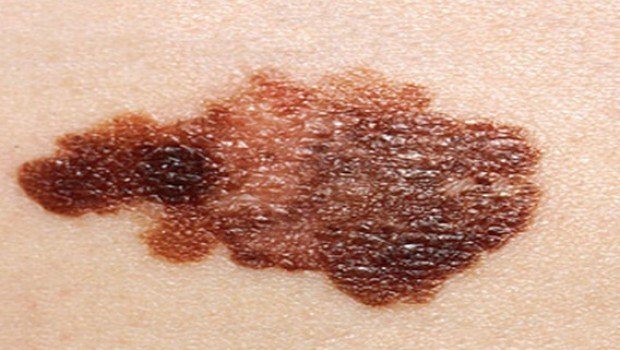
Moles

Moles are common skin growths that can appear anywhere on the body. Most moles are harmless, but it is important to monitor them for any changes that could indicate skin cancer.
Monitoring Moles

- The ABCDEs of Melanoma: Use the ABCDE criteria to assess moles for potential signs of melanoma:
- Asymmetry: One half of the mole does not match the other.
- Border: The edges of the mole are irregular, scalloped, or poorly defined.
- Color: The mole has varying shades of brown, black, or tan, or it may appear red, white, or blue.
- Diameter: The mole is larger than 6 millimeters (about the size of a pencil eraser) or has recently grown in size.
- Evolution: The mole has changed in size, shape, color, or texture over time.
- Regular Skin Checks: Perform monthly self-examinations and consult a dermatologist if you notice any concerning changes in your moles.
Warts

Warts are small, rough growths on the skin caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). They are common and can appear on various body parts, including the hands, feet, and genitals. Warts are typically harmless but can be unsightly and uncomfortable.
Treatment Options for Warts

- Over-the-Counter Treatments: Salicylic acid-based products can help dissolve the wart over time.
- Cryotherapy: This procedure involves freezing the wart with liquid nitrogen, causing it to eventually fall off.
- Prescription Medications: For persistent or multiple warts, a dermatologist may prescribe stronger medications or perform minor surgical procedures to remove them.
Skin Tags

Skin tags are small, soft growths that hang off the skin. They are common and often appear in areas where the skin folds or rubs together, such as the neck, armpits, and groin. Skin tags are harmless and usually do not require treatment unless they cause discomfort or embarrassment.
Managing Skin Tags

- Leave Them Alone: Most skin tags do not cause any harm and can be left untreated.
- Removal Options: If skin tags are bothersome, a dermatologist can remove them through various methods, including cutting, freezing, or burning them off.
Sunburn and Sun Damage

Sunburn is a common skin condition caused by excessive exposure to the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) rays. It results in red, painful, and sometimes blistered skin. Repeated sun exposure can lead to long-term skin damage, including premature aging and an increased risk of skin cancer.
Preventing and Treating Sunburn

- Sun Protection: Use sunscreen with a high SPF, wear protective clothing, and seek shade during peak sun hours.
- Cool Compresses: Applying cool, damp cloths to the affected areas can help relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
- Moisturizers: Use gentle, fragrance-free moisturizers to soothe and hydrate sunburned skin.
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen can help reduce pain and inflammation associated with sunburn.
Melanoma and Skin Cancer

Melanoma is a serious form of skin cancer that develops from abnormal pigment-producing cells called melanocytes. It can appear as a new mole or a change in an existing mole. Early detection and treatment are crucial for improving the chances of successful outcomes.
Skin Cancer Prevention and Detection
- Sun Protection: Limit sun exposure, especially during peak hours, and wear protective clothing and sunscreen.
- Regular Skin Exams: Perform monthly self-examinations and schedule annual skin checks with a dermatologist.
- Recognize Warning Signs: Be aware of the ABCDEs of melanoma and consult a dermatologist if you notice any concerning changes in your skin.
Fungal Infections
Fungal infections, such as ringworm, athlete’s foot, and yeast infections, are common skin conditions caused by various types of fungi. They can cause itching, redness, and scaling on the skin.
Treating Fungal Infections
- Topical Antifungal Medications: Creams, lotions, or powders containing antifungal agents can be applied to the affected areas to eliminate the infection.
- Oral Antifungal Medications: For more severe or persistent infections, oral antifungal medications may be prescribed.
- Good Hygiene: Maintaining proper hygiene, including regular washing and drying of affected areas, can help prevent the spread of fungal infections.
Cellulitis
Cellulitis is a bacterial skin infection that causes redness, swelling, and pain. It typically affects the lower legs but can occur anywhere on the body. Cellulitis can spread quickly and become serious if left untreated.
Managing Cellulitis
- Antibiotics: Oral or intravenous antibiotics are usually prescribed to treat cellulitis and prevent the infection from spreading.
- Rest and Elevation: Resting and elevating the affected area can help reduce swelling and promote healing.
- Warm Compresses: Applying warm, moist compresses to the affected area can provide relief and improve circulation.
Cold Sores (Fever Blisters)
Cold sores, also known as fever blisters, are small, painful blisters that usually appear on or around the lips. They are caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV) and can be triggered by stress, illness, or sun exposure.
Managing Cold Sores
- Antiviral Medications: Prescription antiviral medications can help shorten the duration and severity of cold sore outbreaks.
- Topical Treatments: Over-the-counter creams or ointments containing ingredients like docosanol or benzyl alcohol can provide relief and speed up healing.
- Cold Compresses: Applying cold compresses to the affected area can help reduce pain and inflammation.
💡 Note: It is important to consult a dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan for any skin condition. They can provide guidance and recommend the most suitable options based on your specific needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I prevent acne breakouts?
+To prevent acne breakouts, it’s important to maintain a consistent skincare routine, avoid touching your face, and keep your skin clean. Use gentle, non-comedogenic products and avoid harsh scrubbing. Additionally, manage stress levels and consider dietary changes, as certain foods may trigger acne.
What are the signs of skin cancer?
+Signs of skin cancer can include changes in existing moles (asymmetry, irregular borders, color variations), the appearance of new moles, or the development of sores that do not heal. It’s important to perform regular self-examinations and consult a dermatologist if you notice any concerning changes.
How can I manage eczema flares?
+To manage eczema flares, it’s crucial to identify and avoid triggers, such as certain fabrics or harsh soaps. Regularly moisturize your skin, take short, lukewarm baths or showers, and use gentle, fragrance-free skincare products. Additionally, stress management techniques and proper hydration can help reduce flare-ups.
Are there any natural remedies for skin conditions?
+While natural remedies may provide temporary relief, it’s important to consult a dermatologist for proper diagnosis and treatment. Some natural remedies, such as tea tree oil for acne or aloe vera for minor skin irritations, can be used as complementary approaches. However, their effectiveness may vary, and they should not replace professional medical advice.
How long does it take for skin conditions to clear up with treatment?
+The time it takes for skin conditions to clear up with treatment can vary depending on the condition and its severity. Some skin conditions, like acne or eczema, may require long-term management, while others, such as cold sores or sunburn, can improve within a few days to weeks with proper treatment. It’s important to follow your dermatologist’s recommendations and be patient during the healing process.
In conclusion, understanding common skin conditions and their treatment options is essential for maintaining healthy and vibrant skin. By being aware of the signs and symptoms, practicing proper skincare, and seeking professional guidance when needed, you can effectively manage and treat various skin concerns. Remember, early detection and treatment are key to achieving optimal skin health.