Understanding the Difference: Sprains vs. Twists

Are you experiencing pain and discomfort in your joints or muscles? It can be challenging to determine whether you're dealing with a sprain or a twist, especially if you're not well-versed in the nuances of these common injuries. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the key differences between sprains and twists, providing you with the knowledge to identify and manage these injuries effectively.
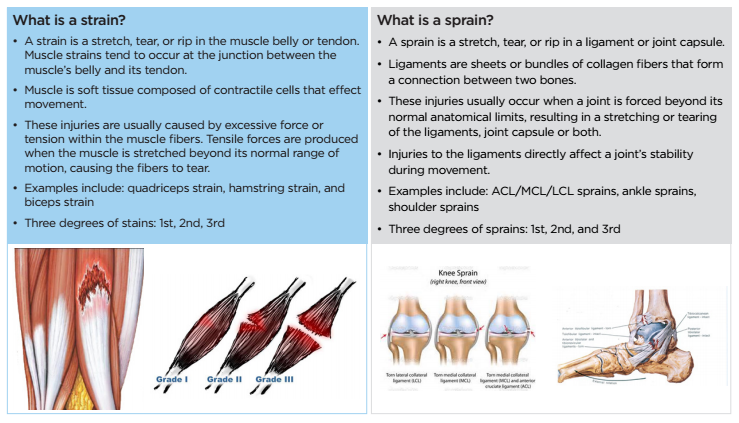
What is a Sprain?

A sprain occurs when the ligaments, which are the tough bands of tissue connecting bones in a joint, are stretched or torn. This type of injury is typically caused by a sudden twist, fall, or blow that forces a joint out of its normal position. Sprains are common in the wrists, ankles, and knees, and can range from mild to severe, depending on the extent of the ligament damage.
Symptoms of a Sprain

- Pain and tenderness around the affected joint
- Swelling and inflammation
- Bruising or discoloration of the skin
- Limited movement or stiffness in the joint
- A feeling of instability or looseness in the joint
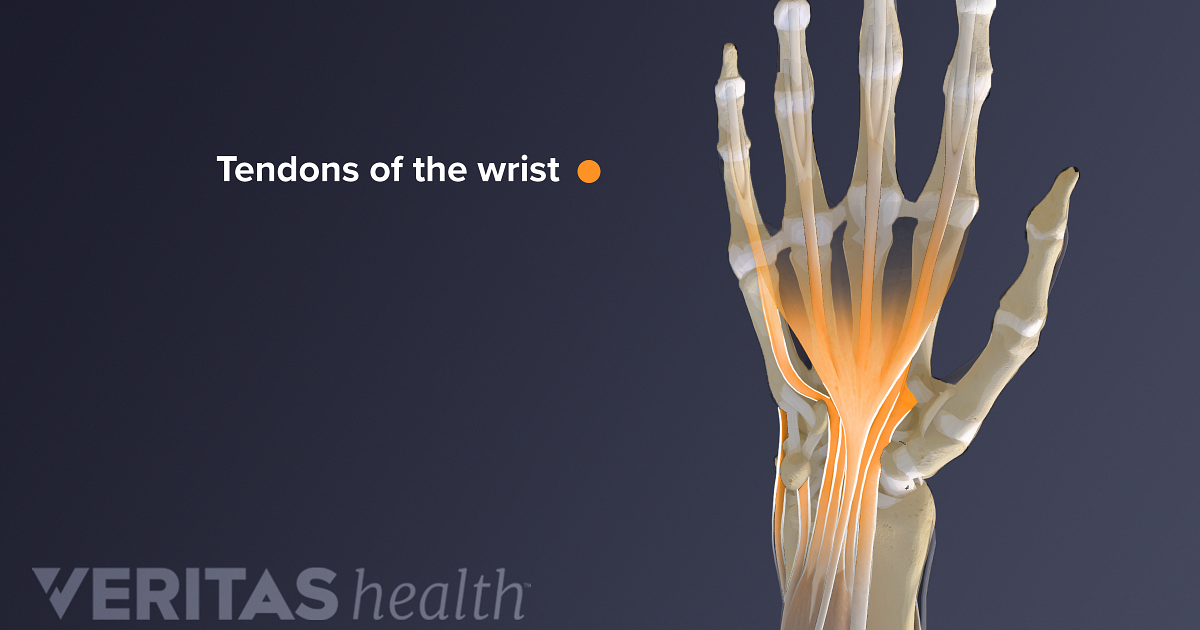
What is a Twist?

A twist, also known as a muscle strain or pull, is an injury to the muscle fibers or tendons. It occurs when a muscle or tendon is stretched beyond its normal range, resulting in tears or damage to the muscle tissue. Twists can happen suddenly or develop over time due to repetitive movements or improper body mechanics.
Symptoms of a Twist

- Sharp or dull pain in the affected muscle
- Muscle spasms or cramping
- Swelling and inflammation
- Weakness or difficulty moving the muscle
- Bruising or discoloration in severe cases
Key Differences Between Sprains and Twists

While both sprains and twists can cause pain and discomfort, there are several key differences to look out for:
Injury Location
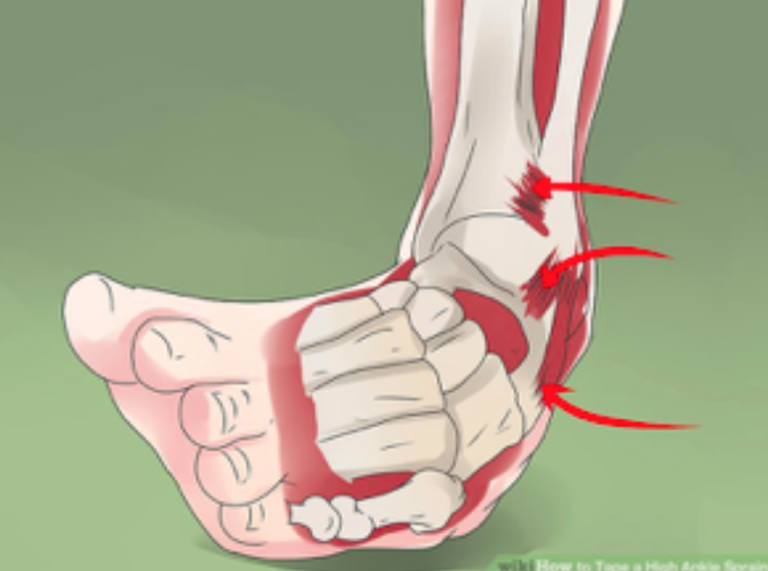
Sprains typically affect the ligaments surrounding a joint, such as the ankle, knee, or wrist. On the other hand, twists are injuries to the muscle fibers or tendons, often occurring in the back, legs, or arms.
Cause of Injury

Sprains are usually the result of a sudden, traumatic event that forces a joint beyond its normal range of motion. Twists, however, can be caused by either sudden movements or repetitive actions that strain the muscles over time.
Severity of Injury
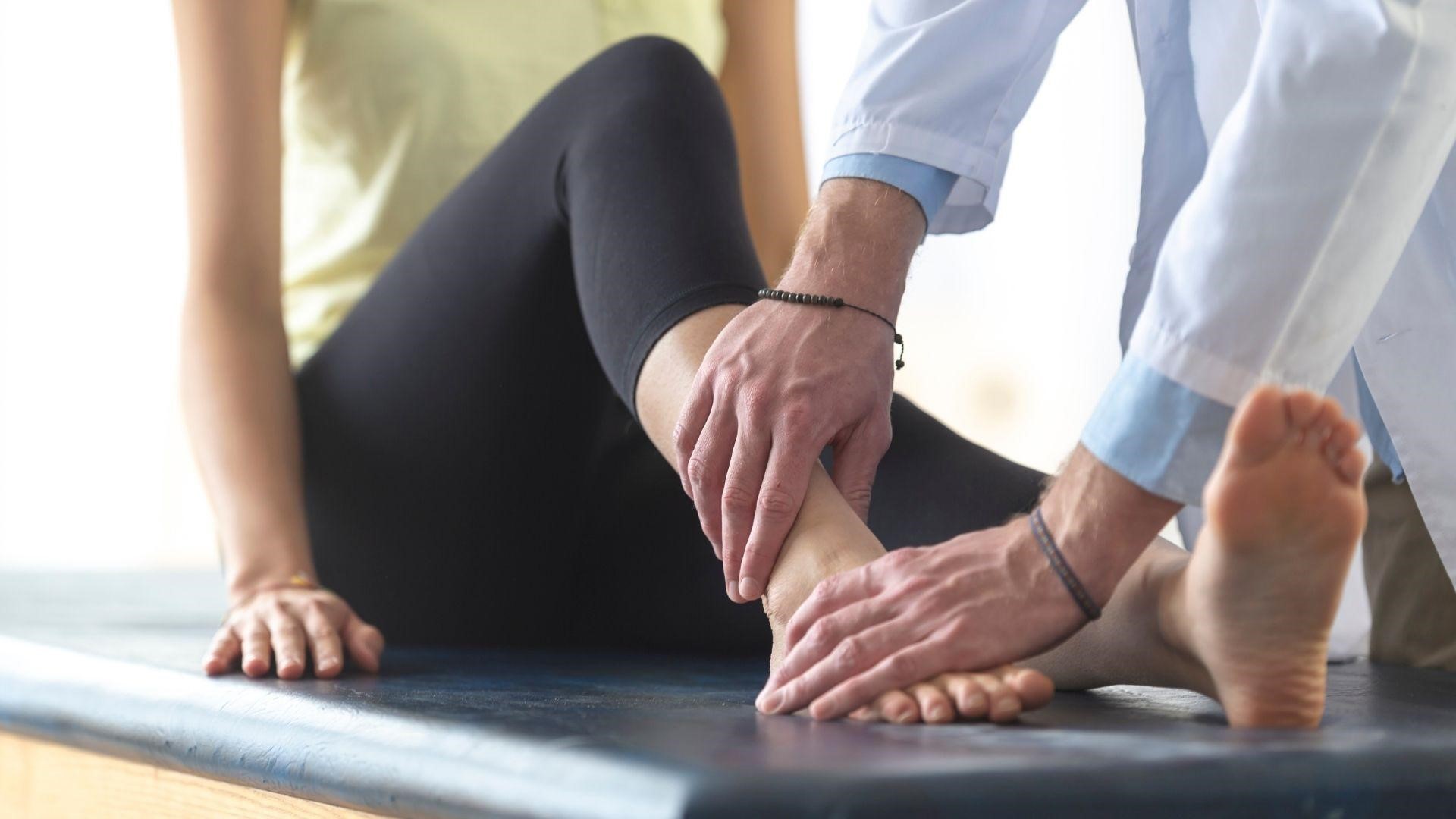

Sprains can range from mild to severe, with more severe sprains resulting in complete ligament tears. Twists, while painful, are generally less severe and typically involve muscle fiber tears or inflammation.
Symptoms

Sprains often present with more localized symptoms around the joint, such as pain, swelling, and limited movement. Twists, on the other hand, may cause more widespread symptoms like muscle spasms, cramping, and weakness throughout the affected muscle group.
Diagnosis and Treatment

If you suspect you have a sprain or twist, it's important to seek medical attention for an accurate diagnosis. A healthcare professional will examine the affected area, assess your symptoms, and may order imaging tests like X-rays or MRI scans to determine the extent of the injury.
Treatment Options

- Rest: Allow the injured area to rest and avoid activities that may aggravate the injury.
- Ice: Apply ice packs to the affected area to reduce swelling and pain.
- Compression: Use compression bandages or wraps to support the joint and reduce swelling.
- Elevation: Keep the injured area elevated to minimize swelling.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs can help manage pain and reduce inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: For more severe injuries, physical therapy may be recommended to improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion.
Prevention

While some injuries are unavoidable, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk of sprains and twists:
- Warm-up and stretch before physical activity to prepare your muscles and joints.
- Use proper technique and form during exercise or sports to avoid placing excessive strain on your body.
- Wear appropriate footwear and protective gear to provide support and reduce the risk of injury.
- Maintain a balanced fitness routine that includes strength training and flexibility exercises.
- Be mindful of your body's limits and avoid pushing yourself too hard.
When to Seek Medical Attention
It's important to seek immediate medical attention if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- Severe pain that doesn't improve with rest and home care
- Inability to bear weight or move the affected joint
- Significant swelling or bruising
- Numbness or tingling in the injured area
- Visible deformity or dislocation of the joint
Conclusion

Distinguishing between a sprain and a twist can be challenging, but understanding the key differences in symptoms, location, and severity can help you identify and manage these injuries effectively. Remember to seek medical attention for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. By taking preventive measures and staying mindful of your body's limits, you can reduce your risk of sprains and twists and maintain an active, healthy lifestyle.
Can a sprain heal on its own without medical treatment?
+
Mild sprains can often heal with rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE). However, more severe sprains may require medical intervention, such as immobilization or surgery, to ensure proper healing and prevent long-term complications.
How long does it take for a twist to heal?
+
The healing time for a twist can vary depending on the severity of the injury. Mild twists may heal within a few days to a week, while more severe cases can take several weeks or even months to fully recover.
Can I continue exercising with a sprain or twist?

+
It’s generally recommended to avoid high-impact activities and exercises that may aggravate the injured area. However, low-impact exercises like swimming or cycling can be beneficial for maintaining fitness while allowing the injury to heal. Consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Are sprains and twists more common in certain sports or activities?
+Yes, certain sports and activities carry a higher risk of sprains and twists. Sports that involve quick changes in direction, jumping, or contact, such as basketball, soccer, and gymnastics, are more likely to result in these types of injuries.
Can sprains and twists be prevented entirely?
+While it’s not possible to eliminate the risk entirely, following preventive measures such as proper warm-up, using protective gear, and maintaining good body mechanics can significantly reduce the likelihood of sprains and twists.