Welcome to the ultimate guide on understanding and mastering the Alternating Group A3! In this comprehensive blog post, we will delve into the fascinating world of group theory and explore the intricacies of this unique mathematical concept. Whether you are a student, a researcher, or simply curious about the beauty of mathematics, this journey through Alternating Group A3 will surely captivate your mind.
The Alternating Group A3, often denoted as A3, is a specific type of group that holds significant importance in various mathematical disciplines. It is a subset of the symmetric group S3, which consists of all permutations of three elements. While the concept of groups and permutations may seem abstract at first, they have profound applications in fields such as algebra, geometry, and even computer science.
Understanding Groups and Permutations

Before we dive into the specifics of Alternating Group A3, let's take a moment to understand the fundamental concepts of groups and permutations. A group, in mathematical terms, is a set of elements along with a binary operation that satisfies certain properties. These properties, known as the group axioms, ensure that the set forms a well-defined algebraic structure.
In the context of Alternating Group A3, we are dealing with a specific type of group known as a permutation group. A permutation group is a group whose elements are bijective functions, also known as permutations, that act on a set. These permutations rearrange the elements of the set in a particular order.
The Structure of Alternating Group A3

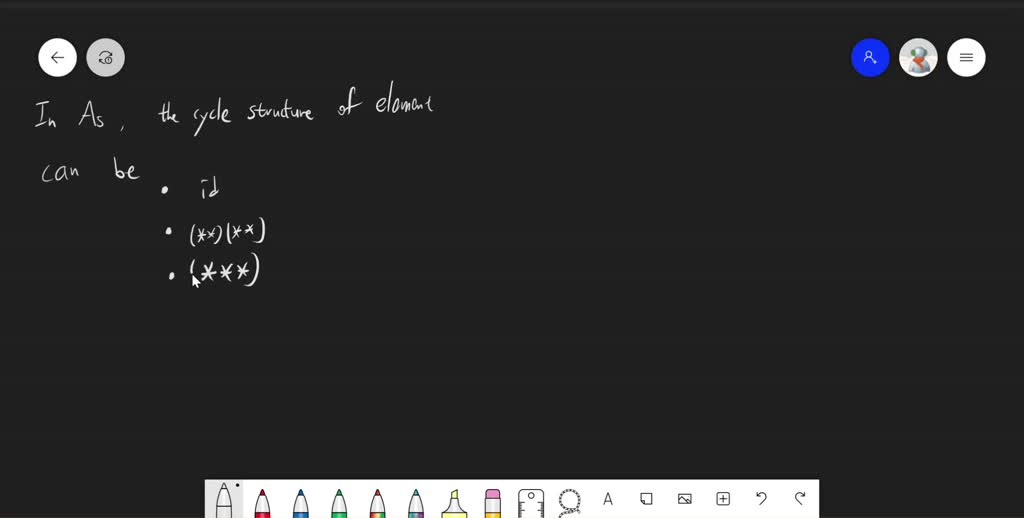
Alternating Group A3 is a subgroup of the symmetric group S3. It consists of all even permutations of three elements. To understand this better, let's explore the elements of S3 and identify the even permutations that form A3.
The symmetric group S3 has six elements, which can be represented as permutations of three elements: a, b, and c.
| Element | Permutation |
|---|---|
| e | (a b c) |
| s1 | (a b) |
| s2 | (b c) |
| s3 | (a c) |
| s1s2 | (a c b) |
| s2s1 | (a b c) |

Now, let's identify the even permutations that belong to Alternating Group A3. Even permutations are those that can be obtained by composing an even number of transpositions (swapping two elements). In the case of S3, the even permutations are:
- e
- s1s2
- s2s1
Therefore, Alternating Group A3 consists of these three even permutations: (a b c), (a c b), and (a b).
Properties of Alternating Group A3

Alternating Group A3 possesses several interesting properties that make it a fascinating object of study. Let's explore some of these properties:
Order of the Group

The order of a group refers to the number of elements it contains. In the case of Alternating Group A3, the order is 3 since it has three elements: (a b c), (a c b), and (a b). This is a relatively small group, but it exhibits intriguing behaviors and relationships.
Group Operation

The group operation in Alternating Group A3 is composition, which means we multiply permutations to obtain new permutations. For example, if we compose the permutations (a b c) and (a c b), we get (a b c) * (a c b) = (a c b c) = (a b c), which is an element of A3.
Commutativity

One important property of Alternating Group A3 is that it is not a commutative group. This means that, in general, the order in which we compose permutations matters. For instance, (a b c) * (a c b) is not equal to (a c b) * (a b c) in A3.
Generators

Generators are elements of a group that can be used to generate all other elements through composition. In Alternating Group A3, the generators are the transpositions: (a b) and (b c). By composing these transpositions, we can obtain all the elements of A3.
Visualizing Alternating Group A3

To gain a deeper understanding of Alternating Group A3, it can be helpful to visualize its elements and their relationships. Let's consider a simple visualization using a graph:

In this graph, each node represents an element of Alternating Group A3, and the edges connect elements that can be obtained by composing permutations. The arrows indicate the direction of composition. This visualization helps us understand the structure and relationships within the group.
Applications of Alternating Group A3

Alternating Group A3, despite its simplicity, finds applications in various mathematical and scientific domains. Here are a few examples:
- Algebra: Alternating groups, including A3, are important in the study of abstract algebra. They provide examples of non-abelian groups and are used in the classification of simple groups.
- Geometry: Alternating groups have connections to geometric transformations, such as rotations and reflections. They can be used to describe the symmetries of certain geometric objects.
- Computer Science: Group theory, including the study of Alternating Group A3, has applications in cryptography and error-correcting codes. It also plays a role in the design of algorithms and data structures.
Exploring Further

Alternating Group A3 serves as a great starting point for exploring the fascinating world of group theory. As you delve deeper into this field, you will encounter more complex groups, such as the alternating groups A4, A5, and beyond. Each group has its own unique properties and applications, offering endless opportunities for mathematical exploration.
Whether you are a student embarking on your mathematical journey or a researcher seeking new insights, the study of Alternating Group A3 and other groups can be both intellectually stimulating and rewarding. So, embrace the beauty of mathematics and continue your exploration of this captivating subject.
Conclusion

In this blog post, we embarked on a journey to understand the Alternating Group A3, a subset of the symmetric group S3. We explored its structure, properties, and applications, showcasing the richness and diversity of group theory. By delving into the world of permutations and groups, we have gained a deeper appreciation for the elegance and power of mathematics.
Remember, mathematics is a vast and ever-evolving field, and there is always more to discover. Keep exploring, asking questions, and pushing the boundaries of your understanding. With each new concept and theory, you unlock a deeper understanding of the world around us.
Thank you for joining me on this mathematical adventure. I hope you found this guide insightful and inspiring. Until next time, keep learning and keep exploring the wonders of mathematics!
What is a group in mathematics?

+
A group is a set of elements along with a binary operation that satisfies certain properties, known as the group axioms. These axioms ensure that the set forms a well-defined algebraic structure.
How is Alternating Group A3 related to the symmetric group S3?

+
Alternating Group A3 is a subgroup of the symmetric group S3. It consists of all even permutations of three elements, while S3 includes all permutations of three elements.
What are the applications of Alternating Group A3?

+
Alternating Group A3 finds applications in algebra, geometry, and computer science. It is used in the study of abstract algebra, geometric transformations, and has implications in cryptography and error-correcting codes.
Can you provide an example of a composition in Alternating Group A3?

+
Sure! For instance, if we compose the permutations (a b c) and (a c b), we get (a b c) * (a c b) = (a c b c) = (a b c), which is an element of A3.
Are there any other interesting groups similar to Alternating Group A3?
+
Absolutely! There are alternating groups for higher orders, such as A4, A5, and beyond. Each of these groups has its own unique properties and applications, offering a wealth of mathematical exploration.