Angular frequency is a fundamental concept in physics and engineering, particularly in the study of oscillatory motion and wave phenomena. It is a measure of how quickly an object or system completes one full cycle of its periodic motion or oscillation. Angular frequency provides a more comprehensive understanding of the behavior of oscillating systems compared to regular frequency, which is measured in hertz (Hz). Angular frequency is denoted by the symbol "ω" (omega) and is measured in radians per second (rad/s). This unit reflects the fact that angular frequency represents the rate of change of the angle of rotation or oscillation.
Understanding Angular Frequency

Angular frequency is a crucial parameter in various fields, including physics, engineering, and mathematics. It plays a central role in describing the behavior of oscillating systems, such as pendulums, springs, and electromagnetic waves. By quantifying the rate of change of angular displacement, angular frequency offers a more precise and detailed insight into the dynamics of these systems.
Converting Angular Frequency to Regular Frequency

While angular frequency is expressed in radians per second, regular frequency, measured in hertz (Hz), is more commonly used in everyday contexts. To convert angular frequency to regular frequency, we use the following formula:
Regular Frequency (f) = Angular Frequency (ω) / (2π)
This conversion allows us to relate the two frequencies and understand how they are interconnected. It is important to note that the conversion factor of 2π arises from the relationship between radians and degrees, as there are 2π radians in a full circle.
Applications of Angular Frequency
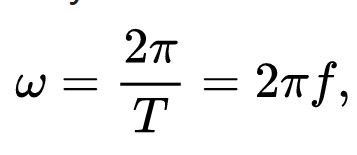
-
Oscillatory Motion: Angular frequency is essential in describing the behavior of oscillating systems. It helps determine the time it takes for an object to complete one full cycle of its motion, known as the period (T). The relationship between angular frequency and period is given by the equation: ω = 2π / T.
-
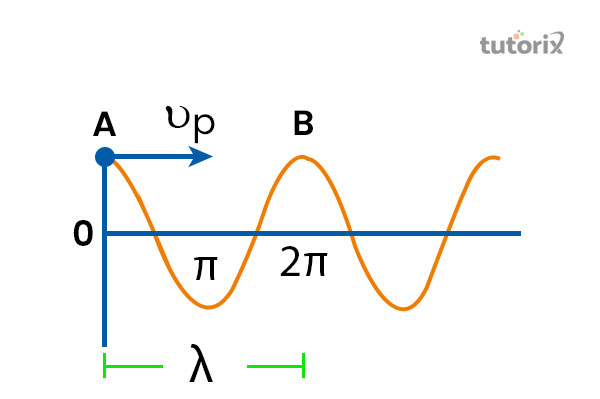
Wave Phenomena: Angular frequency is a key parameter in the study of waves, including sound waves and electromagnetic waves. It is used to describe the rate at which the wave oscillates or vibrates. In the case of electromagnetic waves, angular frequency is directly related to the wave's wavelength (λ) and speed (v) through the equation: ω = 2πv / λ.
-
Resonance and Harmonic Motion: Angular frequency is crucial in understanding resonance, which occurs when the frequency of an external force matches the natural frequency of an oscillating system. This phenomenon is observed in various systems, such as musical instruments and mechanical structures. Angular frequency helps determine the conditions for resonance and the behavior of harmonic oscillators.
SI Units and Angular Frequency

The International System of Units (SI) is the modern form of the metric system and is widely used in scientific and technological fields. Angular frequency, being a fundamental quantity, is also defined within the SI system. The SI unit for angular frequency is radians per second (rad/s). This unit is derived from the base SI units, specifically the radian (rad) for angular measurement and the second (s) for time.
The choice of radians as the unit for angular measurement is significant. Radians provide a natural and intuitive way to describe angular displacement and frequency in circular motion and oscillations. By using radians, we can directly relate angular frequency to the rate of change of angular displacement, making it a more meaningful and useful quantity.
Converting Angular Frequency to Other Units
While radians per second is the standard SI unit for angular frequency, there may be situations where it is necessary to convert angular frequency to other units. One common conversion is to degrees per second, which can be useful in certain engineering and practical applications. The conversion formula is as follows:
Degrees per second = Angular Frequency (ω) × (360 / 2π)
This conversion allows us to express angular frequency in terms of degrees, which is a more familiar unit for many people. However, it is important to note that the conversion factor of 360/2π arises from the relationship between degrees and radians, as there are 360 degrees in a full circle.
Practical Examples of Angular Frequency
-
Pendulum Motion: Consider a simple pendulum swinging back and forth. The angular frequency of the pendulum's motion depends on its length and the acceleration due to gravity. By measuring the period of the pendulum's oscillation, we can calculate its angular frequency using the formula: ω = 2π / T.
-
Electromagnetic Waves: Angular frequency plays a crucial role in the study of electromagnetic waves, such as light and radio waves. The angular frequency of these waves is directly related to their wavelength and speed of propagation. For example, the angular frequency of visible light is approximately 6 × 10^14 rad/s.
-
AC Circuits: In alternating current (AC) circuits, angular frequency is used to describe the rate of change of voltage and current. It is a key parameter in analyzing the behavior of capacitors, inductors, and resistors in AC circuits. The angular frequency of AC power is typically 2π × 50 Hz or 2π × 60 Hz, depending on the region.
Conclusion

Angular frequency is a fundamental concept that provides a deeper understanding of oscillatory motion and wave phenomena. By quantifying the rate of change of angular displacement, angular frequency offers a more precise and meaningful description of the behavior of oscillating systems. With its SI unit of radians per second, angular frequency plays a crucial role in various scientific and engineering applications, from pendulum motion to electromagnetic waves and AC circuits. By grasping the concept of angular frequency, we can better analyze and predict the behavior of these systems, leading to advancements in technology and a deeper understanding of the natural world.
What is the difference between angular frequency and regular frequency?

+
Angular frequency (ω) is measured in radians per second (rad/s) and describes the rate of change of angular displacement. Regular frequency (f), measured in hertz (Hz), is the number of complete cycles per second. Angular frequency provides a more detailed understanding of oscillatory motion and is directly related to the rate of change of angular displacement.
How is angular frequency related to the period of an oscillating system?
+
The angular frequency (ω) of an oscillating system is related to its period (T) by the equation: ω = 2π / T. This equation allows us to calculate the angular frequency based on the period of the system’s oscillation.
What are some practical applications of angular frequency?

+
Angular frequency is used in various applications, including the study of pendulums, electromagnetic waves, and AC circuits. It helps determine the behavior of oscillating systems, calculate wave properties, and analyze the performance of electrical components in AC circuits.