Understanding the Importance of Anxiety Screening

Anxiety disorders are among the most common mental health issues, yet they often go unrecognized and untreated. Implementing anxiety screening in your medical practice is a crucial step towards early detection and effective management. This guide will walk you through the process of integrating anxiety assessments into your routine office visits, empowering you to provide comprehensive care for your patients.
Step 1: Recognizing the Need for Anxiety Screening

Anxiety disorders can manifest in various ways, from generalized anxiety to panic attacks and phobias. Recognizing the signs and symptoms is the first step in identifying patients who may benefit from further evaluation. Some common indicators include:
- Excessive worry or fear that interferes with daily life
- Restlessness, irritability, or difficulty concentrating
- Physical symptoms such as rapid heartbeat, sweating, or muscle tension
- Avoidance of situations or activities due to anxiety
- Sleep disturbances or fatigue
By paying attention to these signs, you can identify patients who may require more specialized care.
Step 2: Choosing the Right Assessment Tools
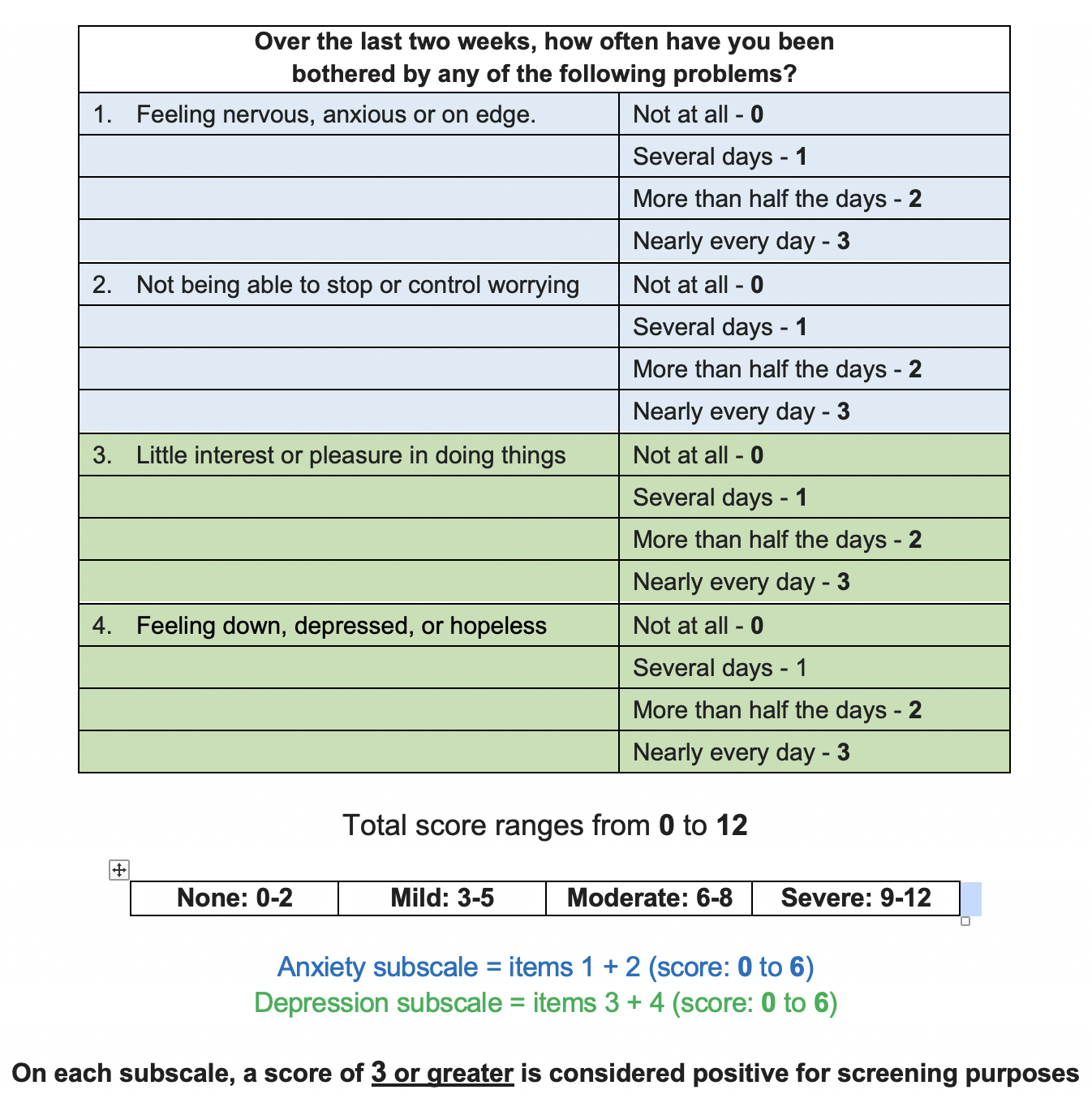
There are numerous validated tools available for anxiety screening. It’s essential to select assessments that are suitable for your practice and patient population. Here are some popular options:
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder 7-item (GAD-7): A brief self-report questionnaire measuring the severity of anxiety symptoms.
- Patient Health Questionnaire-4 (PHQ-4): A shorter version of the PHQ-9, assessing both anxiety and depression.
- Social Phobia Inventory (SPIN): Specifically designed to evaluate social anxiety disorder.
- Panic Disorder Severity Scale (PDSS): Useful for assessing panic disorder and its impact on daily functioning.
Consider the specific needs of your practice and the resources available when choosing an assessment tool.
Step 3: Integrating Screening into Office Visits

Incorporating anxiety screening into your routine office visits is crucial for early detection. Here’s how you can make it a seamless process:
- Inform Patients: Explain the purpose of the screening and assure patients of confidentiality. Emphasize that it’s a standard part of your comprehensive care approach.
- Provide Privacy: Ensure a private and comfortable environment for patients to complete the assessment.
- Offer Multiple Formats: Provide both paper-based and digital options to accommodate different patient preferences.
- Train Staff: Educate your staff on the importance of anxiety screening and how to assist patients during the process.
- Set Reminders: Implement reminders in your electronic health record system to prompt you to conduct anxiety screenings during relevant visits.
By integrating screening into your workflow, you can identify anxiety disorders early and initiate appropriate treatment plans.
Step 4: Interpreting Screening Results

Once patients have completed the assessment, it’s essential to interpret the results accurately. Each screening tool has its own scoring system and cutoff points for further evaluation. Here’s a simplified breakdown:
| Tool | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| GAD-7 | Scores of 5, 10, and 15 indicate mild, moderate, and severe anxiety, respectively. |
| PHQ-4 | A score of 3 or more suggests further evaluation for anxiety or depression. |
| SPIN | Scores of 20 or more indicate significant social anxiety symptoms. |
| PDSS | Scores of 5 or more suggest the presence of panic disorder. |

Remember, these tools provide an initial assessment, and further evaluation may be necessary to confirm a diagnosis.
Step 5: Developing a Treatment Plan

Based on the screening results and further evaluation, you can develop a tailored treatment plan for your patients. This may include:
- Psychotherapy: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is highly effective for anxiety disorders. Refer patients to a qualified mental health professional for therapy sessions.
- Medication: In some cases, medication may be prescribed to manage anxiety symptoms. Collaborate with psychiatrists or other specialists to determine the most suitable options.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Encourage patients to adopt healthy habits such as regular exercise, stress management techniques, and a balanced diet.
- Support Groups: Connect patients with local or online support groups to provide additional support and coping strategies.
Regular follow-ups are crucial to monitor the effectiveness of the treatment plan and make any necessary adjustments.
Implementing Anxiety Screening in Practice

To successfully implement anxiety screening in your practice, consider the following tips:
- Staff Training: Ensure your staff understands the importance of anxiety screening and can assist patients effectively.
- Electronic Health Records (EHR): Utilize your EHR system to track screening results, monitor progress, and generate reports for further analysis.
- Referral Networks: Establish relationships with mental health professionals and support groups in your area to facilitate seamless referrals.
- Patient Education: Provide educational materials and resources to help patients understand anxiety disorders and their treatment options.
Conclusion

By implementing anxiety screening in your medical practice, you take a proactive approach to mental health care. Early detection and intervention can significantly improve the lives of your patients, reducing the impact of anxiety disorders and promoting overall well-being. Remember, effective anxiety management is a collaborative effort between healthcare providers and patients, and your practice can play a vital role in this journey.
FAQ

How often should anxiety screening be conducted?

+
Anxiety screening should be conducted annually or as needed, especially if patients present with symptoms or risk factors for anxiety disorders.
Can anxiety screening be done remotely?

+
Yes, many screening tools can be completed remotely, either through online forms or over the phone. Ensure patients understand the process and provide support as needed.
What if a patient refuses screening or is hesitant to participate?

+
Respect patient autonomy and provide education on the benefits of screening. Offer alternatives or modifications to make the process more comfortable for hesitant patients.
How can I ensure the confidentiality of screening results?

+
Maintain strict confidentiality practices, including secure storage of paper records and encryption of digital data. Train staff on privacy protocols and obtain patient consent for sharing information with other healthcare providers.