Introduction
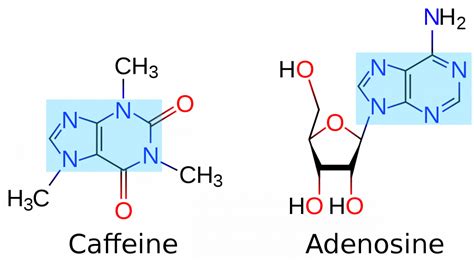
Caffeine is a commonly used stimulant that can have various effects on the human body, including potential benefits and risks. When it comes to premature neonates, caffeine therapy is often administered to treat certain conditions. However, a unique complication associated with caffeine use in this population is caffeine-induced hyponatremia. This blog post aims to delve into the understanding, diagnosis, and management of caffeine-induced hyponatremia in premature neonates.
What is Caffeine-Induced Hyponatremia?

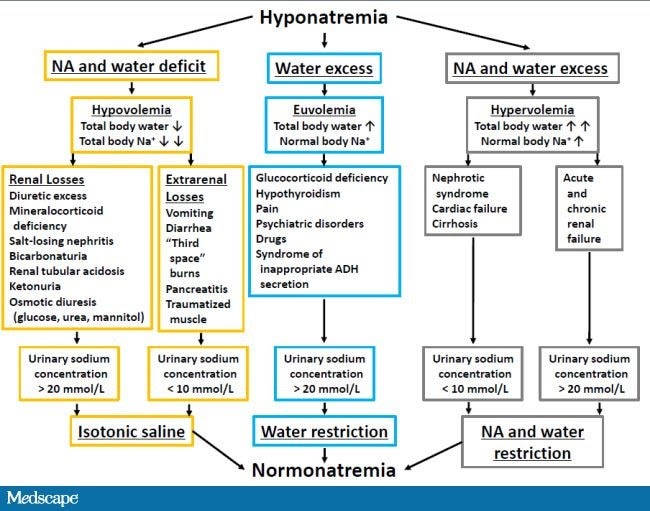
Hyponatremia is a condition characterized by low sodium levels in the blood. In the context of premature neonates receiving caffeine therapy, hyponatremia can occur due to the effects of caffeine on fluid and electrolyte balance. Caffeine has diuretic properties, which can lead to increased urination and, consequently, a loss of sodium and water from the body.
Risk Factors and Pathophysiology

Premature neonates are particularly susceptible to caffeine-induced hyponatremia due to their immature kidneys and limited ability to regulate fluid and electrolyte balance. The following factors contribute to the risk:
- Immature Renal Function: Premature neonates have underdeveloped kidneys, which may struggle to maintain proper sodium and water balance.
- Caffeine Dose and Duration: Higher doses of caffeine and prolonged treatment can increase the risk of hyponatremia.
- Fluid Intake: Inadequate fluid intake or excessive fluid loss can exacerbate the effects of caffeine-induced diuresis.
- Underlying Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as renal dysfunction or cardiac problems, can further impair the body’s ability to regulate sodium levels.
Diagnosis and Clinical Presentation

Recognizing the signs and symptoms of caffeine-induced hyponatremia is crucial for timely diagnosis and management. Common clinical presentations include:
- Nausea and Vomiting: Neonates may experience gastrointestinal symptoms, leading to further fluid and electrolyte imbalances.
- Seizures: In severe cases, hyponatremia can cause seizures, which are a medical emergency.
- Lethargy and Irritability: Premature neonates may become more lethargic or irritable than usual.
- Poor Feeding: Reduced appetite and difficulty feeding can be observed.
- Laboratory Findings: Blood tests will reveal low sodium levels (usually below 135 mmol/L) and potential electrolyte imbalances.
Management and Treatment

The management of caffeine-induced hyponatremia in premature neonates involves a multidisciplinary approach, including:
- Discontinuing Caffeine Therapy: In mild cases, temporarily stopping caffeine treatment may be sufficient to allow the body to restore sodium balance.
- Fluid and Electrolyte Replacement: Intravenous (IV) fluid therapy with sodium-containing solutions can help correct hyponatremia and restore fluid balance.
- Close Monitoring: Frequent monitoring of sodium levels, vital signs, and overall clinical status is essential to ensure the effectiveness of treatment.
- Medications: In severe cases, medications like vasopressin receptor antagonists or loop diuretics may be considered to help manage hyponatremia.
- Nutritional Support: Ensuring adequate nutrition and calorie intake is crucial to support the neonate’s overall health and recovery.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing caffeine-induced hyponatremia is of utmost importance in the care of premature neonates. Healthcare providers can implement the following strategies:
- Cautious Caffeine Administration: Carefully monitor caffeine doses and duration of treatment, especially in neonates with underlying medical conditions.
- Adequate Fluid Intake: Ensure proper fluid intake to match the neonate’s needs and prevent excessive fluid loss.
- Regular Sodium Monitoring: Routine monitoring of sodium levels can help identify early signs of hyponatremia and allow for prompt intervention.
- Education and Awareness: Healthcare providers and parents should be educated about the potential risks of caffeine therapy and the signs of hyponatremia.
Table: Caffeine Therapy Dosing Guidelines
| Age | Recommended Caffeine Dose (mg/kg/day) |
|---|---|
| 32-36 weeks gestational age | 10-20 |
| 28-31 weeks gestational age | 20-30 |
| <28 weeks gestational age | 20-40 |

Conclusion

Caffeine-induced hyponatremia is a significant concern in the management of premature neonates receiving caffeine therapy. By understanding the risk factors, recognizing the clinical presentation, and implementing appropriate management strategies, healthcare providers can effectively address this complication. Close collaboration between healthcare professionals, regular monitoring, and a proactive approach to prevention are key to ensuring the best possible outcomes for these vulnerable infants.
FAQ

What are the long-term effects of caffeine-induced hyponatremia in premature neonates?

+
Long-term effects of caffeine-induced hyponatremia in premature neonates can include neurological complications, such as cognitive impairments and developmental delays. Severe and untreated hyponatremia can lead to permanent brain damage. Therefore, early detection and management are crucial to minimize these potential long-term consequences.
Can caffeine-induced hyponatremia be reversed, and what is the recovery process like?

+
Yes, caffeine-induced hyponatremia can be reversed with prompt and appropriate treatment. The recovery process involves close monitoring of sodium levels, ensuring adequate fluid and electrolyte balance, and providing nutritional support. With timely intervention, most neonates can recover from hyponatremia without long-term complications.
Are there any alternative treatments to caffeine therapy for respiratory distress in premature neonates?

+
Yes, alternative treatments for respiratory distress in premature neonates include supportive care, such as oxygen therapy, nasal continuous positive airway pressure (nCPAP), and mechanical ventilation if necessary. Additionally, surfactant therapy and other medications may be considered to improve lung function. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of respiratory distress and the neonate’s overall condition.