The CRISPR-Cas9 system has revolutionized the field of genetic engineering, offering precise and efficient gene editing capabilities. Among its many applications, one intriguing area of research involves the creation of organoids, which are three-dimensional (3D) structures that mimic the architecture and functionality of human organs. In this blog post, we will explore the fascinating process of using CRISPR to form organoids and understand its potential impact on medical research and personalized medicine.
Understanding Organoids and Their Significance

Organoids are miniature, simplified versions of organs that are grown in a laboratory setting. These tiny structures are derived from stem cells, which have the remarkable ability to differentiate into various cell types. By providing the right conditions and cues, scientists can guide the stem cells to develop into specific organ-like structures.
The significance of organoids lies in their potential to revolutionize drug discovery, disease modeling, and personalized medicine. Organoids can be generated from patient-specific cells, allowing researchers to study diseases in a more personalized manner. This approach enables the identification of effective treatments tailored to an individual's unique genetic makeup.
CRISPR-Cas9: A Powerful Gene Editing Tool
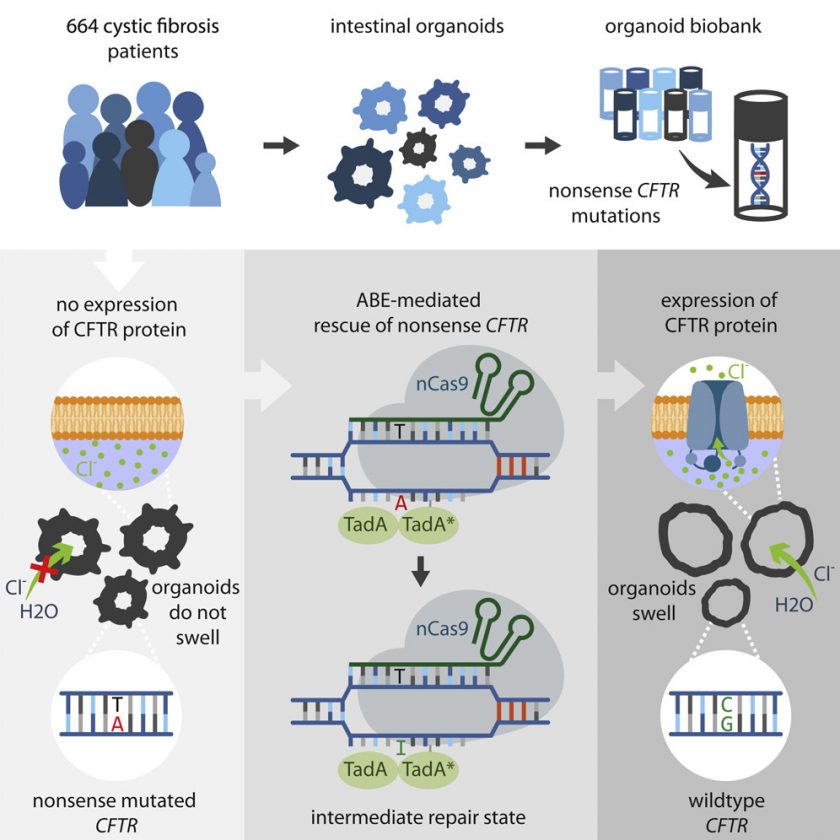
CRISPR-Cas9 is a genome editing technology derived from a bacterial immune system. It consists of two key components: the CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) and the Cas9 (CRISPR-associated protein 9) enzyme. This system allows scientists to make precise cuts at specific locations in the genome, enabling the insertion, deletion, or modification of DNA sequences.
The CRISPR-Cas9 system has gained immense popularity due to its simplicity, efficiency, and versatility. It has become a powerful tool in various fields, including biology, biotechnology, and medicine. With its ability to edit genes with high precision, CRISPR has opened up new possibilities for understanding and manipulating biological processes.
The Role of CRISPR in Organoid Formation

CRISPR-Cas9 plays a crucial role in the formation of organoids by enabling the manipulation of genes involved in organ development and function. By targeting specific genes, scientists can control the behavior and differentiation of stem cells, guiding them to form organ-like structures.
One of the key advantages of using CRISPR in organoid formation is its ability to introduce precise genetic modifications. This allows researchers to study the effects of specific gene mutations or variations on organ development and function. By comparing organoids with different genetic modifications, scientists can gain insights into the underlying mechanisms of various diseases and identify potential therapeutic targets.
Steps Involved in Creating Organoids with CRISPR

The process of creating organoids using CRISPR involves several key steps:
- Stem Cell Isolation and Culture: The first step is to isolate stem cells from the desired tissue or organ. These stem cells can be obtained from various sources, including embryonic stem cells, induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), or adult stem cells. The isolated stem cells are then cultured in a controlled environment to maintain their pluripotency.
- Genetic Modification with CRISPR: Once the stem cells are prepared, the CRISPR-Cas9 system is employed to introduce specific genetic modifications. This can involve knocking out genes, introducing point mutations, or inserting new genetic material. The choice of genetic modification depends on the research question or disease model being studied.
- Organoid Culture and Differentiation: After the genetic modification, the stem cells are cultured in a 3D environment that mimics the natural conditions of the target organ. This environment provides the necessary cues and growth factors to promote the differentiation of stem cells into organ-specific cell types. Over time, the cells self-organize and form complex 3D structures resembling the organ of interest.
- Organoid Characterization and Analysis: Once the organoids have reached a mature stage, they are characterized and analyzed to assess their functionality and similarity to the native organ. This involves various techniques such as immunohistochemistry, gene expression analysis, and functional assays. By comparing the organoids to the original tissue or organ, researchers can evaluate the success and accuracy of the organoid model.
Applications and Benefits of CRISPR-Generated Organoids

The use of CRISPR-generated organoids has several exciting applications and benefits:
- Disease Modeling: Organoids derived from patient-specific cells can serve as powerful models for studying various diseases. By introducing disease-causing mutations or genetic variations into the organoids, researchers can recreate and study the disease environment in a controlled manner. This allows for a deeper understanding of disease mechanisms and the development of targeted therapies.
- Drug Screening and Discovery: Organoids provide a valuable platform for drug screening and discovery. By exposing organoids to different compounds or drugs, researchers can assess their effectiveness and toxicity. This approach accelerates the drug development process and increases the likelihood of identifying successful treatments.
- Personalized Medicine: CRISPR-generated organoids have the potential to revolutionize personalized medicine. By creating organoids from an individual's own cells, researchers can tailor treatments specifically to that person's genetic makeup. This personalized approach can improve treatment outcomes and reduce the risk of adverse effects.
- Regenerative Medicine: Organoids hold promise in the field of regenerative medicine. By developing organoids that closely resemble native organs, scientists can explore the possibility of using them for transplantation or tissue repair. This could offer new hope for patients with organ failure or severe injuries.
Challenges and Future Perspectives

While the use of CRISPR-generated organoids shows immense potential, there are still challenges to be addressed. One of the main challenges is the complexity of organ development and the need to accurately replicate it in vitro. Organoids are simplified models, and further research is required to enhance their functionality and structural complexity.
Additionally, the ethical considerations surrounding the use of CRISPR and organoids must be carefully considered. The ability to modify genes and create organ-like structures raises important questions about safety, consent, and the potential impact on society. Striking a balance between scientific progress and ethical boundaries is crucial.
Despite these challenges, the future of CRISPR-generated organoids looks promising. With ongoing advancements in genome editing technologies and organoid culture techniques, we can expect to see more sophisticated and functional organoid models. These advancements will further our understanding of human biology, improve disease modeling, and pave the way for personalized and regenerative medicine.
Conclusion

In conclusion, the CRISPR-Cas9 system has emerged as a powerful tool for forming organoids, offering new opportunities for medical research and personalized medicine. By harnessing the precision of CRISPR, scientists can create organ-like structures that mimic the architecture and functionality of human organs. The applications of CRISPR-generated organoids in disease modeling, drug discovery, and personalized medicine are vast and hold the potential to transform healthcare.
As research in this field continues to evolve, we can anticipate exciting breakthroughs and advancements. The use of CRISPR-generated organoids may eventually lead to more effective treatments, improved patient outcomes, and a deeper understanding of human biology. The future of organoid research is indeed bright, and with continued efforts, we can expect to see its impact on healthcare and scientific discovery.
What are organoids and why are they important in medical research?

+
Organoids are 3D structures that mimic the architecture and function of human organs. They are important in medical research as they allow scientists to study diseases in a more personalized manner, identify effective treatments, and develop new therapies.
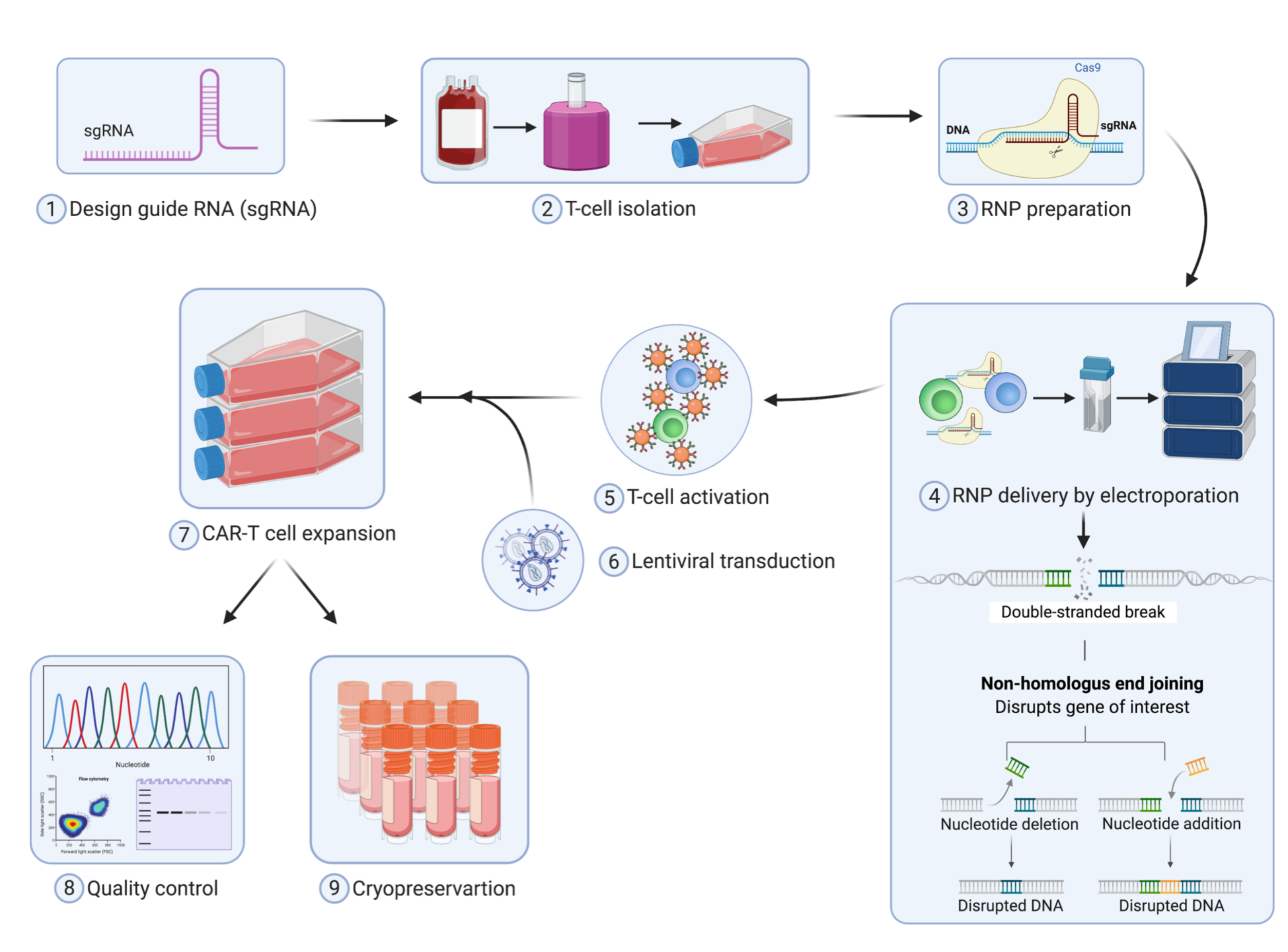
How does CRISPR-Cas9 work in gene editing?
+
CRISPR-Cas9 is a genome editing technology that uses a guide RNA to direct the Cas9 enzyme to a specific location in the genome. The Cas9 enzyme then makes a precise cut in the DNA, allowing for the insertion, deletion, or modification of genetic material.
What are the advantages of using CRISPR in organoid formation?

+
CRISPR allows for precise genetic modifications, enabling researchers to study the effects of specific gene mutations or variations on organ development and function. It also provides a platform for creating patient-specific organoids, facilitating personalized medicine approaches.
What are the potential applications of CRISPR-generated organoids?
+
CRISPR-generated organoids can be used for disease modeling, drug screening and discovery, personalized medicine, and regenerative medicine. They offer a valuable tool for understanding diseases, developing targeted therapies, and exploring tissue repair and transplantation.