Understanding the Conservative Hyperbolic PDE

The Conservative Hyperbolic Partial Differential Equation (PDE) is a fundamental concept in mathematics and physics, playing a crucial role in various scientific and engineering disciplines. This equation describes the behavior of conserved quantities, such as mass, momentum, or energy, as they evolve over time and space. In this blog post, we will delve into the intricacies of the Conservative Hyperbolic PDE, exploring its definition, characteristics, and applications.
Definition and Characteristics
The Conservative Hyperbolic PDE is a mathematical equation that represents the conservation of a specific quantity within a system. It is characterized by the following features:
- Conservation Principle: The equation ensures that the total amount of the conserved quantity remains constant over time. This principle is based on the fundamental laws of conservation, such as the conservation of mass or energy.
- Hyperbolic Nature: Hyperbolic PDEs exhibit a wave-like behavior, where information propagates through the system at a finite speed. This behavior is distinct from elliptic or parabolic PDEs, which have different characteristics.
- Partial Differentiation: The equation involves partial derivatives with respect to time and spatial coordinates. These derivatives capture the rate of change of the conserved quantity in both time and space.
- Initial and Boundary Conditions: The solution to the Conservative Hyperbolic PDE depends on the initial conditions, which describe the state of the system at a specific time, and the boundary conditions, which define the behavior of the system at its boundaries.
Mathematical Representation

The general form of the Conservative Hyperbolic PDE can be written as:
\[ \frac{\partial \mathbf{u}}{\partial t} + \nabla \cdot \mathbf{F}(\mathbf{u}) = \mathbf{0} \]
Where:
- \mathbf{u} is the vector of conserved quantities (e.g., mass density, momentum density, energy density).
- \mathbf{F}(\mathbf{u}) is the flux vector, which represents the flow of the conserved quantities across the system.
- \nabla \cdot denotes the divergence operator, which calculates the divergence of the flux vector.
- \frac{\partial \mathbf{u}}{\partial t} represents the rate of change of the conserved quantities with respect to time.
Applications and Examples
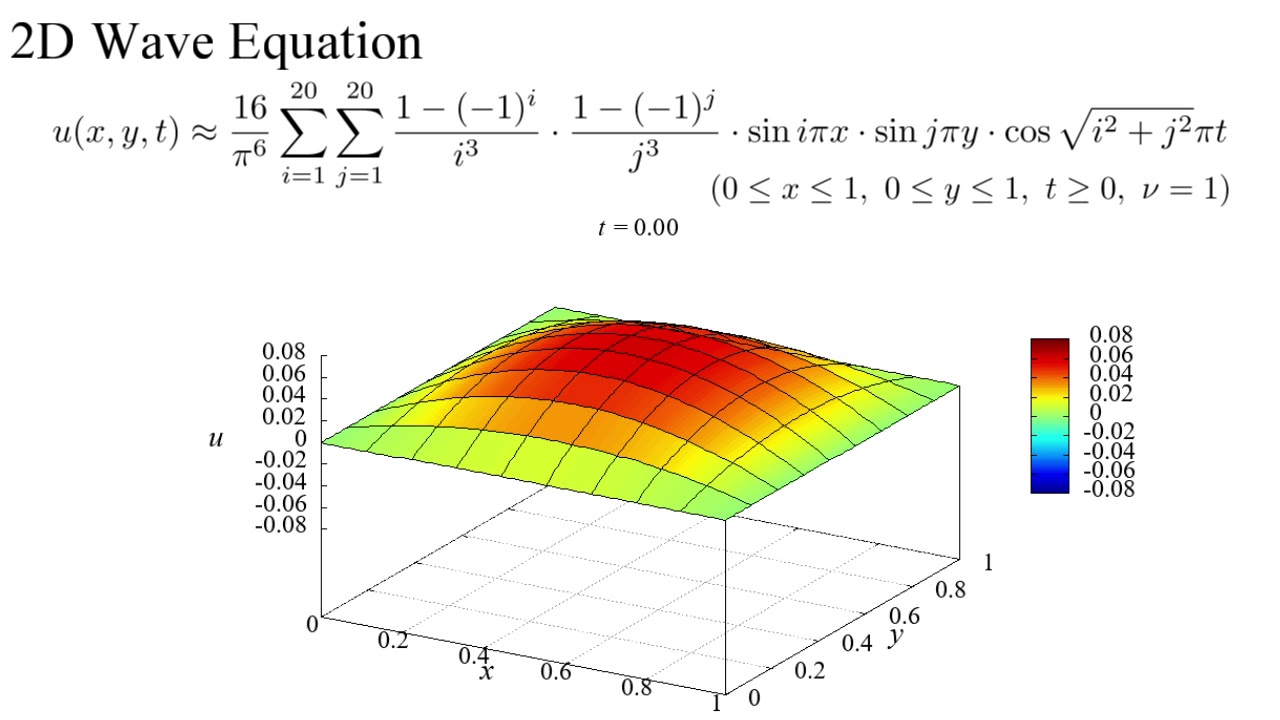
The Conservative Hyperbolic PDE finds applications in various fields, including:
Fluid Dynamics

In fluid dynamics, the Euler equations, which describe the conservation of mass, momentum, and energy in an inviscid fluid, are a classic example of the Conservative Hyperbolic PDE. These equations are used to model the behavior of gases and liquids in various scenarios, such as:
- Aerodynamics: Understanding the flow of air around aircraft or vehicles.
- Weather Forecasting: Predicting atmospheric conditions and modeling the behavior of storms.
- Hydrodynamics: Studying the motion of water in rivers, oceans, and other bodies of water.
Electromagnetism

Maxwell’s equations, which describe the behavior of electric and magnetic fields, can be formulated as a set of Conservative Hyperbolic PDEs. These equations are fundamental in understanding electromagnetic waves, such as light, and have applications in:
- Optics: Modeling the propagation of light through different media.
- Electrical Engineering: Designing and analyzing electrical circuits and systems.
- Radar and Communication Systems: Understanding the behavior of electromagnetic waves in communication and radar technologies.
Solid Mechanics

In solid mechanics, the conservation of momentum and energy is described by the Cauchy momentum equation, which is a Conservative Hyperbolic PDE. This equation is used to analyze the deformation and motion of solids, with applications in:
- Structural Analysis: Studying the behavior of bridges, buildings, and other structures under various loads.
- Earthquake Engineering: Understanding the response of structures to seismic events.
- Rock Mechanics: Modeling the behavior of rocks and geological formations.
Numerical Methods for Solving Conservative Hyperbolic PDEs
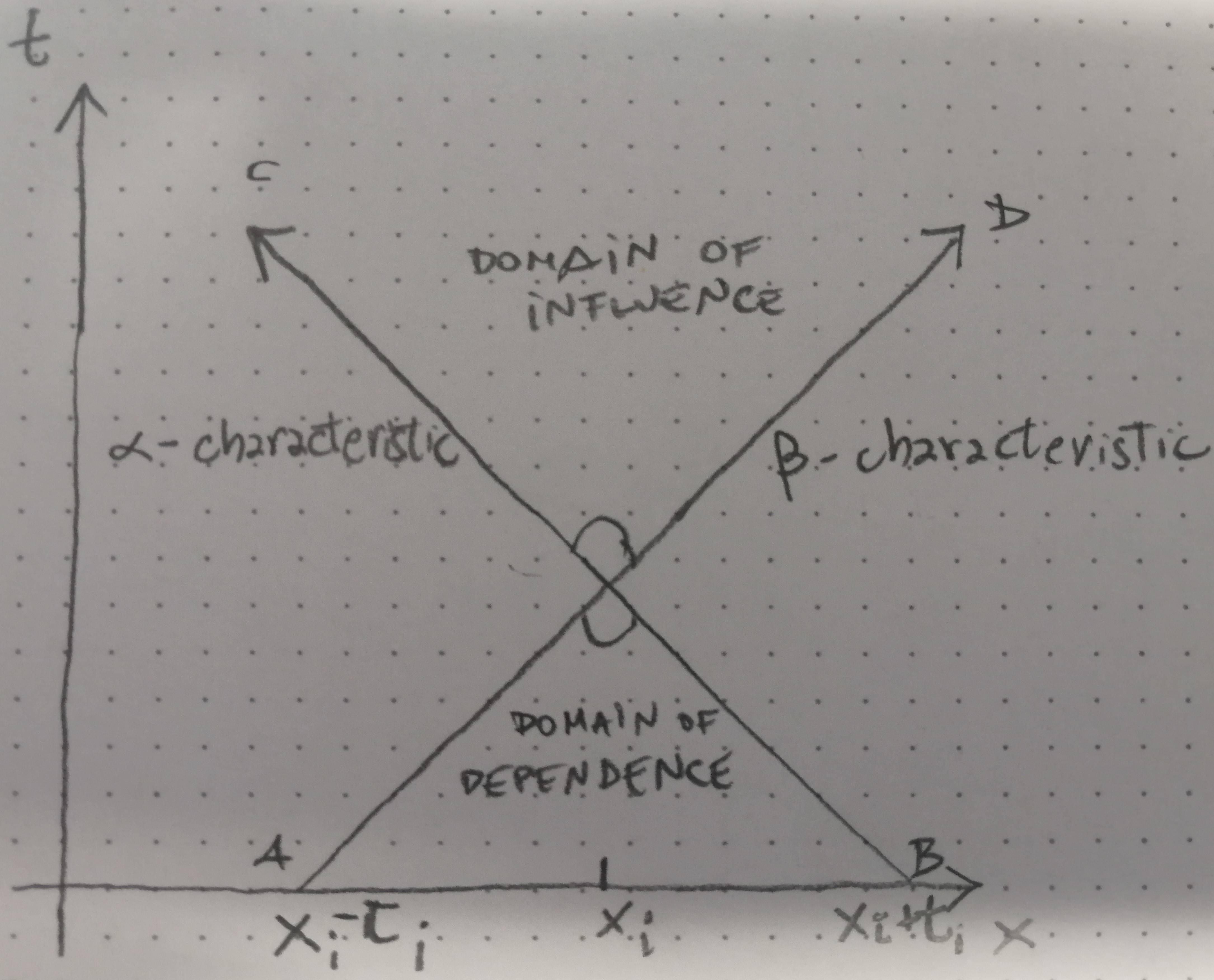
Solving Conservative Hyperbolic PDEs analytically can be challenging, especially for complex systems. Therefore, numerical methods are often employed to approximate solutions. Some common numerical techniques include:
- Finite Difference Method (FDM): Discretizes the spatial domain into a grid of points and approximates derivatives using finite differences. FDM is straightforward to implement but may suffer from numerical diffusion and stability issues.
- Finite Volume Method (FVM): Divides the domain into control volumes and conserves the fluxes across these volumes. FVM is widely used in computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and is known for its ability to handle complex geometries and adaptive meshes.
- Finite Element Method (FEM): Divides the domain into small elements and approximates the solution within each element using basis functions. FEM is versatile and can handle a wide range of PDEs, including Conservative Hyperbolic PDEs.
Challenges and Future Directions
While the Conservative Hyperbolic PDE has been well-studied, there are still open challenges and areas for further exploration:
- High-Order Accurate Schemes: Developing numerical methods that can accurately capture the fine details of the solution while maintaining stability is an ongoing research topic.
- Multidimensional Problems: Extending the numerical methods to handle complex, multidimensional problems, such as 3D fluid flows or electromagnetic wave propagation, remains a challenge.
- Boundary Conditions: Accurately representing and handling boundary conditions, especially in complex geometries, is crucial for obtaining accurate solutions.
- Parallel Computing: With the increasing demand for computational power, exploring parallel computing techniques to solve Conservative Hyperbolic PDEs efficiently is an active area of research.
Conclusion

The Conservative Hyperbolic PDE is a powerful tool for modeling and understanding the behavior of conserved quantities in various physical systems. Its applications span across fluid dynamics, electromagnetism, solid mechanics, and beyond. While analytical solutions are often challenging to obtain, numerical methods provide a versatile approach to approximate solutions and gain valuable insights into the behavior of these systems. As computational capabilities continue to advance, we can expect further developments in the numerical simulation of Conservative Hyperbolic PDEs, leading to more accurate and efficient modeling techniques.
What is the difference between a Conservative Hyperbolic PDE and an Elliptic PDE?

+
Conservative Hyperbolic PDEs exhibit wave-like behavior, with information propagating at a finite speed. In contrast, Elliptic PDEs have no time dependence and describe steady-state solutions, often used in problems with no time evolution.
How are numerical methods chosen for solving Conservative Hyperbolic PDEs?

+
The choice of numerical method depends on factors such as the complexity of the problem, the desired accuracy, and the available computational resources. Finite Difference, Finite Volume, and Finite Element Methods are commonly used, each with its strengths and limitations.
Can Conservative Hyperbolic PDEs be solved analytically?

+
Analytical solutions to Conservative Hyperbolic PDEs are often challenging to obtain, especially for complex systems. However, in simpler cases or with specific assumptions, analytical solutions may be possible, providing valuable insights into the behavior of the system.
What are some real-world applications of Conservative Hyperbolic PDEs in engineering?

+
Conservative Hyperbolic PDEs are used in engineering disciplines such as aerospace, automotive, and civil engineering. They help in designing aircraft wings, optimizing vehicle aerodynamics, and analyzing the structural integrity of buildings and bridges.
