The Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor (CSTR) is a versatile and widely used chemical reactor in various industries. Its unique design and operational principles make it an essential tool for chemical processes, offering efficient and controlled reactions. In this blog post, we will delve into the world of CSTRs, exploring their workings, advantages, and applications.
Understanding the Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor
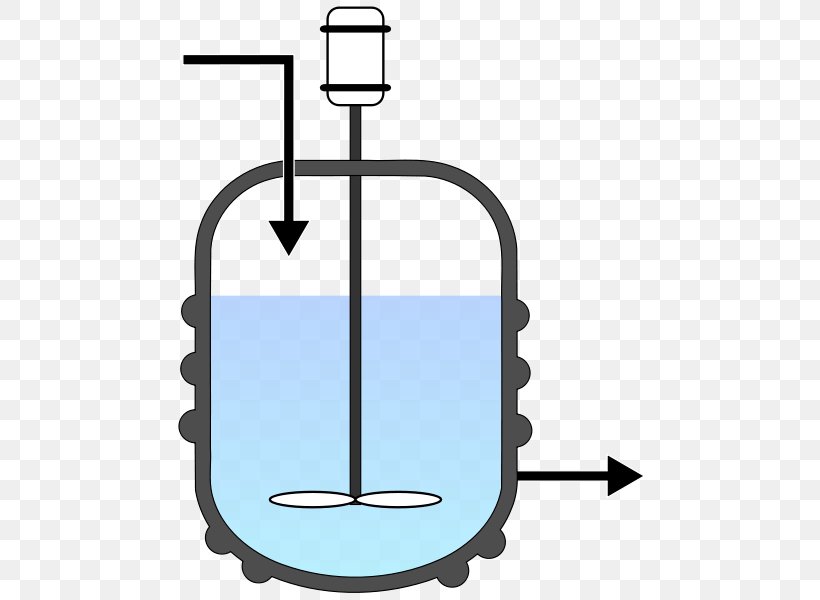
A Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor, often referred to as a CSTR, is a type of chemical reactor that operates continuously, meaning that reactants are continuously fed into the reactor while products are continuously removed. This distinct feature sets it apart from other reactor designs and provides several advantages in chemical engineering processes.
Key Characteristics of CSTRs
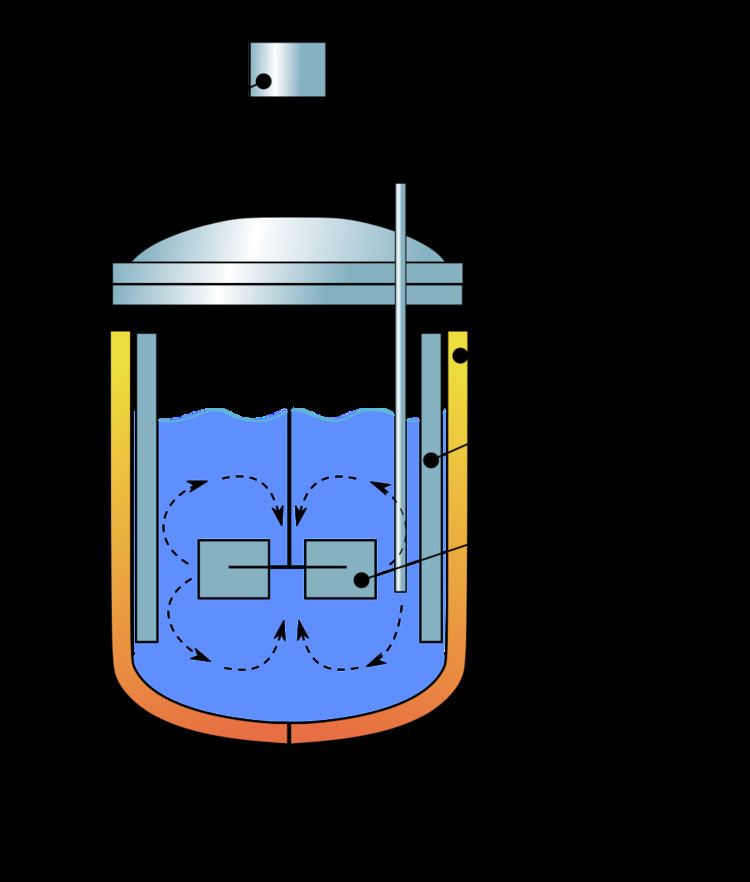
- Continuous Operation: CSTRs maintain a steady-state operation, ensuring a constant flow of reactants and products.
- Well-Mixed Reactants: The reactor's design promotes thorough mixing, resulting in a homogeneous reaction mixture.
- Uniform Conditions: Temperature, pressure, and composition remain consistent throughout the reactor, facilitating controlled reactions.
- Rapid Reaction: The continuous nature of CSTRs allows for quick reactions, making them suitable for processes with short residence times.
Design and Components of a CSTR

A CSTR consists of several key components that work together to facilitate efficient chemical reactions. These components include:
Reactor Vessel
The reactor vessel is the heart of the CSTR. It is a cylindrical or conical tank equipped with an agitator or impeller to ensure thorough mixing of the reactants. The vessel's size and shape are designed to accommodate the desired reaction volume and provide optimal mixing conditions.
Feed Streams

CSTRs are fed with reactants through multiple feed streams. These streams can be adjusted to control the flow rate and composition of the reactants, allowing for precise control over the reaction conditions.
Agitator or Impeller

The agitator or impeller is a crucial component that ensures the reactants are well-mixed within the reactor. It promotes the rapid and efficient mixing of the reactants, resulting in a homogeneous reaction mixture.
Exit Stream
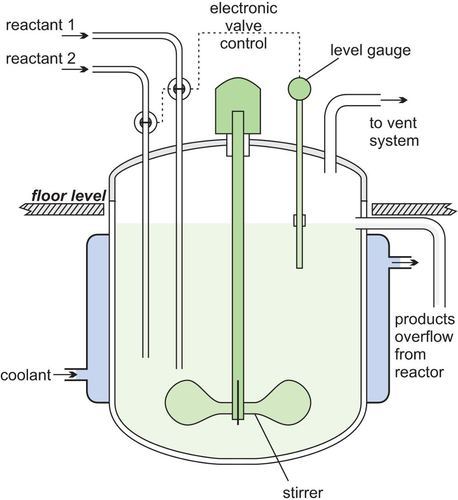
The exit stream is where the reaction products are continuously removed from the CSTR. This stream can be adjusted to control the residence time of the reactants within the reactor, allowing for fine-tuning of the reaction kinetics.
Advantages of Continuous Stirred Tank Reactors

CSTRs offer several advantages over other reactor designs, making them a popular choice in chemical engineering applications. Some of the key benefits include:
Enhanced Mixing

The continuous stirring or agitation within the CSTR ensures that reactants are thoroughly mixed, resulting in a homogeneous reaction mixture. This leads to improved reaction efficiency and product quality.
Rapid Reactions

The continuous operation of CSTRs allows for quick reactions, making them ideal for processes with short residence times. This rapid reaction capability is particularly advantageous in industries where time is a critical factor.
Flexible Operation

CSTRs offer flexibility in terms of operating conditions. By adjusting the feed rates and composition, engineers can control the reaction kinetics and optimize the process for different reactants and desired products.
Easy Scale-Up

The design of CSTRs allows for easy scale-up. Multiple CSTRs can be connected in series or parallel to increase the production capacity, making them suitable for both small-scale and large-scale operations.
Applications of Continuous Stirred Tank Reactors

CSTRs find applications in a wide range of industries due to their versatility and efficiency. Some common applications include:
Chemical Synthesis

CSTRs are widely used in chemical synthesis processes, such as the production of pharmaceuticals, fine chemicals, and specialty chemicals. Their ability to provide controlled reaction conditions and rapid reactions makes them ideal for these applications.
Petrochemical Industry
In the petrochemical industry, CSTRs play a crucial role in processes like catalytic cracking and hydrocracking. These reactors help convert crude oil into valuable products like gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel.
Food and Beverage Industry
CSTRs are utilized in the food and beverage industry for processes such as fermentation and enzymatic reactions. They enable the production of various food products, including beer, wine, and dairy products, with consistent quality and taste.
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
The pharmaceutical industry relies on CSTRs for the synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and other critical processes. Their ability to maintain uniform conditions and control reaction kinetics is essential for producing high-quality medications.
Modeling and Simulation of CSTRs

Modeling and simulation play a crucial role in understanding and optimizing the performance of CSTRs. By using mathematical models and computer simulations, engineers can predict the behavior of the reactor under different operating conditions, helping to design and operate CSTRs efficiently.
Mathematical Models
Mathematical models are developed to describe the behavior of CSTRs. These models take into account factors such as reaction kinetics, mass transfer, and heat transfer. By solving these models, engineers can predict the concentration of reactants and products, as well as the overall reaction rate.
Simulation Software
Various simulation software tools are available to simulate the operation of CSTRs. These tools allow engineers to input different operating parameters, such as feed rates, temperatures, and reactor dimensions, and obtain insights into the reactor's performance. Simulation helps in optimizing the design and operation of CSTRs for specific applications.
Safety Considerations in CSTR Operations

While CSTRs offer numerous advantages, it is essential to consider safety aspects when operating these reactors. Some key safety considerations include:
Pressure and Temperature Control
CSTRs operate under controlled pressure and temperature conditions. It is crucial to monitor and regulate these parameters to prevent any potential hazards, such as overpressure or thermal runaway.
Reactor Agitation
The agitation system within the CSTR must be properly designed and maintained to ensure efficient mixing without causing excessive wear and tear on the reactor components.
Material Compatibility
When selecting materials for the construction of CSTRs, it is important to consider the compatibility of the reactor components with the reactants and products. Incompatible materials can lead to corrosion, degradation, or even failure of the reactor.
Safety Protocols
Implementing robust safety protocols and training personnel on emergency procedures is vital. This includes regular maintenance, leak detection systems, and emergency shutdown procedures to ensure the safe operation of CSTRs.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of CSTRs

Proper maintenance and troubleshooting are essential to ensure the smooth operation of CSTRs. Some common maintenance practices and troubleshooting techniques include:
Regular Inspections
Conducting regular inspections of the reactor vessel, agitator, and other components is crucial to identify any signs of wear, corrosion, or damage. This helps in preventing unexpected failures and ensures the longevity of the reactor.
Cleaning and Sanitization
Cleaning and sanitizing the CSTR after each batch or at regular intervals is necessary to prevent contamination and ensure product quality. Proper cleaning procedures should be followed to remove any residues or byproducts from previous reactions.
Agitator Maintenance
The agitator or impeller is a critical component that requires regular maintenance. This includes inspecting for wear, balancing the impeller, and ensuring proper alignment to maintain efficient mixing.
Leak Detection and Repair
Leak detection systems should be in place to identify any leaks in the reactor vessel or feed/exit streams. Prompt repair of leaks is essential to prevent product loss and potential safety hazards.
Case Studies: Successful Implementation of CSTRs

The successful implementation of CSTRs in various industries has led to significant advancements and improved process efficiency. Here are a few case studies showcasing the impact of CSTRs:
Pharmaceutical Industry
A leading pharmaceutical company implemented CSTRs in their manufacturing process for a critical API. The CSTRs enabled them to achieve higher reaction yields, reduce reaction times, and improve product purity. This resulted in increased production capacity and reduced costs.
Chemical Synthesis
A specialty chemical manufacturer utilized CSTRs for the synthesis of a complex organic compound. The continuous operation of the CSTRs allowed for precise control over the reaction conditions, resulting in a higher-quality product with reduced byproducts. This led to a significant improvement in product consistency and reduced waste generation.
Petrochemical Industry
In the petrochemical industry, CSTRs have been employed for catalytic cracking processes. By optimizing the reactor design and operating conditions, companies have achieved higher conversion rates, improved product selectivity, and reduced energy consumption. This has resulted in increased profitability and reduced environmental impact.
Conclusion

The Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor is a versatile and powerful tool in the chemical engineering toolkit. Its continuous operation, efficient mixing, and control over reaction conditions make it an ideal choice for a wide range of applications. From chemical synthesis to the petrochemical and pharmaceutical industries, CSTRs play a crucial role in achieving efficient and high-quality reactions. By understanding the design, advantages, and applications of CSTRs, engineers can leverage this technology to optimize chemical processes and drive innovation in various industries.
What are the key advantages of using a CSTR over other reactor designs?
+CSTRs offer enhanced mixing, rapid reactions, flexible operation, and easy scale-up. These advantages make them suitable for a wide range of chemical processes, especially those requiring controlled reaction conditions and quick turnover.
How does the design of a CSTR promote efficient mixing of reactants?
+The reactor vessel of a CSTR is equipped with an agitator or impeller that ensures thorough mixing of the reactants. This continuous stirring results in a homogeneous reaction mixture, leading to improved reaction efficiency and product quality.
What are some common applications of CSTRs in the pharmaceutical industry?
+CSTRs are widely used in the pharmaceutical industry for the synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and other critical processes. Their ability to maintain uniform conditions and control reaction kinetics is crucial for producing high-quality medications.
How can modeling and simulation be used to optimize CSTR performance?
+By using mathematical models and simulation software, engineers can predict the behavior of CSTRs under different operating conditions. This allows for the optimization of reactor design, operating parameters, and process control, leading to improved efficiency and product quality.
What are some key safety considerations when operating CSTRs?
+Safety considerations include pressure and temperature control, proper reactor agitation, material compatibility, and the implementation of robust safety protocols. Regular maintenance, leak detection systems, and emergency shutdown procedures are also vital for safe CSTR operations.