In today's data-driven world, creating informative and visually appealing dashboards is crucial for businesses to gain insights and make informed decisions. Tableau, a powerful data visualization tool, offers a wide range of features to design dashboards that are not only functional but also aesthetically pleasing. In this blog post, we will explore the art of designing ultimate Tableau dashboards and uncover the key elements that make them effective.
Understanding the Purpose and Audience

Before diving into the design process, it's essential to define the purpose of your dashboard and identify your target audience. Consider the following questions:
- What specific insights or information do you want to convey?
- Who will be using the dashboard, and what is their level of expertise or familiarity with data visualization?
- What actions or decisions do you want the audience to take based on the dashboard's insights?
By clearly understanding the purpose and audience, you can tailor your dashboard design to meet their needs and ensure a seamless user experience.
Data Preparation and Visualization Techniques

Effective data visualization starts with clean and organized data. Ensure that your data is well-prepared, with consistent formatting and relevant metadata. Here are some key considerations for data preparation:
- Clean and validate your data to remove any errors or inconsistencies.
- Standardize units and labels to maintain consistency.
- Create calculated fields or measures to derive new insights from your data.
- Apply appropriate data transformations, such as aggregation or normalization, to facilitate effective visualization.
Once your data is prepared, choose the right visualization techniques to represent your insights accurately. Consider the nature of your data and the story you want to tell. Some common visualization types include:
- Bar charts and line charts for comparing values over time or categories.
- Pie charts and donut charts for displaying proportional data.
- Scatter plots for exploring relationships between variables.
- Heatmaps for visualizing data distribution or patterns.
- Maps for geographical data representation.
Experiment with different visualization types and explore Tableau's extensive gallery of charts and graphs to find the best fit for your data.
Dashboard Layout and Organization
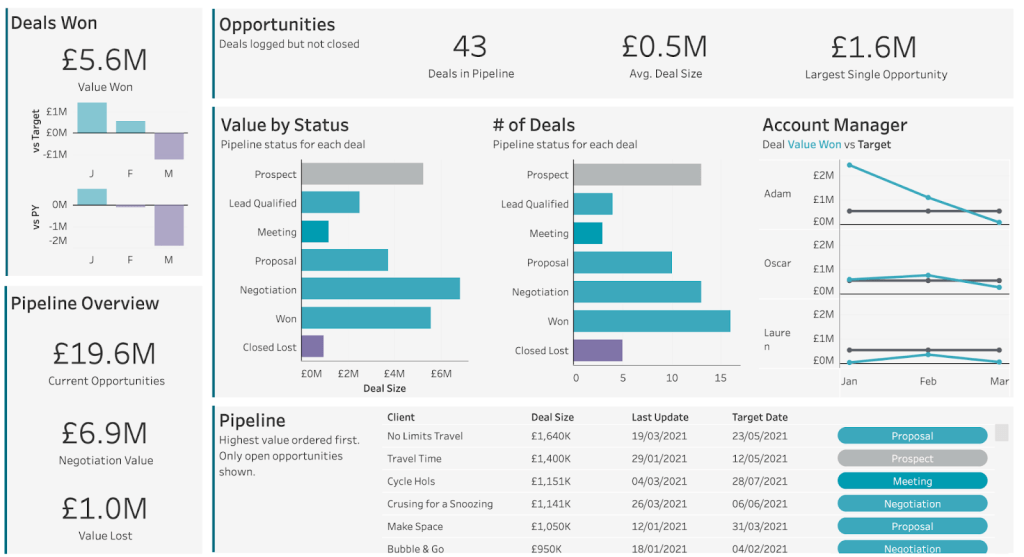
A well-organized dashboard layout is crucial for guiding users through the insights and ensuring a smooth navigation experience. Here are some best practices to consider:
- Use a consistent layout pattern throughout your dashboard to maintain a sense of familiarity.
- Group related visualizations together and provide clear labels or headings to indicate their purpose.
- Utilize white space effectively to improve readability and visual hierarchy.
- Consider the flow of information and ensure that the most important insights are easily accessible.
- Incorporate interactive elements, such as filters, sliders, or drill-down options, to allow users to explore the data further.
Keep in mind that simplicity is key. Avoid overcrowding your dashboard with unnecessary visuals or clutter. Focus on delivering the most relevant and actionable insights to your audience.
Color and Formatting for Impact
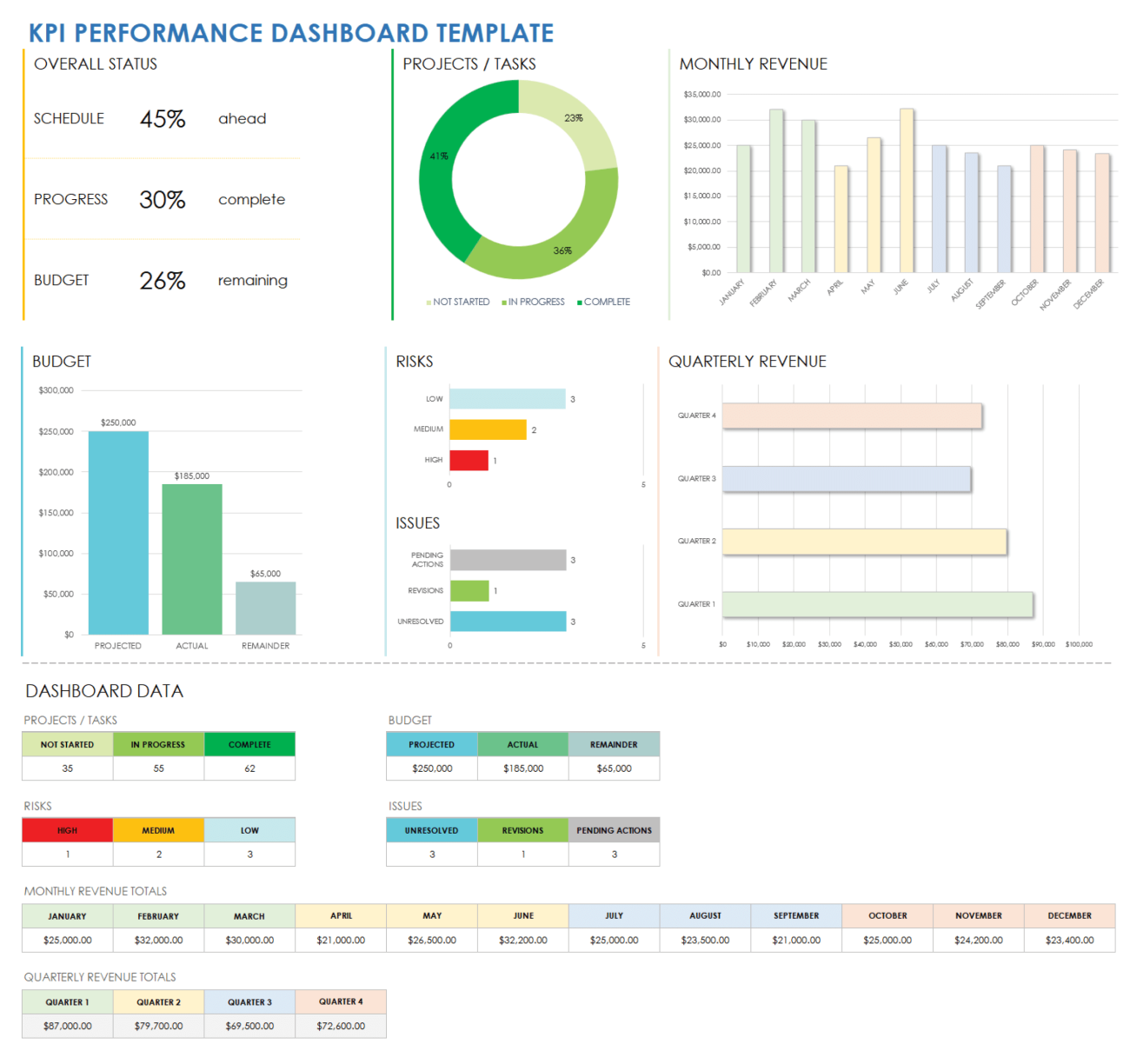
Color and formatting play a significant role in the visual appeal and effectiveness of your dashboard. Here are some tips to enhance your design:
- Choose a color palette that aligns with your brand guidelines or complements the data being presented.
- Use color to highlight important trends, anomalies, or key performance indicators.
- Avoid using too many colors or overly bright shades, as they may distract from the data.
- Apply consistent formatting across similar visualizations to maintain a cohesive look.
- Consider using tooltips or pop-up boxes to provide additional context or detailed information when users hover over a specific data point.
Remember, the goal is to enhance the clarity and understandability of your dashboard, not to overwhelm users with excessive visual elements.
Storytelling with Data

Dashboards are not just about presenting data; they are a powerful tool for storytelling. By arranging your visualizations in a logical sequence, you can guide users through a narrative that highlights the most important insights. Consider the following storytelling techniques:
- Start with an overview or summary visualization to provide a high-level view of the data.
- Follow up with more detailed visualizations that support the initial insights.
- Use annotations or callouts to draw attention to specific data points or trends.
- Incorporate text boxes or narratives to provide context and explain the significance of the insights.
- Consider adding interactive elements, such as buttons or sliders, to allow users to explore different scenarios or drill down into specific areas of interest.
By crafting a compelling data story, you can engage your audience and ensure that the insights are not only understood but also remembered.
Dashboard Interactivity and User Engagement
Interactivity is a powerful feature of Tableau dashboards, allowing users to explore and interact with the data in real-time. Here are some ways to enhance user engagement:
- Implement filters to allow users to focus on specific subsets of data.
- Use parameters to enable users to adjust certain variables and see the impact on the visualizations.
- Create dashboards with drill-down capabilities, enabling users to delve deeper into the data hierarchy.
- Incorporate tooltips or pop-ups to provide additional information or context when users hover over visualizations.
- Utilize actions, such as highlighting or filtering, to connect different visualizations and create a seamless user experience.
By incorporating interactivity, you empower your users to explore the data, uncover hidden insights, and make more informed decisions.
Performance and Optimization

As your dashboard becomes more complex, ensuring optimal performance becomes crucial. Consider the following tips to maintain a smooth and responsive dashboard:
- Optimize your data sources and connections to reduce loading times.
- Use Tableau's data engine efficiently by avoiding unnecessary calculations or large data sets.
- Apply aggregation or sampling techniques to handle large datasets without compromising performance.
- Test your dashboard on different devices and browsers to ensure cross-platform compatibility.
- Consider using Tableau Server or Tableau Online to host your dashboard and take advantage of their robust infrastructure.
By optimizing your dashboard's performance, you can provide a seamless user experience and ensure that your insights are delivered promptly.
Collaborative Dashboarding
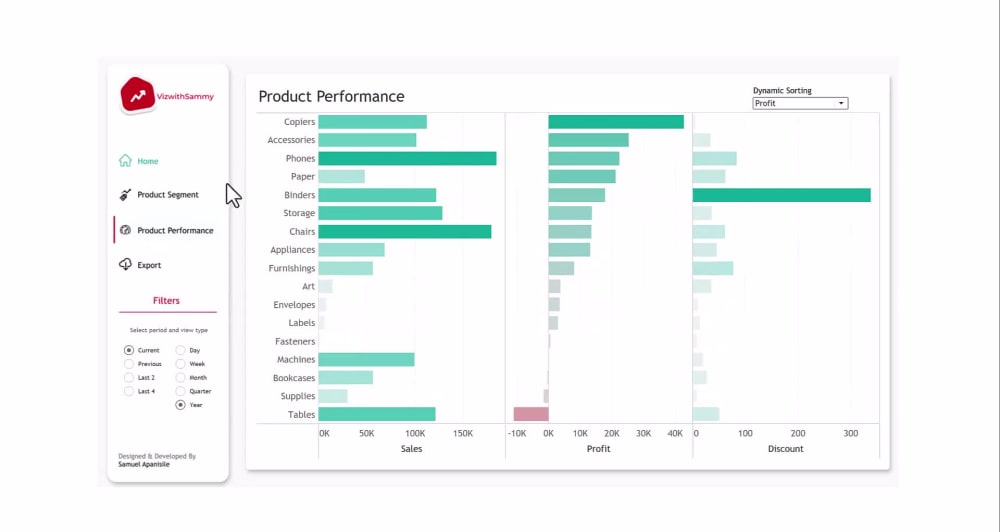
Tableau offers collaborative features that allow multiple users to work together on a dashboard. This can be especially beneficial for teams working on complex projects or when seeking feedback from stakeholders. Here's how you can leverage collaboration:
- Use Tableau's commenting feature to gather feedback and suggestions from team members or clients.
- Share your dashboard with colleagues or clients and invite them to provide insights or make suggestions.
- Incorporate feedback into your dashboard design to enhance its effectiveness and meet the needs of your audience.
- Utilize Tableau's version control and collaboration tools to track changes and ensure a seamless workflow.
By embracing collaboration, you can create dashboards that are not only visually appealing but also aligned with the needs and insights of your team or stakeholders.
Conclusion
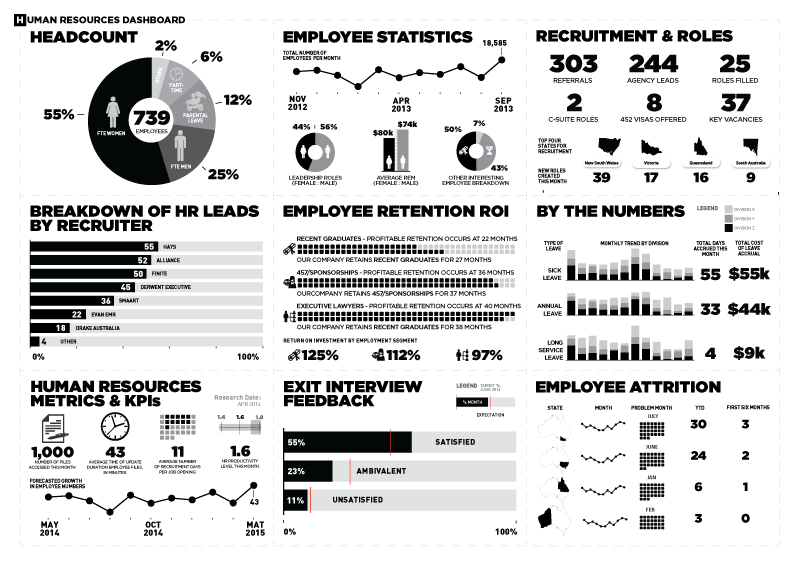
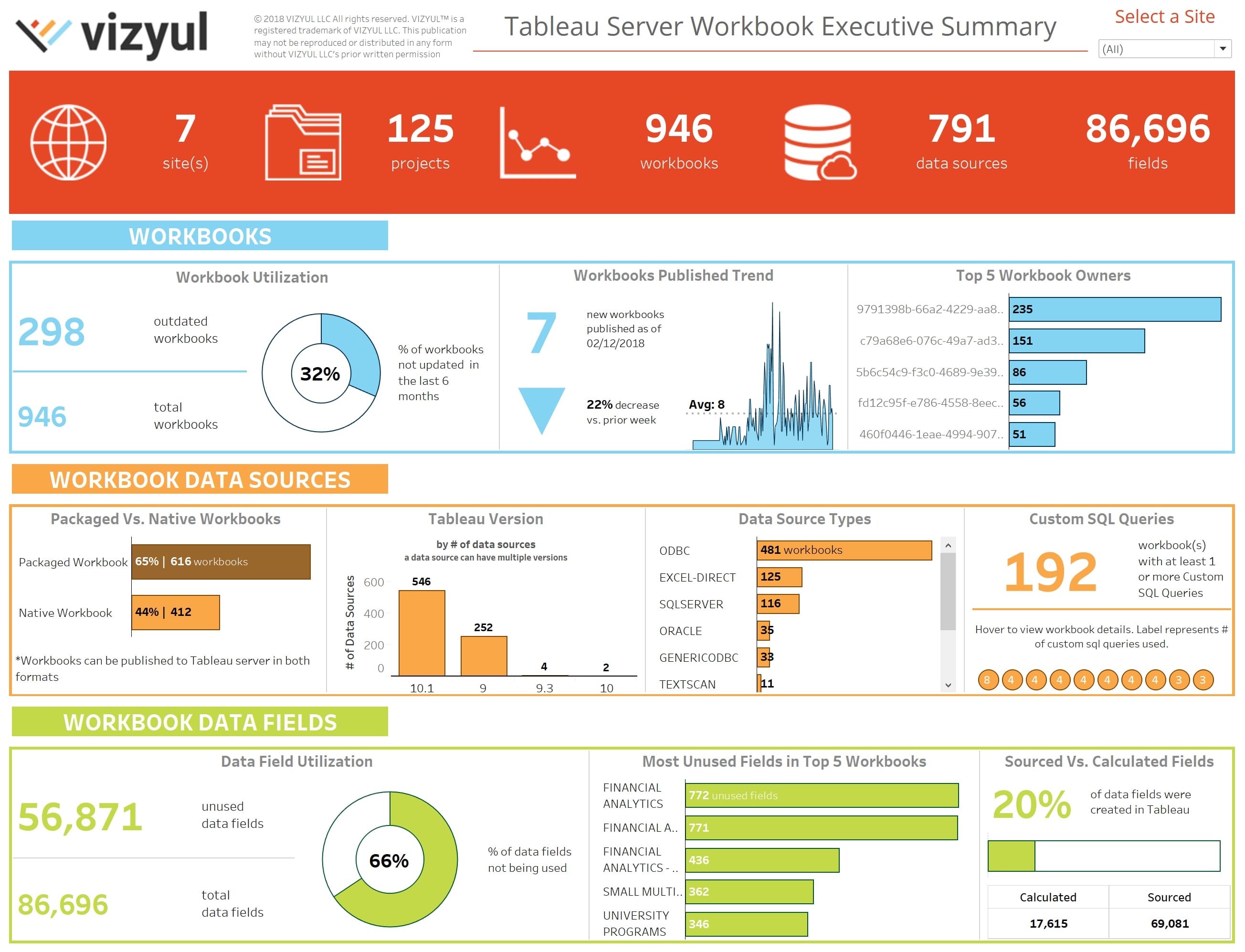
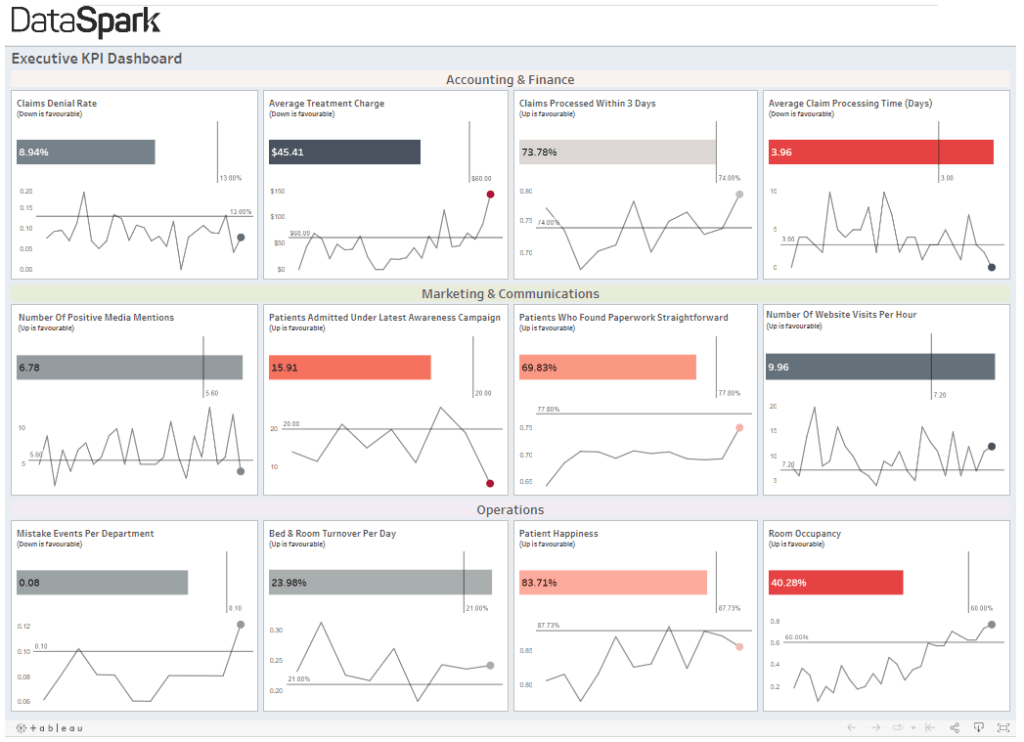
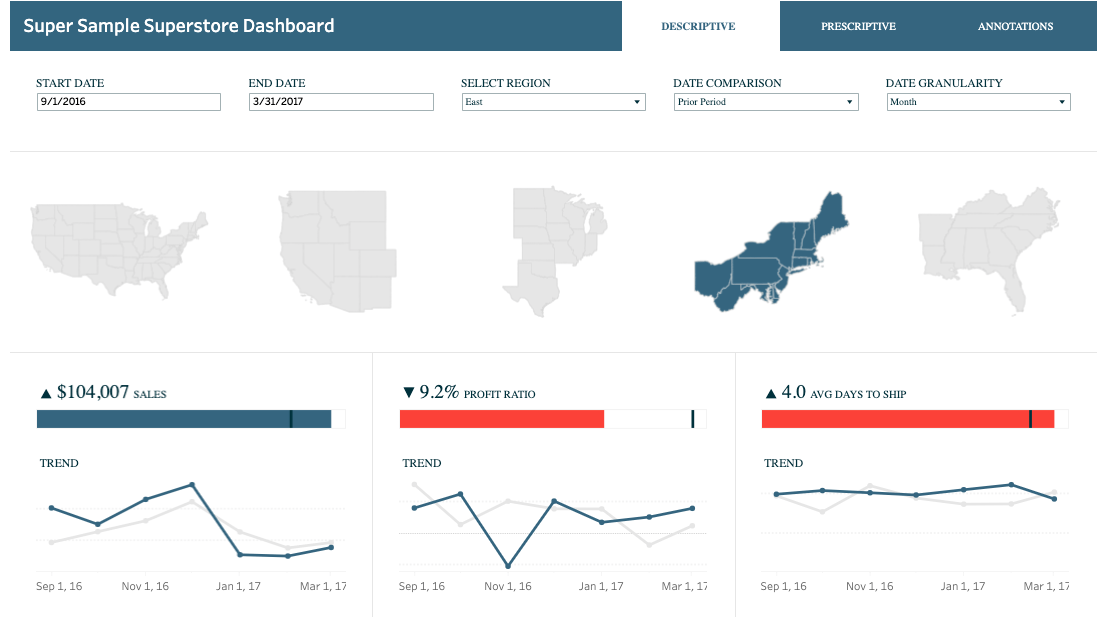
Designing ultimate Tableau dashboards requires a combination of data preparation, visualization techniques, thoughtful layout, and storytelling. By understanding your audience, organizing your data effectively, and applying interactive elements, you can create dashboards that not only showcase insights but also engage and inspire action. Remember, a well-designed dashboard is a powerful tool for data-driven decision-making, and with Tableau's extensive features, the possibilities are endless.
FAQ
How can I ensure my dashboard is accessible to users with visual impairments?
+
To make your dashboard accessible, consider using high-contrast colors, providing alternative text for images, and ensuring that all interactive elements are keyboard-accessible. Additionally, consider using screen reader-friendly formats and providing clear labels for visualizations.
What is the best way to handle large datasets in Tableau?

+
When working with large datasets, it’s important to optimize your data connections and utilize aggregation or sampling techniques. Consider using Tableau’s data engine efficiently and avoid unnecessary calculations to maintain performance.
How can I incorporate advanced analytics into my Tableau dashboard?

+
Tableau offers a range of advanced analytics features, such as forecasting, what-if analysis, and predictive modeling. You can leverage these tools to incorporate advanced insights into your dashboard. Additionally, you can integrate external data sources or connect to R or Python for more complex analytics.
What are some best practices for designing dashboards for mobile devices?
+
When designing for mobile, keep the layout simple and focus on the most critical insights. Use responsive design techniques to ensure your dashboard adapts to different screen sizes. Consider the user’s interaction patterns and prioritize touch-friendly elements.