In the realm of medical imaging, the visualization of the intricate intestinal system is a crucial aspect, aiding in the diagnosis and treatment of various gastrointestinal conditions. This article delves into the process of creating comprehensive and detailed images of the intestines, highlighting the importance of advanced imaging techniques and their impact on patient care.
Understanding the Intestinal Anatomy
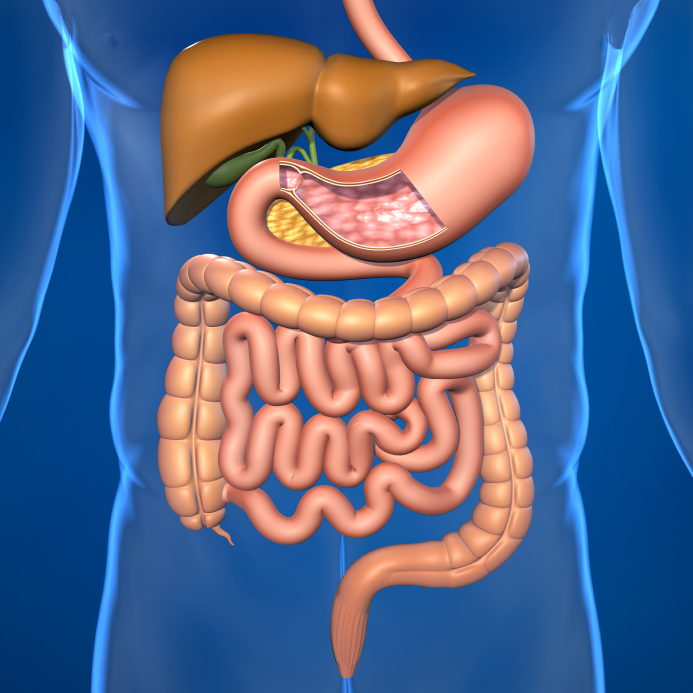
The human intestine, a complex organ, is divided into two main parts: the small intestine and the large intestine. Each part serves unique functions, making their accurate imaging essential for a proper diagnosis.
The small intestine, consisting of the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum, is responsible for the majority of digestion and absorption of nutrients. It is a long, coiled tube with a surface area enhanced by folds and villi, increasing its efficiency. On the other hand, the large intestine, also known as the colon, is shorter and wider, primarily responsible for the absorption of water and electrolytes, and the formation and elimination of waste products.
Advanced Imaging Techniques
To visualize the intricate details of the intestines, advanced imaging techniques are employed, offering a non-invasive approach to diagnosis. These techniques provide a detailed view of the intestinal anatomy, aiding in the identification of abnormalities and the assessment of their severity.
Computed Tomography (CT) Scan

A CT scan is a powerful imaging tool that uses X-rays and computer processing to create detailed images of the body's internal structures. In the context of intestinal imaging, a CT scan can provide cross-sectional images of the abdomen, offering a clear view of the intestines and any potential abnormalities.
CT scans are particularly useful in detecting intestinal obstructions, inflammation, and masses. They can also help identify complications associated with inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) such as Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)

MRI is another advanced imaging technique that utilizes strong magnetic fields and radio waves to generate detailed images of the body's internal structures. In intestinal imaging, MRI can provide high-resolution images of the intestinal wall, aiding in the diagnosis of various conditions.
MRI is particularly effective in assessing the extent and severity of inflammatory bowel diseases, as it can detect subtle changes in the intestinal wall that may not be visible on other imaging modalities.
Ultrasound Imaging
Ultrasound imaging, also known as sonography, is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the body's internal structures. In intestinal imaging, ultrasound can provide real-time images of the intestines, offering a dynamic view of their function and any abnormalities.
Ultrasound is particularly useful in detecting intestinal wall thickening, which can be a sign of inflammation or malignancy. It is also a valuable tool for guiding biopsies and other interventional procedures.
Creating Comprehensive Intestinal Images

To create the ultimate intestinal images, a combination of these advanced imaging techniques is often employed. Each technique offers unique advantages, and their complementary nature enhances the overall diagnostic accuracy.
For instance, a CT scan can provide a comprehensive view of the abdomen, identifying potential issues throughout the intestinal tract. MRI, with its high-resolution capabilities, can then be used to further assess the severity of any abnormalities detected, particularly in the context of IBD.
Ultrasound imaging, with its real-time capabilities, can be used to monitor the intestinal function and assess the response to treatment. It can also guide interventional procedures, ensuring precision and minimizing risks.
The Impact on Patient Care

The creation of comprehensive intestinal images has a significant impact on patient care. Accurate and detailed imaging allows for early detection of gastrointestinal conditions, leading to timely intervention and improved outcomes.
With advanced imaging techniques, healthcare professionals can accurately diagnose and stage various intestinal disorders, such as inflammatory bowel diseases, intestinal obstructions, and cancers. This enables the development of personalized treatment plans, optimizing patient care and improving quality of life.
Additionally, the non-invasive nature of these imaging techniques reduces the need for more invasive procedures, such as exploratory surgery, minimizing patient discomfort and potential complications.
Notes

![]() Note: The use of advanced imaging techniques in intestinal imaging should be complemented by a comprehensive clinical assessment, including patient history and physical examination.
Note: The use of advanced imaging techniques in intestinal imaging should be complemented by a comprehensive clinical assessment, including patient history and physical examination.
![]() Note: While advanced imaging techniques offer significant advantages, they should be used judiciously, considering the potential risks and benefits for each patient.
Note: While advanced imaging techniques offer significant advantages, they should be used judiciously, considering the potential risks and benefits for each patient.
![]() Note: Ongoing research and advancements in imaging technology continue to enhance our ability to visualize and understand the intricacies of the intestinal system.
Note: Ongoing research and advancements in imaging technology continue to enhance our ability to visualize and understand the intricacies of the intestinal system.
Conclusion

The creation of ultimate intestinal images is a complex process, requiring a combination of advanced imaging techniques and a thorough understanding of intestinal anatomy. By employing these techniques, healthcare professionals can provide accurate diagnoses, leading to effective treatment and improved patient outcomes. As technology advances, the field of intestinal imaging continues to evolve, offering new opportunities for enhanced patient care.
FAQ

What are the advantages of advanced imaging techniques in intestinal imaging?
+
Advanced imaging techniques offer a non-invasive approach to diagnosis, providing detailed images of the intestinal anatomy. They aid in the early detection of abnormalities, allowing for timely intervention and improved patient outcomes.
How do CT scans contribute to intestinal imaging?

+
CT scans provide cross-sectional images of the abdomen, offering a comprehensive view of the intestines. They are particularly useful in detecting intestinal obstructions, inflammation, and masses.
What are the benefits of MRI in intestinal imaging?
+
MRI offers high-resolution images of the intestinal wall, aiding in the diagnosis of inflammatory bowel diseases and other conditions. It can detect subtle changes that may not be visible on other imaging modalities.
How does ultrasound imaging contribute to intestinal imaging?
+
Ultrasound imaging provides real-time images of the intestines, offering a dynamic view of their function. It is useful in detecting intestinal wall thickening and guiding interventional procedures.