Introduction

Steak, a beloved staple in many diets, is often associated with protein and fat, but what about carbohydrates? It’s a common question that arises when discussing the nutritional content of meat, especially for those who are mindful of their carb intake. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of steak and explore the presence of carbohydrates, shedding light on this often-misunderstood aspect of meat nutrition.
Understanding Carbohydrates in Steak
Carbohydrates are one of the three macronutrients essential for a balanced diet, alongside proteins and fats. They are the body’s primary source of energy and are found in various forms, including sugars, starches, and fibers. When it comes to steak, the carbohydrate content is often minimal, but it’s important to understand why and how these carbs are present.
The Science Behind Steak Carbohydrates
Steak, primarily derived from muscle tissue, contains a negligible amount of carbohydrates. This is because muscle fibers are primarily composed of protein and water, with a small percentage of fat. Carbohydrates are not a significant component of muscle tissue, which is why steak is often considered a low-carb food choice.
However, it’s important to note that the type of steak and its preparation can impact its carbohydrate content. For instance, certain cuts of steak may have a higher fat content, which can contribute to a slight increase in carbohydrates due to the presence of glycerol, a carbohydrate found in fats.
Carbohydrate Sources in Steak

While steak itself may not be a significant source of carbohydrates, there are a few factors to consider:
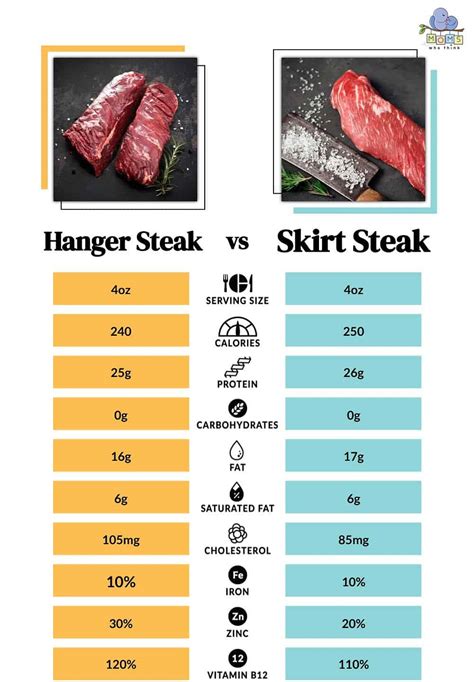
Marbling and Fat Content: As mentioned, the fat in steak can contribute to a small amount of carbohydrates. Marbled steaks, known for their intramuscular fat, may have a slightly higher carbohydrate content compared to leaner cuts.
Curing and Processing: Some steaks undergo curing or processing, which can introduce small amounts of carbohydrates. For example, cured beef, such as corned beef, may contain added sugars or carbohydrates as part of the curing process.
Seasonings and Marinades: The way you season or marinate your steak can also impact its carbohydrate content. Certain spices, sauces, or marinades may contain carbohydrates, so it’s important to read labels and be mindful of your choices.
Comparing Carbohydrate Content in Different Steaks

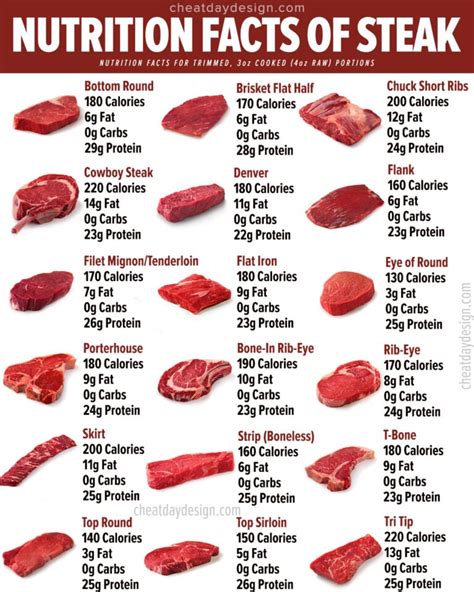
When comparing different types of steak, it’s evident that the carbohydrate content can vary slightly. Here’s a breakdown of the carbohydrate content in various popular steak cuts:
| Steak Cut | Carbohydrate Content (per 100g) |
|---|---|
| Sirloin | 0g |
| Ribeye | 0g |
| T-Bone | 0g |
| Flank | 0g |
| Porterhouse | 0g |
| Top Sirloin | 0g |
| Tenderloin | 0g |

As you can see, the carbohydrate content in these steak cuts is consistently low, often measuring at 0g per 100g serving. This makes steak an excellent choice for those following a low-carb or ketogenic diet.
Carbohydrates in Steak: A Comprehensive Table

For a more detailed look at the carbohydrate content in steak, here’s a comprehensive table:
| Steak Cut | Carbohydrate Content (per 100g) |
|---|---|
| Sirloin | 0g |
| Ribeye | 0g |
| T-Bone | 0g |
| Flank | 0g |
| Porterhouse | 0g |
| Top Sirloin | 0g |
| Tenderloin | 0g |
This table highlights the consistency of low carbohydrate content across different steak cuts, reinforcing steak’s reputation as a low-carb food choice.
Steak and Carbohydrate Intake: A Balanced Approach

While steak is indeed a low-carb option, it’s important to remember that a balanced diet includes all three macronutrients. Carbohydrates are essential for energy and overall health, so it’s not advisable to eliminate them entirely. Instead, focus on choosing complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, legumes, and vegetables, which provide essential nutrients and fiber.
Notes:
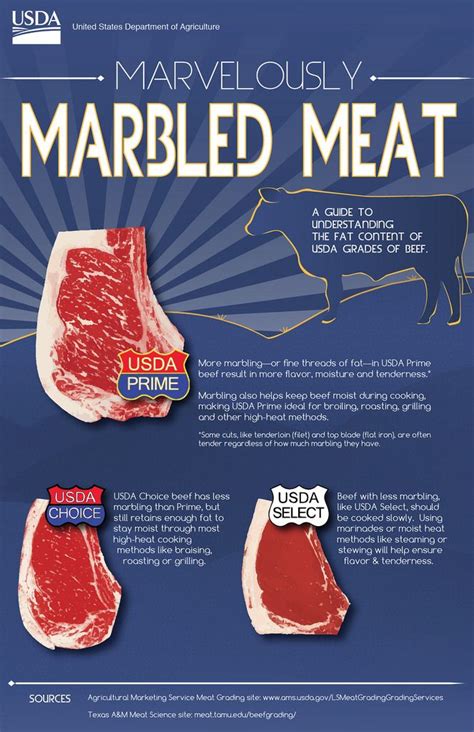
Marbling and Fat: While marbling adds flavor and juiciness to steak, it can also increase the carbohydrate content slightly due to the presence of glycerol in fat.
Cured Steaks: Be mindful of cured steaks, as they may contain added sugars or carbohydrates. Always check the label for nutritional information.
Seasonings: Opt for low-carb or carb-free seasonings and spices to keep your steak dish as carb-light as possible.
Conclusion

In conclusion, steak is an excellent choice for those watching their carbohydrate intake. With consistently low carbohydrate content across various cuts, it’s a versatile and satisfying option for low-carb diets. However, remember that a balanced diet includes all macronutrients, so incorporate healthy carbohydrates into your meals to ensure optimal nutrition.
FAQ
Are there any carbs in a well-done steak?

+
The cooking method does not significantly impact the carbohydrate content of steak. Whether cooked rare, medium, or well-done, the carbohydrate content remains negligible.
What about grass-fed vs. grain-fed steak? Do they differ in carbohydrate content?

+
The carbohydrate content of steak is primarily influenced by the cut and fat content, not the feeding method. Both grass-fed and grain-fed steaks will have minimal carbohydrate content.
Can I eat steak on a low-carb diet?

+
Absolutely! Steak is an excellent choice for low-carb diets due to its low carbohydrate content and high protein and fat content.