The emergence of CRISPR technology has revolutionized the field of biotechnology, offering unprecedented precision and efficiency in genetic engineering. As this revolutionary tool continues to advance, its potential economic impacts are becoming increasingly evident across various sectors. From agriculture to healthcare and beyond, CRISPR is poised to reshape industries and drive significant economic transformations.
Agricultural Revolution: Boosting Productivity and Sustainability
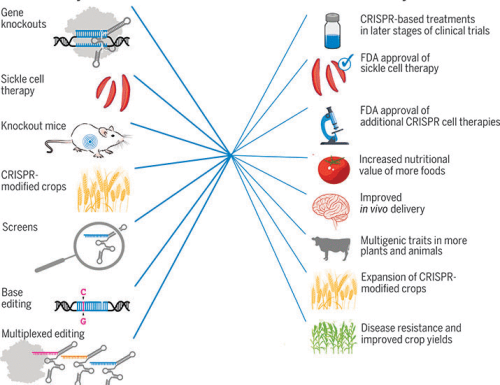
CRISPR technology has the potential to revolutionize agriculture, offering innovative solutions to enhance crop yields and address global food security challenges. By precisely editing the genetic makeup of plants, CRISPR enables the development of crops with improved traits, such as increased resistance to pests and diseases, enhanced nutritional value, and better adaptation to changing environmental conditions.
One of the key economic impacts of CRISPR in agriculture lies in its ability to reduce reliance on chemical pesticides and fertilizers. Through precise genetic modifications, CRISPR can create crops that are naturally resistant to pests, thereby minimizing the need for costly and environmentally harmful chemical interventions. This not only reduces input costs for farmers but also promotes sustainable agricultural practices, benefiting both the environment and consumers.
Furthermore, CRISPR technology can accelerate the development of new crop varieties, shortening the time required for traditional breeding methods. This rapid development cycle enables farmers to adapt more quickly to changing market demands and emerging challenges, such as the need for drought-resistant or nutrient-rich crops. By enhancing crop productivity and resilience, CRISPR has the potential to boost agricultural productivity and contribute to global food security.
Healthcare Breakthroughs: Personalized Medicine and Gene Therapy

In the realm of healthcare, CRISPR technology is paving the way for groundbreaking advancements in personalized medicine and gene therapy. By enabling precise editing of the human genome, CRISPR offers the potential to treat and even cure a wide range of genetic disorders and diseases.
One of the most significant economic impacts of CRISPR in healthcare is its ability to reduce healthcare costs in the long run. By targeting the root cause of genetic diseases, CRISPR-based therapies can potentially provide lifelong cures, eliminating the need for lifelong treatments and reducing the overall financial burden on healthcare systems. Additionally, the precision and efficiency of CRISPR technology reduce the risk of adverse side effects, leading to more effective and safer treatments.
CRISPR-based gene therapies have already shown promising results in clinical trials for various conditions, including rare genetic disorders and certain types of cancer. The success of these therapies has the potential to revolutionize the healthcare industry, attracting significant investment and fostering the development of a robust gene therapy market. As CRISPR technology continues to advance and become more accessible, it is expected to drive innovation and competition, leading to further cost reductions and improved accessibility of gene therapy treatments.
Industrial Applications: Biomanufacturing and Biofuels

CRISPR technology is not limited to agriculture and healthcare; it also holds immense potential in various industrial applications. One of the key areas where CRISPR is making an impact is biomanufacturing, which involves the use of living organisms or their components to produce valuable products.
By employing CRISPR-based genetic engineering, industries can enhance the production of bio-based chemicals, materials, and fuels. For instance, CRISPR can be used to modify microorganisms, such as bacteria or yeast, to optimize their ability to produce biofuels or bioplastics. This not only reduces the reliance on fossil fuels but also contributes to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly industrial sector.
Additionally, CRISPR technology can be applied in the production of enzymes and other biological molecules with specific functions. These molecules can be used in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, food, and cosmetics, to enhance product quality and efficiency. The precision and efficiency of CRISPR-based biomanufacturing processes have the potential to revolutionize industrial production, leading to increased productivity and reduced costs.
Ethical and Regulatory Considerations

While the economic potential of CRISPR technology is undeniable, it is important to address the ethical and regulatory considerations surrounding its use. The ability to precisely edit the human genome raises complex ethical questions, particularly in relation to germline editing, which involves making changes that can be inherited by future generations.
Regulatory bodies play a crucial role in ensuring the safe and responsible use of CRISPR technology. They establish guidelines and standards to govern its application, including strict oversight of clinical trials and the implementation of safety measures. Striking a balance between promoting innovation and protecting public health and ethical standards is essential to maximize the benefits of CRISPR while minimizing potential risks.
Future Prospects and Challenges

The future of CRISPR technology holds immense promise, with ongoing research and development efforts aimed at expanding its applications and improving its efficiency. However, several challenges need to be addressed to fully realize its economic potential.
One of the key challenges is ensuring the accessibility and affordability of CRISPR-based technologies. While significant progress has been made in recent years, further research and investment are required to make CRISPR-based therapies and applications more widely available, particularly in developing countries. Addressing these accessibility issues is crucial to ensure that the benefits of CRISPR technology are distributed equitably across the globe.
Additionally, continued research is needed to enhance the precision and specificity of CRISPR editing, particularly in complex organisms. Improving the accuracy of CRISPR technology will not only reduce the risk of off-target effects but also enhance its therapeutic potential. Addressing these technical challenges will be essential to unlock the full economic and societal benefits of CRISPR.
Furthermore, public awareness and education play a vital role in shaping the perception and acceptance of CRISPR technology. By engaging in open dialogue and providing accurate information, we can foster a society that understands and supports the responsible use of CRISPR, leading to greater acceptance and adoption of its applications.
Conclusion

CRISPR technology has emerged as a powerful tool with far-reaching economic impacts across various sectors. From revolutionizing agriculture and healthcare to driving innovation in industrial applications, CRISPR has the potential to transform industries and improve lives. As we navigate the ethical and regulatory considerations surrounding its use, it is essential to strike a balance between promoting innovation and ensuring responsible and equitable access to this groundbreaking technology. With continued research, investment, and public engagement, the economic potential of CRISPR can be fully realized, leading to a more sustainable, healthy, and prosperous future.
What is CRISPR technology, and how does it work?

+
CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) is a gene-editing technology that allows scientists to make precise changes to the DNA of living organisms. It works by using a guided RNA molecule to target a specific DNA sequence, which is then cut by an enzyme called Cas9. This cutting process enables the insertion, deletion, or modification of genetic material, allowing for precise genetic engineering.
How does CRISPR impact the agricultural industry?
+
CRISPR technology has the potential to revolutionize agriculture by enabling the development of crops with improved traits, such as increased pest and disease resistance, enhanced nutritional value, and better adaptation to changing environmental conditions. It can reduce reliance on chemical pesticides and fertilizers, promote sustainable farming practices, and accelerate the development of new crop varieties, contributing to global food security.
What are the economic implications of CRISPR in healthcare?

+
CRISPR technology has the potential to reduce healthcare costs by providing lifelong cures for genetic disorders and diseases. By targeting the root cause of these conditions, CRISPR-based therapies can eliminate the need for lifelong treatments, reducing the financial burden on healthcare systems. Additionally, the precision and efficiency of CRISPR technology reduce the risk of adverse side effects, leading to more effective and safer treatments.
What are the industrial applications of CRISPR technology?

+
CRISPR technology has various industrial applications, including biomanufacturing and the production of biofuels. By modifying microorganisms, CRISPR can enhance the production of bio-based chemicals, materials, and fuels, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and promoting sustainability. It can also be used to produce enzymes and other biological molecules with specific functions, benefiting industries such as pharmaceuticals, food, and cosmetics.