The elastic modulus, also known as Young's modulus, is a fundamental mechanical property that describes the stiffness and elasticity of a material. It quantifies the relationship between the stress applied to a material and the resulting strain, providing insights into how a material will behave under different loading conditions. In this blog post, we will delve into the elastic modulus of aluminum, exploring its definition, significance, calculation methods, and real-world applications.
Understanding Elastic Modulus

Elastic modulus is a measure of a material's ability to resist deformation when subjected to an external force. It represents the ratio of stress to strain within the elastic limit of the material. When a material is within its elastic limit, it will return to its original shape once the force is removed. The elastic modulus is a crucial parameter in the field of materials science and engineering, as it helps engineers and designers select appropriate materials for various applications.
Significance of Elastic Modulus in Aluminum
Aluminum is a widely used metal known for its lightweight nature, corrosion resistance, and excellent mechanical properties. Its elastic modulus plays a vital role in determining its suitability for different structural applications. Understanding the elastic modulus of aluminum allows engineers to predict how the metal will respond to various loads and design structures accordingly.
Calculating Elastic Modulus

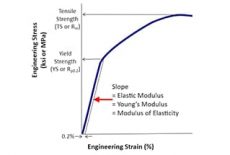
The elastic modulus of a material can be calculated using the following formula:
E = σ / ε
Where:
- E is the elastic modulus (Young's modulus)
- σ is the tensile stress applied to the material
- ε is the resulting strain
To calculate the elastic modulus of aluminum, we need to conduct tensile tests on aluminum specimens. During these tests, the specimen is subjected to an increasing tensile load until it reaches its yield point or ultimate tensile strength. By measuring the stress and strain values at different points during the test, we can determine the elastic modulus.
Tensile Tests for Aluminum

Tensile tests are essential to determine the mechanical properties of aluminum, including its elastic modulus. These tests involve pulling a sample of aluminum in tension until it fails. By analyzing the load-deformation curve obtained during the test, engineers can calculate the elastic modulus and other important parameters such as yield strength and ultimate tensile strength.
Factors Affecting Elastic Modulus

The elastic modulus of aluminum can be influenced by several factors, including:
- Alloy Composition: Different aluminum alloys have varying elastic moduli due to their unique compositions. Alloying elements such as magnesium, silicon, and copper can significantly impact the material's stiffness.
- Temperature: Temperature variations can affect the elastic modulus of aluminum. As the temperature increases, the elastic modulus generally decreases, leading to a more flexible material.
- Microstructure: The microstructure of aluminum, including grain size and orientation, can influence its elastic properties. Fine-grained aluminum tends to have higher elastic moduli compared to coarse-grained aluminum.
- Processing Techniques: The manufacturing process and heat treatment techniques used in producing aluminum can impact its elastic modulus. Cold working, for example, can increase the elastic modulus by introducing dislocations and strengthening the material.
Applications of Aluminum's Elastic Modulus

The elastic modulus of aluminum finds extensive applications in various industries, including:
- Aerospace: Aluminum's high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent elastic properties make it a preferred material for aircraft construction. The elastic modulus is crucial in designing aircraft structures that can withstand aerodynamic loads.
- Automotive: Aluminum is widely used in the automotive industry for manufacturing lightweight and fuel-efficient vehicles. The elastic modulus helps engineers design safe and durable car frames and body panels.
- Construction: Aluminum's elastic modulus plays a significant role in the construction industry. It is used in building structures, roofing, and window frames, where its stiffness and resistance to deformation are essential.
- Electrical and Electronics: Aluminum's good electrical conductivity and high elastic modulus make it suitable for electrical wiring and electronic components. Its ability to withstand mechanical stresses without deformation is crucial in these applications.
Real-World Examples

Let's explore a couple of real-world examples to illustrate the importance of aluminum's elastic modulus:
Aircraft Wings

In the aerospace industry, the elastic modulus of aluminum is critical in designing aircraft wings. The wings must withstand the aerodynamic forces during flight while maintaining their shape and stability. By selecting aluminum alloys with appropriate elastic moduli, engineers can ensure the structural integrity of the wings, reducing the risk of deformation or failure.
Aluminum Canisters

Aluminum canisters, commonly used for packaging beverages and food, rely on the elastic modulus of aluminum to maintain their shape and structural integrity. The canisters must withstand internal pressure and external forces without deforming or bursting. The elastic modulus of aluminum ensures that the canisters can withstand these stresses, providing a safe and reliable packaging solution.
Comparison with Other Materials

Aluminum's elastic modulus can be compared to that of other commonly used materials. Here's a table comparing the elastic moduli of aluminum, steel, and titanium:
| Material | Elastic Modulus (GPa) |
|---|---|
| Aluminum | 70 |
| Steel | 200 |
| Titanium | 110 |

As shown in the table, steel has a significantly higher elastic modulus compared to aluminum, indicating that steel is stiffer and less flexible. Titanium, on the other hand, has an elastic modulus between that of aluminum and steel, making it a suitable choice for applications requiring a balance between stiffness and flexibility.
Conclusion

The elastic modulus of aluminum is a crucial parameter that influences its mechanical behavior and suitability for various applications. By understanding the factors affecting its elastic modulus and conducting tensile tests, engineers can make informed decisions when selecting aluminum alloys for specific structural designs. The real-world examples highlighted in this blog post demonstrate the practical significance of aluminum's elastic modulus in industries such as aerospace, automotive, construction, and electrical engineering.
FAQ
How does the elastic modulus of aluminum compare to other metals like steel and titanium?

+
Aluminum has a lower elastic modulus compared to steel, which means it is more flexible and less stiff. Titanium, on the other hand, has an elastic modulus between that of aluminum and steel, offering a balance between stiffness and flexibility.
Can the elastic modulus of aluminum be improved through alloying or heat treatment?

+
Yes, the elastic modulus of aluminum can be enhanced by alloying it with elements like magnesium, silicon, or copper. Additionally, heat treatment techniques such as aging or solution treatment can further improve its elastic properties.
What are the advantages of using aluminum with a higher elastic modulus in structural applications?

+
Aluminum alloys with higher elastic moduli offer increased stiffness and resistance to deformation. This makes them suitable for applications where structural integrity and stability are crucial, such as aircraft wings or load-bearing components in buildings.