High Rupturing Capacity (HRC) fuses are an essential component in electrical systems, designed to protect circuits and prevent damage caused by excessive current flow. These fuses are a critical safety measure, ensuring the stability and reliability of electrical networks. In this blog post, we will delve into the world of HRC fuses, exploring their function, types, selection criteria, and installation guidelines. By the end of this article, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of HRC fuses and their role in maintaining a safe and efficient electrical infrastructure.
Understanding High Rupturing Capacity Fuses

HRC fuses are specifically engineered to handle high-energy faults and overcurrent situations. Unlike standard fuses, which operate within a narrower current range, HRC fuses are designed to withstand higher currents and provide an extra layer of protection for sensitive equipment and systems. They are commonly used in industrial, commercial, and residential settings, where electrical safety is of utmost importance.
The primary function of an HRC fuse is to interrupt the flow of current in the event of an overload or short circuit. When an excessive current passes through the fuse, it heats up and melts the fusible element, breaking the circuit and preventing further damage. This rapid response time ensures that potential hazards are mitigated, reducing the risk of fires, equipment damage, and electrical accidents.
Types of HRC Fuses

HRC fuses come in various types, each designed for specific applications and voltage levels. Understanding the different types is crucial for selecting the right fuse for your electrical system.
Cartridge Fuses

Cartridge fuses are one of the most common types of HRC fuses. They are cylindrical in shape and typically have a ceramic or glass body with metal end caps. Cartridge fuses are widely used in low-voltage applications, such as residential and commercial electrical panels. They are available in different sizes and current ratings, making them versatile for various load requirements.
Blade Fuses

Blade fuses, also known as plug-in fuses, are another popular type of HRC fuse. They feature a blade-like design with two prongs that fit into a fuse holder. Blade fuses are commonly used in automotive and marine applications, as well as in some low-voltage electrical systems. They offer a compact and easy-to-install solution, making them convenient for quick fuse replacements.
D-Type Fuses
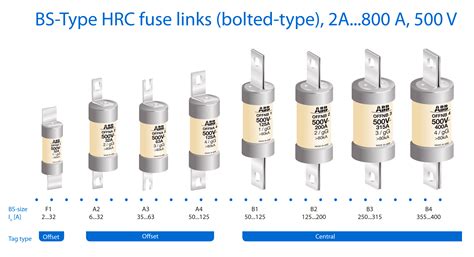
D-type fuses, named after their distinctive D-shaped body, are often used in industrial and commercial settings. They are designed to handle higher voltage and current levels compared to cartridge and blade fuses. D-type fuses are commonly found in control panels, switchboards, and motor control centers, providing reliable protection for critical equipment.
NH Fuses

NH fuses, also known as DIN rail fuses, are a type of HRC fuse designed for easy installation on DIN rail systems. They are commonly used in industrial applications and offer a wide range of current ratings. NH fuses are known for their compact size and ability to handle high-current faults, making them suitable for protection in motor circuits and transformers.
Selecting the Right HRC Fuse

Choosing the appropriate HRC fuse for your electrical system requires careful consideration of several factors. Here are some key criteria to keep in mind:
- Voltage Rating: Ensure that the fuse's voltage rating matches the system's voltage level. Using a fuse with a lower voltage rating can lead to premature failure and inadequate protection.
- Current Rating: Select a fuse with a current rating that is slightly higher than the normal operating current of your circuit. This allows for a safety margin and prevents nuisance tripping.
- Application: Consider the specific application and load requirements. Different types of HRC fuses are designed for various applications, such as motor protection, lighting circuits, or sensitive electronic equipment.
- Interchangeability: Ensure that the chosen fuse is compatible with the fuse holder or base in your system. Incompatible fuses can lead to improper installation and reduced protection.
- Environmental Factors: Take into account the operating environment, including temperature, humidity, and potential exposure to corrosive substances. Some HRC fuses are designed for harsh environments and offer additional protection against these factors.
Installation Guidelines
Proper installation of HRC fuses is crucial for ensuring their effectiveness and maintaining electrical safety. Follow these guidelines for a safe and reliable installation:
- Fuse Holder: Use a fuse holder or base that is compatible with the chosen HRC fuse. Ensure that the holder is securely mounted and properly rated for the fuse's current and voltage.
- Wiring: Connect the fuse to the circuit using appropriate gauge wires. Make sure the wires are securely tightened to prevent loose connections, which can lead to arcing and potential hazards.
- Polarity: Pay attention to the polarity of the fuse and the circuit. Incorrect polarity can result in improper operation and reduced protection.
- Accessibility : Install the fuse in a location that is easily accessible for inspection and replacement. This allows for quick maintenance and ensures that the fuse can be checked regularly for any signs of damage or wear.
- Documentation: Keep a record of the installed HRC fuse, including its rating, manufacturer, and installation date. This documentation is essential for future maintenance and replacement purposes.
Maintenance and Replacement

Regular maintenance and timely replacement of HRC fuses are vital for the overall performance and safety of your electrical system. Here are some key points to consider:
- Inspection: Inspect HRC fuses regularly for any signs of damage, corrosion, or wear. Look for discolored or burnt elements, which may indicate a blown fuse or a potential issue with the circuit.
- Replacement: Replace blown or damaged HRC fuses immediately. Delaying replacement can lead to further damage to the circuit and increase the risk of electrical accidents.
- Storage: Store spare HRC fuses in a dry and secure location. Ensure that they are properly labeled and easily accessible for quick replacements.
- Upgrades: Stay updated with the latest HRC fuse technology and standards. Consider upgrading to more advanced fuses that offer improved protection and features, such as time-delay or arc-quenching capabilities.
HRC Fuses and Electrical Safety

HRC fuses play a critical role in ensuring electrical safety in various settings. By interrupting excessive current flow, they prevent electrical fires, equipment damage, and potential injuries. Here are some key safety considerations:
- Overcurrent Protection: HRC fuses provide essential overcurrent protection, safeguarding against short circuits and overloads. This protection helps prevent electrical faults from spreading and causing further damage.
- Arc Fault Protection: Some HRC fuses are designed with arc-fault protection, which detects and interrupts arc faults. Arc faults can occur due to loose connections or damaged insulation, and these fuses help mitigate the risk of fires caused by arcing.
- Ground Fault Protection: In certain applications, HRC fuses can be combined with ground fault protection devices. This combination provides an added layer of safety by detecting and interrupting ground faults, preventing potential electrocution hazards.
Real-World Applications
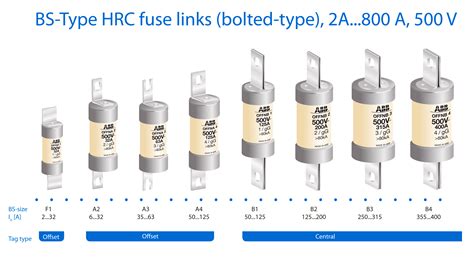
HRC fuses find applications in a wide range of industries and settings. Here are a few examples:
- Residential Electrical Systems: HRC fuses are commonly used in residential electrical panels to protect circuits and appliances. They provide overcurrent protection for lighting circuits, kitchen appliances, and HVAC systems, ensuring the safety of homeowners.
- Commercial Buildings: In commercial buildings, HRC fuses are employed in electrical distribution systems. They protect critical equipment, such as HVAC systems, elevators, and lighting circuits, ensuring uninterrupted operation and minimizing downtime.
- Industrial Facilities: Industrial facilities rely on HRC fuses for protection in various applications. From motor control centers to power distribution panels, HRC fuses safeguard equipment, machinery, and personnel from electrical hazards.
- Automotive and Marine: Blade-type HRC fuses are widely used in automotive and marine applications. They protect electrical systems in vehicles and boats, ensuring the safe operation of engines, lighting, and electronic components.
Conclusion
High Rupturing Capacity fuses are an integral part of electrical safety, providing protection against overcurrent and fault conditions. By understanding the different types of HRC fuses, their selection criteria, and installation guidelines, you can ensure the reliability and safety of your electrical system. Regular maintenance, timely replacement, and staying updated with the latest advancements in HRC fuse technology are essential for maintaining a robust electrical infrastructure. With proper care and attention to detail, HRC fuses will continue to play a vital role in safeguarding lives and property from electrical hazards.
What is the difference between HRC fuses and standard fuses?
+
HRC fuses are designed to handle higher current levels and have a higher rupturing capacity compared to standard fuses. They are specifically engineered to provide enhanced protection for critical equipment and systems.
Can I use any HRC fuse in my electrical system?

+
No, it is crucial to select the appropriate HRC fuse based on the voltage rating, current rating, and application. Using an incompatible fuse can lead to inadequate protection and potential hazards.
How often should I inspect and replace HRC fuses?

+
Regular inspection of HRC fuses is recommended. It is advisable to visually inspect them at least once a year. If a fuse is blown or damaged, it should be replaced immediately to maintain electrical safety.
Are there any special considerations for HRC fuse installation in outdoor environments?

+
Yes, when installing HRC fuses in outdoor environments, it is important to use weatherproof fuse holders and ensure proper sealing to protect against moisture and environmental factors. Additionally, consider using fuses with enhanced protection against corrosion.
Can HRC fuses be reused after they have blown?

+
No, HRC fuses should not be reused after they have blown. Once a fuse has operated and interrupted the circuit, it should be replaced with a new fuse to ensure proper protection and avoid potential hazards.