The management of industrial solid waste is a critical aspect of environmental sustainability and responsible business practices. While the focus is often on the challenges and potential hazards associated with industrial waste, it is essential to acknowledge the positive aspects and benefits that effective waste management brings to industries and the environment.
In this blog post, we will explore the advantages and positive impacts of implementing robust industrial solid waste management strategies. By understanding these pros, we can appreciate the importance of sustainable practices and their role in creating a greener and more sustainable future.
Environmental Benefits
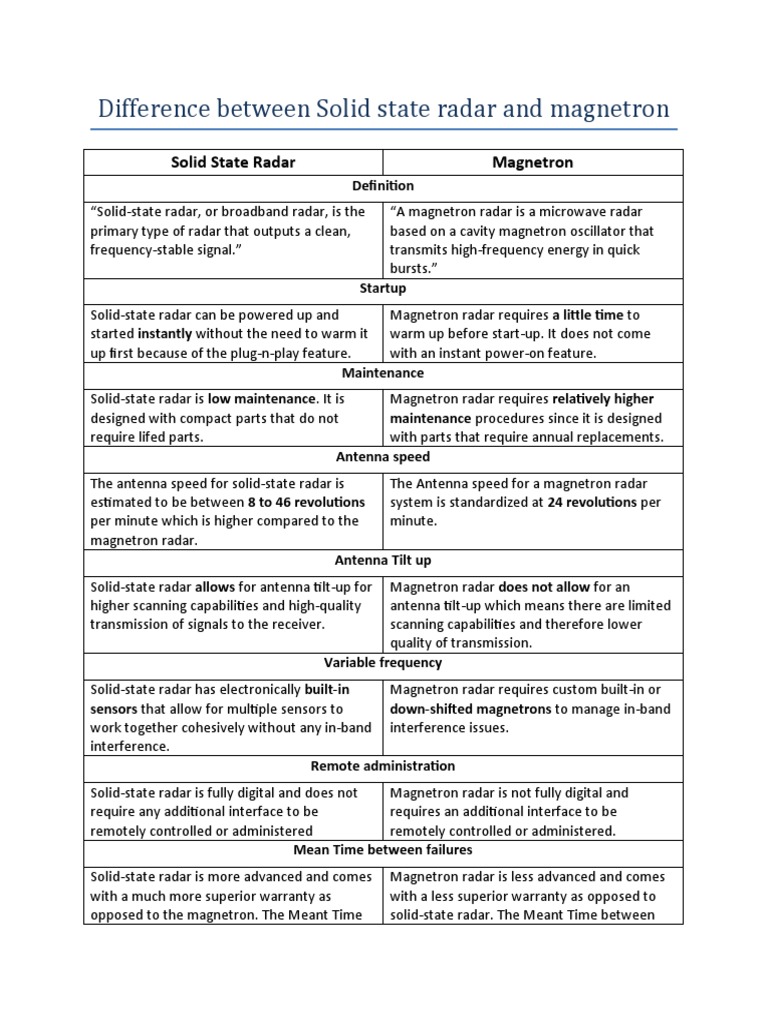
Industrial solid waste management plays a crucial role in preserving the environment and reducing the negative impacts of industrial activities.
Reduced Pollution and Environmental Degradation

- Proper waste management practices minimize the release of harmful substances into the air, water, and soil, thereby reducing pollution levels.
- By treating and disposing of waste responsibly, industries can prevent soil contamination, water pollution, and air pollution, protecting natural resources and ecosystems.
Conservation of Natural Resources

- Effective waste management strategies encourage the recycling and reuse of materials, reducing the need for virgin resources.
- Recycling processes help conserve valuable natural resources such as metals, minerals, and timber, promoting a more sustainable use of Earth's finite resources.
Protection of Biodiversity

- Industrial waste, if not managed properly, can pose a threat to biodiversity by contaminating habitats and harming wildlife.
- By implementing strict waste management protocols, industries can mitigate these risks, ensuring the protection of diverse ecosystems and the species that depend on them.
Economic Advantages

Industrial solid waste management offers several economic benefits that contribute to the long-term sustainability and success of businesses.
Cost Savings

- Adopting waste reduction and recycling practices can lead to significant cost savings for industries.
- By minimizing waste generation and maximizing resource efficiency, businesses can reduce their waste disposal costs and lower their overall operational expenses.
Increased Resource Efficiency

- Waste management strategies often involve implementing processes to optimize resource utilization.
- By recycling and reusing materials, industries can reduce their reliance on raw materials, leading to cost savings and a more stable supply chain.
Improved Reputation and Brand Value

- Consumers and investors are increasingly conscious of environmental issues and prefer sustainable and responsible businesses.
- By demonstrating a commitment to sustainable waste management, industries can enhance their reputation, attract environmentally conscious customers, and increase their brand value.
Social and Community Benefits

Industrial solid waste management initiatives can have a positive impact on local communities and society as a whole.
Job Creation

- The waste management industry provides numerous employment opportunities, contributing to local job creation and economic development.
- From waste collection and sorting to recycling and disposal, a range of skilled and unskilled jobs are generated, benefiting the community.
Community Engagement and Education

- Industrial waste management programs often involve community engagement and education initiatives.
- By raising awareness about the importance of waste reduction and proper disposal, industries can empower individuals to make more sustainable choices, fostering a culture of environmental responsibility.
Improved Public Health

- Effective waste management practices help prevent the spread of diseases and reduce health risks associated with improper waste disposal.
- By minimizing the presence of hazardous materials and promoting safe waste handling, industries can contribute to the overall well-being of the community.
Technological Innovations

The field of industrial solid waste management has seen significant technological advancements, leading to more efficient and sustainable practices.
Advanced Recycling Technologies

- Innovations in recycling technologies have improved the efficiency and effectiveness of material recovery.
- Advanced sorting and processing techniques allow for the recycling of a wider range of materials, reducing waste sent to landfills and promoting a circular economy.
Waste-to-Energy Solutions
- Waste-to-energy technologies convert waste into usable energy, providing an alternative energy source.
- By harnessing the energy potential of waste, industries can reduce their reliance on fossil fuels and contribute to a more sustainable energy landscape.
Digitalization and Data Analytics
- The integration of digital technologies and data analytics has revolutionized waste management.
- Smart waste management systems enable real-time monitoring, efficient route planning, and optimized waste collection, leading to cost savings and improved resource management.
Regulatory Compliance and Risk Mitigation

Industrial solid waste management is governed by strict regulations to ensure environmental protection and public safety.
Compliance with Environmental Laws
- Industries that prioritize waste management can ensure compliance with environmental regulations, avoiding legal consequences and penalties.
- By implementing proper waste management practices, businesses can maintain a positive relationship with regulatory bodies and avoid potential disruptions to their operations.
Risk Mitigation and Liability Reduction
- Proper waste management reduces the risk of environmental incidents and liability claims.
- By following established protocols and best practices, industries can minimize the potential for accidents, leaks, or contamination, protecting their reputation and financial stability.
Conclusion
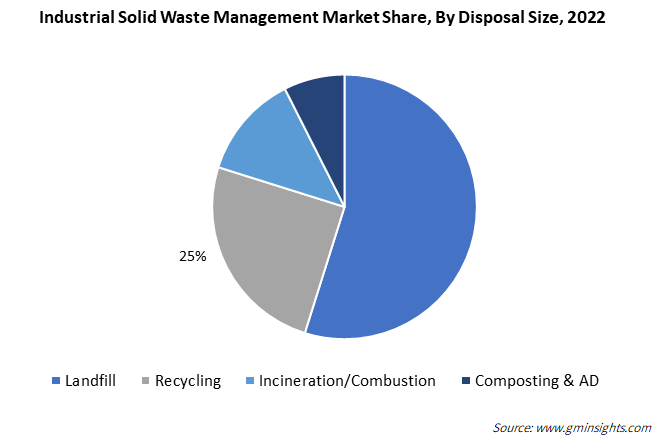
Industrial solid waste management is not solely about addressing challenges; it presents a multitude of benefits and opportunities for industries, the environment, and society. By embracing sustainable practices and innovative technologies, businesses can drive positive change, reduce their environmental footprint, and contribute to a greener and more sustainable future. Effective waste management strategies offer economic advantages, promote social well-being, and ensure compliance with environmental regulations. As industries continue to prioritize waste management, we can expect further advancements and a more sustainable approach to industrial operations.
FAQ

What are the key benefits of industrial solid waste management for the environment?
+Industrial solid waste management helps reduce pollution, conserve natural resources, and protect biodiversity. By treating and disposing of waste responsibly, industries can minimize their environmental impact and contribute to a healthier planet.
How does waste management impact the economy?
+Effective waste management strategies lead to cost savings, increased resource efficiency, and improved brand value for industries. By reducing waste generation and maximizing recycling, businesses can lower their operational expenses and attract environmentally conscious consumers.
What are the social benefits of industrial solid waste management initiatives?
+Industrial waste management initiatives create job opportunities, engage communities through education, and improve public health. By involving local communities, industries can foster a sense of environmental responsibility and contribute to a healthier and more sustainable society.
How do technological advancements benefit waste management practices?
+Technological innovations such as advanced recycling technologies, waste-to-energy solutions, and digitalization have revolutionized waste management. These advancements enhance efficiency, promote a circular economy, and contribute to a more sustainable energy landscape.
What are the regulatory aspects of industrial solid waste management?
+Industrial solid waste management is subject to strict environmental regulations. By adhering to these regulations, industries can ensure compliance, avoid legal consequences, and maintain a positive relationship with regulatory bodies.