Understanding the results of your MPV blood test is crucial for assessing your overall health and detecting any potential health issues. MPV, which stands for Mean Platelet Volume, is a measurement that provides valuable insights into your platelet health and can indicate underlying conditions. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of the MPV blood test, helping you interpret your results and take proactive steps towards maintaining optimal health.
What is an MPV Blood Test?

The MPV blood test is a simple and routine diagnostic tool used to measure the average size of platelets in your blood. Platelets, also known as thrombocytes, are tiny cell fragments responsible for blood clotting and wound healing. By analyzing the MPV, healthcare professionals can gain insights into the production, activation, and function of platelets, which play a vital role in maintaining proper blood circulation and preventing excessive bleeding.
Why is the MPV Blood Test Important?

The MPV blood test serves as a valuable indicator of your overall health and can help detect various medical conditions. Here are some key reasons why this test is important:
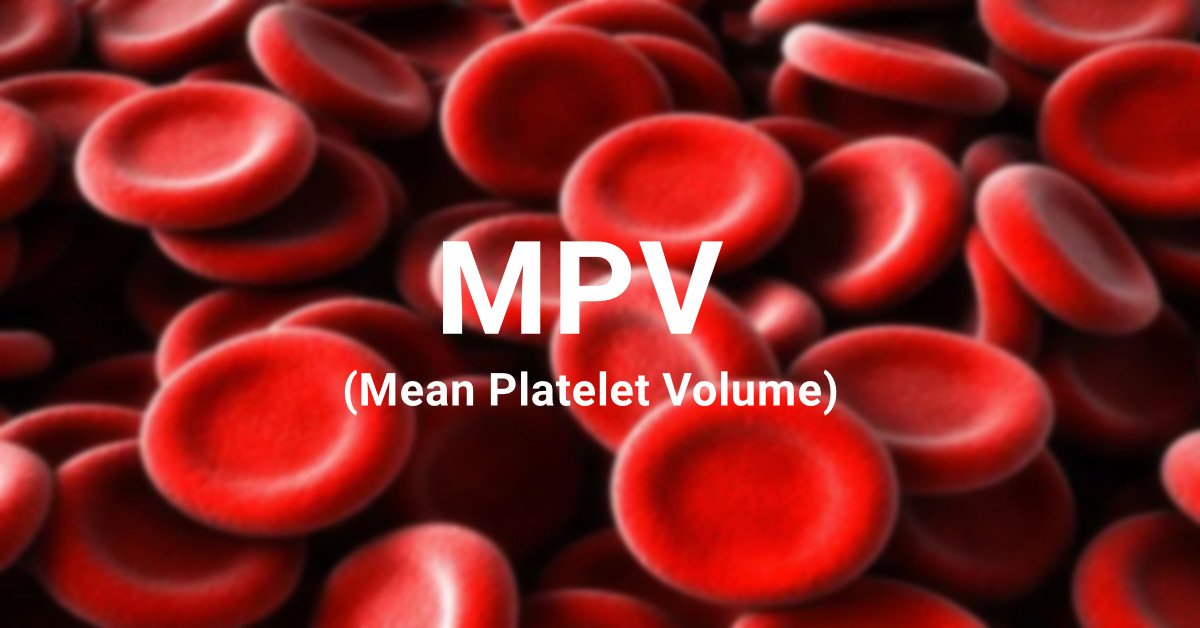
- Detecting Platelet Disorders: Abnormal MPV levels can indicate platelet disorders, such as thrombocytopenia (low platelet count) or thrombocytosis (high platelet count). These conditions can affect blood clotting and increase the risk of bleeding or thrombosis (blood clots).
- Monitoring Treatment: If you are undergoing treatment for a platelet-related condition, regular MPV tests can help monitor the effectiveness of the treatment and adjust medications accordingly.
- Identifying Inflammation: Elevated MPV levels may suggest the presence of inflammation in the body. Chronic inflammation is associated with various health issues, including cardiovascular disease and autoimmune disorders.
- Cancer Screening: In some cases, abnormal MPV levels can be an early indicator of certain types of cancer, such as leukemia or other blood-related cancers.
- Heart Health: Research suggests a link between MPV levels and cardiovascular health. Elevated MPV may be associated with an increased risk of heart disease and stroke.
Interpreting MPV Results

Interpreting MPV results requires understanding the normal range and any deviations from it. Here's a breakdown of what different MPV values may indicate:
| MPV Range | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| Normal Range (7.5-12.5 fL) | A normal MPV value suggests that your platelets are functioning adequately and within the expected range. No further action is typically required. |
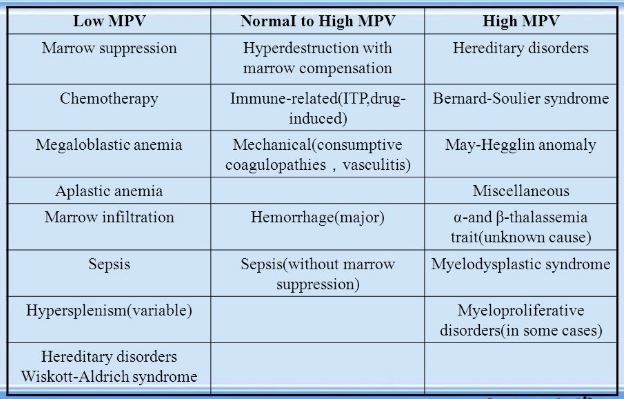
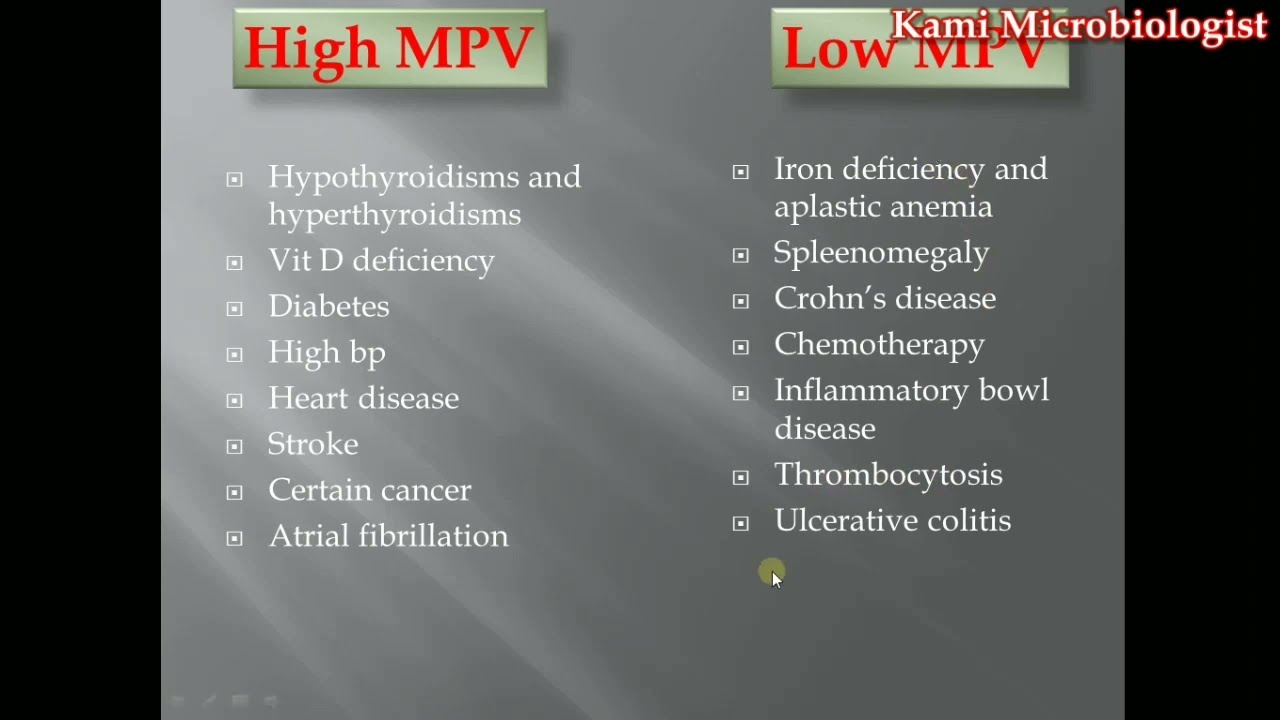
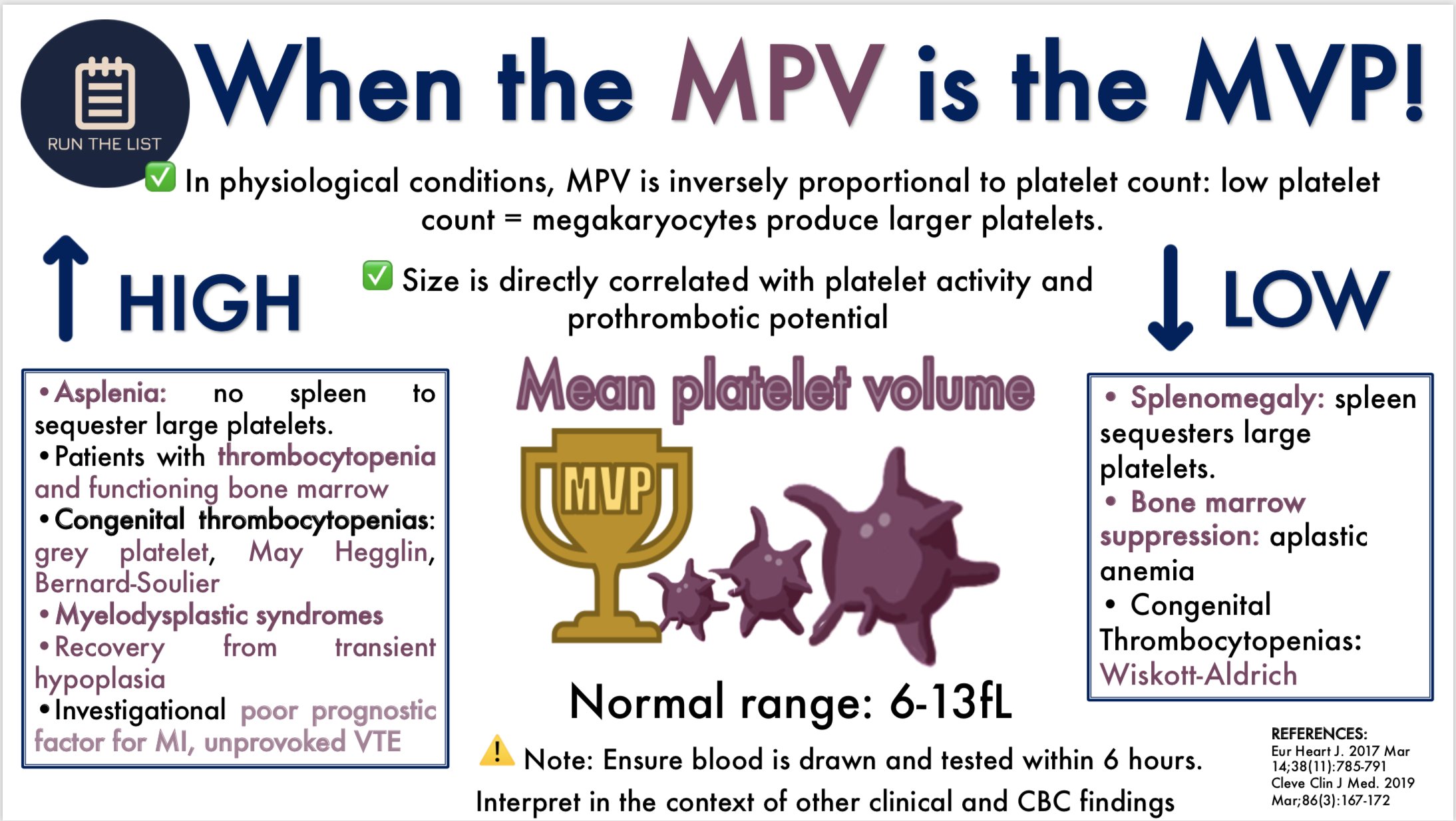
| Low MPV (below 7.5 fL) | A low MPV value may indicate a condition called thrombocytopenia, where the body produces fewer platelets than normal. This can lead to excessive bleeding and bruising. Common causes include immune disorders, certain medications, or underlying medical conditions. |
| High MPV (above 12.5 fL) | Elevated MPV levels can be a sign of thrombocytosis, where the body produces an excessive number of platelets. This condition is often associated with inflammation, infection, or certain types of cancer. It can increase the risk of blood clots and thrombosis. |
Factors Affecting MPV Results
It's important to note that various factors can influence MPV results, and interpreting them requires a comprehensive assessment by a healthcare professional. Here are some factors that can impact MPV levels:
- Age: MPV values tend to increase with age, especially in older adults.
- Gender: Women generally have slightly higher MPV levels than men.
- Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups may have naturally higher or lower MPV values.
- Medication: Some medications, such as aspirin or certain anti-inflammatory drugs, can affect MPV levels.
- Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and obesity can influence MPV results.
- Underlying Health Conditions: Chronic illnesses, such as kidney disease or liver disease, can impact MPV levels.
Understanding MPV in Combination with Other Tests
MPV results are often most informative when considered alongside other blood test results. Here are some common combinations:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): The CBC test provides a comprehensive analysis of your blood, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Combining MPV with CBC can help identify underlying conditions more accurately.
- Platelet Count: The platelet count test measures the number of platelets in your blood. When interpreted together with MPV, it can provide a clearer picture of your platelet health.
- Inflammatory Markers: If your MPV is elevated, your healthcare provider may recommend additional tests to assess inflammation levels, such as C-reactive protein (CRP) or erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) tests.
What to Do if Your MPV Results Are Abnormal

If your MPV results fall outside the normal range, it's important to consult with a healthcare professional. They will consider your medical history, symptoms, and other test results to determine the underlying cause and develop an appropriate treatment plan. Here are some possible steps that may be taken:
- Further Testing: Additional blood tests or imaging studies may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions.
- Medications: Depending on the underlying condition, your healthcare provider may prescribe medications to manage symptoms and regulate platelet production.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Making healthy lifestyle changes, such as adopting a balanced diet, quitting smoking, and exercising regularly, can improve overall health and potentially impact MPV levels.
- Monitoring: In some cases, your healthcare provider may recommend regular MPV tests to monitor the progression of a condition or the effectiveness of treatment.
Precautions and Considerations
While the MPV blood test is a valuable tool, it's essential to keep the following precautions and considerations in mind:
- Reference Ranges: Reference ranges for MPV may vary slightly between laboratories. It's important to discuss your results with a healthcare professional who can interpret them accurately.
- Individual Variations: MPV values can vary from person to person, and what is considered "normal" for one individual may not be the same for another. Contextual factors, such as age and gender, should be taken into account.
- False Positives/Negatives: MPV results can sometimes be affected by factors like medication use or recent blood transfusions. It's crucial to provide your healthcare provider with a complete medical history to ensure accurate interpretation.
🌟 Note: Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional for personalized advice and interpretation of your MPV results.
Conclusion
The MPV blood test is a powerful tool for assessing your platelet health and detecting a range of medical conditions. By understanding your MPV results and their implications, you can take proactive steps towards maintaining optimal health and well-being. Remember, interpreting MPV results requires a comprehensive approach, and consulting with a healthcare professional is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Can a high MPV level be a sign of cancer?
+
Yes, elevated MPV levels can sometimes be an early indicator of certain types of cancer, particularly blood-related cancers like leukemia. However, further testing is necessary to confirm a cancer diagnosis.
What lifestyle changes can improve MPV levels?

+
Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption, can positively impact MPV levels and overall health.
Are there any specific medications that affect MPV results?
+
Yes, certain medications, such as aspirin and anti-inflammatory drugs, can influence MPV levels. It’s important to inform your healthcare provider about any medications you are taking to ensure accurate interpretation of your results.