Understanding the Nitriding Process for Alloys
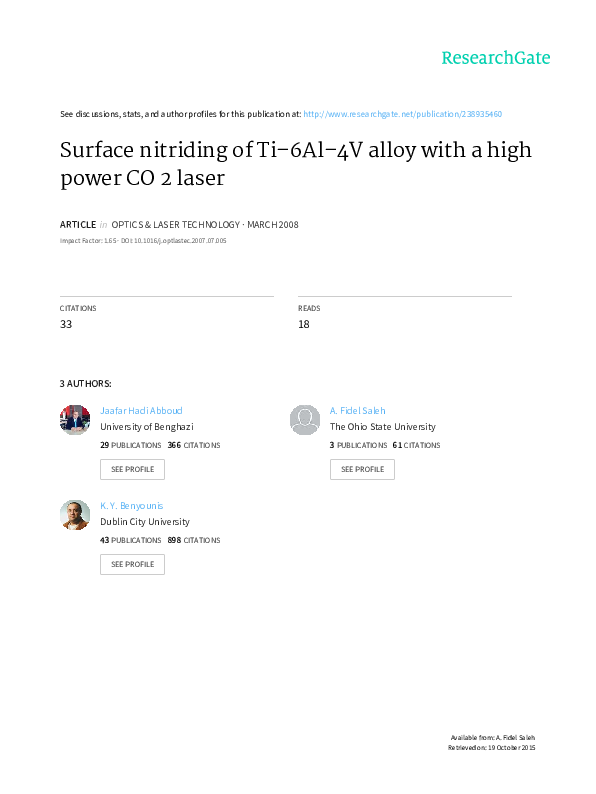
The nitriding process is a vital technique used in the enhancement of alloy properties, particularly for steel and stainless steel. It involves the diffusion of nitrogen into the surface of the alloy, resulting in a hardened, wear-resistant, and corrosion-resistant layer. This process is widely applied in various industries, from automotive to aerospace, to improve the performance and longevity of alloy components.
The Science Behind Nitriding
Nitriding is a thermochemical process that alters the surface composition of an alloy. It is typically carried out at temperatures ranging from 490°C to 580°C, below the alloy's transformation temperature. During nitriding, nitrogen atoms are introduced into the alloy, usually from a gas mixture of ammonia and other gases. These nitrogen atoms diffuse into the surface, reacting with the alloy's constituent elements to form nitrides.
The formation of nitrides leads to the creation of a hardened layer on the alloy's surface. This layer, known as the nitrided case, provides excellent wear resistance and fatigue strength. Additionally, the nitrided layer acts as a barrier, preventing corrosive substances from reaching the base material, thus enhancing the alloy's corrosion resistance.
Types of Nitriding Processes

There are several types of nitriding processes, each with its own unique characteristics and applications:
- Gas Nitriding: This process involves exposing the alloy to a gas mixture containing ammonia and other gases. It is a versatile method, suitable for a wide range of alloys and can be easily automated.
- Plasma Nitriding: Plasma nitriding utilizes ionized gas to accelerate the nitriding process. It is particularly effective for producing deep nitrided cases and is often used for components requiring high wear resistance.
- Salt Bath Nitriding: In this process, the alloy is immersed in a molten salt bath containing nitrogen-bearing compounds. Salt bath nitriding is a cost-effective method, but it may not be suitable for all alloys due to the risk of decarburization.
- Ferritic Nitrocarburizing: Also known as tenifer or melonite treatment, this process involves the diffusion of nitrogen and carbon into the alloy's surface. It results in a thin, hard case with excellent corrosion resistance.
Benefits of Nitriding Alloys

The nitriding process offers several advantages for alloys, making it a popular choice in various industries:
- Improved Wear Resistance: The hardened nitrided case significantly enhances the alloy's resistance to wear, making it ideal for components subjected to friction and abrasion.
- Enhanced Fatigue Strength: Nitriding increases the alloy's resistance to fatigue, improving its performance in cyclic loading applications.
- Corrosion Resistance: The nitrided layer acts as a protective barrier, preventing corrosion and extending the alloy's service life, especially in harsh environments.
- Dimensional Stability: Unlike other heat treatment processes, nitriding does not cause significant dimensional changes, making it suitable for precision components.
- Cost-Effectiveness: While the initial setup cost can be high, nitriding is a relatively cost-effective process due to its energy efficiency and the extended lifespan it provides to components.
Applications of Nitrided Alloys

Nitrided alloys find extensive use in various industries due to their enhanced properties:
- Automotive Industry: Nitrided alloys are used in engine components, such as camshafts, gears, and valve springs, to improve wear resistance and reduce friction.
- Aerospace Industry: In aerospace, nitrided alloys are employed in landing gear, engine components, and structural parts, where high strength and corrosion resistance are crucial.
- Oil and Gas Industry: Nitrided alloys are ideal for drilling and extraction equipment, as they can withstand the harsh, corrosive environments encountered in these industries.
- Manufacturing and Machinery: Nitrided alloys are used in various manufacturing processes, from tooling to machine components, to improve productivity and reduce downtime.
- Medical Devices: The biocompatibility and corrosion resistance of nitrided alloys make them suitable for medical implants and surgical instruments.
The Future of Nitriding Technology

Ongoing research and development in the field of nitriding technology continue to enhance the process's efficiency and effectiveness. Advanced techniques, such as plasma-assisted nitriding and pulse nitriding, are being explored to further improve the quality and performance of nitrided alloys. Additionally, the development of new nitriding salts and gas mixtures is expanding the range of alloys that can benefit from this process.
Furthermore, the integration of nitriding with other surface treatment processes, such as carburizing and boronizing, is being studied to create multi-functional surface layers with tailored properties. This combination of processes has the potential to revolutionize the performance and longevity of alloy components in various industries.
Conclusion

The nitriding process is a powerful tool for enhancing the properties of alloys, particularly steel and stainless steel. By diffusing nitrogen into the alloy's surface, a hardened, wear-resistant, and corrosion-resistant layer is created, resulting in improved performance and longevity. With ongoing advancements in nitriding technology, the future looks bright for the further development and application of this vital process across various industries.
What is the ideal temperature range for nitriding alloys?

+
The ideal temperature range for nitriding alloys is typically between 490°C and 580°C. This temperature range ensures effective nitrogen diffusion into the alloy’s surface without causing excessive grain growth or decarburization.
Can nitriding be applied to all types of alloys?

+
While nitriding is commonly used for steel and stainless steel, it can also be applied to other alloys, such as cast iron and nickel-based alloys. However, the suitability of nitriding for a specific alloy depends on its chemical composition and the desired properties.
How does nitriding compare to other heat treatment processes?
+
Nitriding differs from other heat treatment processes like carburizing and hardening in that it focuses on altering the surface composition rather than the entire alloy. This results in a hardened surface layer while maintaining the core properties of the alloy. Additionally, nitriding does not cause significant dimensional changes, making it suitable for precision components.
What are the main advantages of nitriding alloys over other surface treatments?

+
The main advantages of nitriding alloys include improved wear resistance, enhanced fatigue strength, and excellent corrosion resistance. Nitriding also offers dimensional stability and is relatively cost-effective, making it a popular choice for various industries.
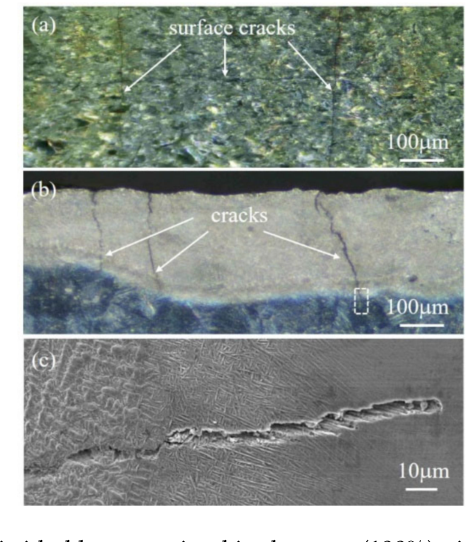
Are there any potential drawbacks to the nitriding process?
+
One potential drawback of nitriding is the risk of decarburization, especially in the case of salt bath nitriding. Decarburization can lead to a reduction in the alloy’s strength and hardness. Additionally, the initial setup cost for nitriding equipment can be high, although the long-term benefits often outweigh this initial investment.