Converting between different units of measurement is a common task in astronomy, especially when dealing with vast distances in space. One such conversion is from parsecs to light years, which can be a bit tricky for those unfamiliar with these units. In this blog post, we will explore the concept of parsecs and light years, understand their relationship, and learn how to make an accurate conversion.
Understanding Parsecs and Light Years

Before we dive into the conversion process, let's familiarize ourselves with these two units of measurement:
Parsecs (pc)
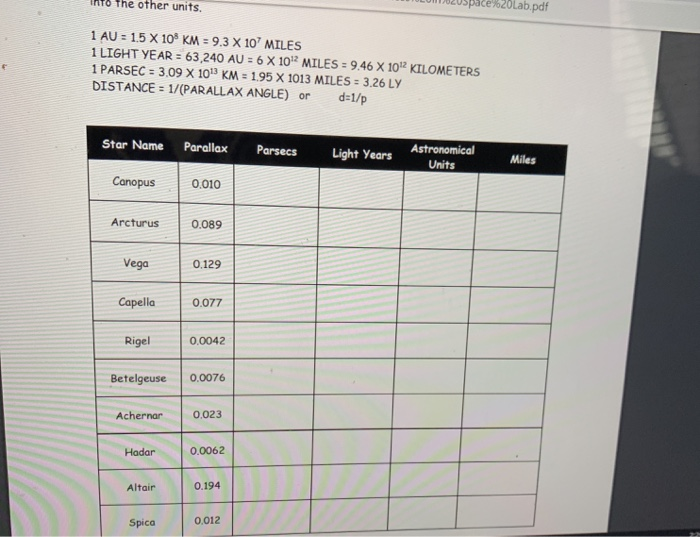
- Definition: A parsec is a unit of length used to measure distances in space, specifically the distance from the Earth to an object that has a parallax angle of one arcsecond.
- Origin: The term "parsec" is derived from "parallax of one arcsecond." It was introduced by British astronomer Herbert Hall Turner in 1913.
- Length: One parsec is approximately equal to 3.26 light years or 31 trillion kilometers.
Light Years (ly)

- Definition: A light year is the distance that light travels in one Earth year. It is a convenient unit for measuring interstellar and intergalactic distances.
- Speed of Light: Light travels at an incredible speed of approximately 300,000 kilometers per second.
- Distance: One light year is equal to the distance light travels in one year, which is approximately 9.46 trillion kilometers.
Converting Parsecs to Light Years

Now that we have a basic understanding of parsecs and light years, let's explore the conversion process. To convert parsecs to light years, we can use the following formula:
Light Years = Parsecs × 3.26
This formula is derived from the fact that one parsec is approximately equal to 3.26 light years. By multiplying the given value in parsecs by 3.26, we can obtain the equivalent distance in light years.
Example Conversion

Let's say we want to convert 5 parsecs to light years. Using the formula:
Light Years = 5 pc × 3.26
Calculating this, we get:
Light Years = 16.3 ly
So, 5 parsecs is approximately equal to 16.3 light years.
Practical Applications
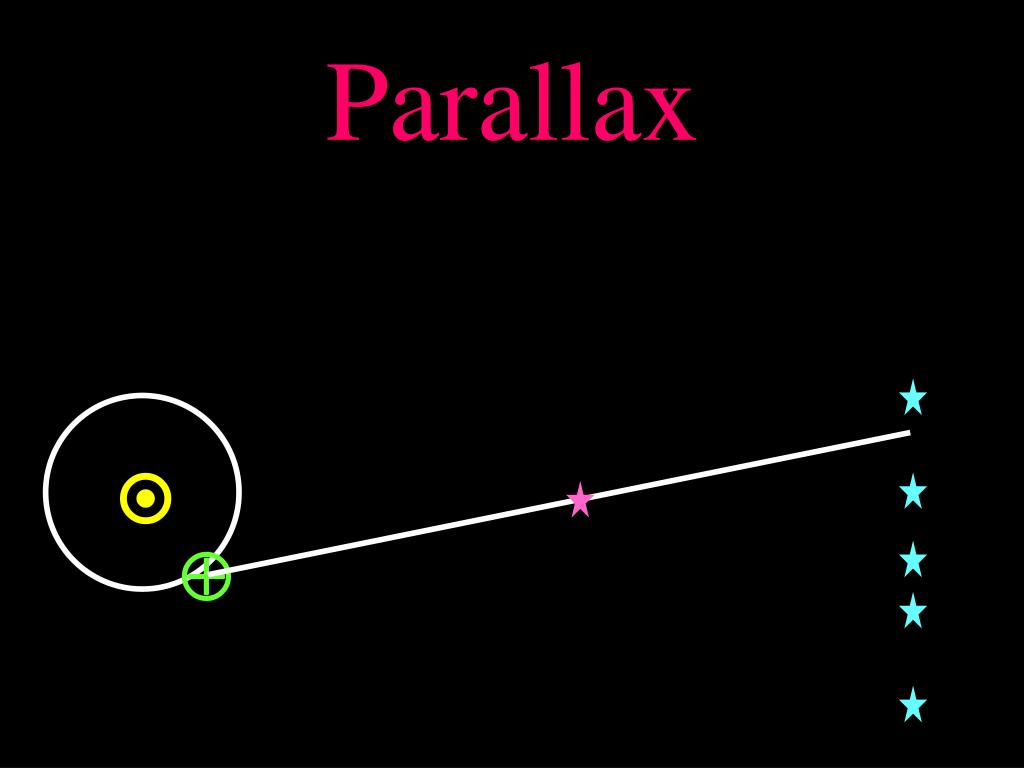
Converting between parsecs and light years is essential for astronomers and space enthusiasts alike. Here are a few practical applications of this conversion:
- Stellar Distance Measurement: Astronomers often use parsecs to measure the distances to nearby stars and celestial objects. Converting these distances to light years provides a more intuitive understanding of the vastness of space.
- Interstellar Travel: When discussing interstellar travel or the potential for human exploration beyond our solar system, converting distances to light years helps us grasp the immense challenges and time scales involved.
- Understanding Cosmic Scales: Converting parsecs to light years allows us to comprehend the sizes of galaxies, nebulae, and other cosmic structures. It helps us visualize the scale of the universe and our place within it.
Common Misconceptions

It's important to note that parsecs and light years are not interchangeable units. While they are both used to measure distance, they have different definitions and origins. Parsecs are specifically related to the Earth's position and the concept of parallax, while light years are based on the speed of light.
Additional Conversion Factors

In addition to converting parsecs to light years, it's worth mentioning other common conversions in astronomy:
- Astronomical Units (AU) to Light Years: One astronomical unit, the average distance from the Earth to the Sun, is approximately 150 million kilometers. To convert AU to light years, you can use the formula: Light Years = AU × 0.00001581
- Kilometers (km) to Light Years: To convert kilometers to light years, you can use the formula: Light Years = km × 1.057 × 10-16
Table: Common Distance Conversions

| Unit | Equivalent Distance |
|---|---|
| 1 Parsec (pc) | 3.26 Light Years (ly) |
| 1 Astronomical Unit (AU) | 0.00001581 Light Years (ly) |
| 1 Kilometer (km) | 1.057 × 10-16 Light Years (ly) |

Conclusion

Converting parsecs to light years is a fundamental skill for anyone interested in astronomy and the exploration of space. By understanding the relationship between these units and applying the appropriate conversion factors, we can better comprehend the vast distances that separate us from distant stars and galaxies. Remember, the universe is an incredible place, and these conversions help us appreciate its grandeur.
How accurate is the parsecs to light years conversion formula?
+
The conversion formula is highly accurate and widely accepted in the scientific community. It is based on the precise definition of a parsec and the speed of light. However, it’s important to note that due to the vastness of space, even small variations in distance can have significant implications. Therefore, it’s crucial to use accurate measurements and consider the context of the conversion.
Can we use light years as a primary unit of measurement in astronomy?

+
While light years are commonly used to express interstellar and intergalactic distances, they are not the primary unit of measurement in astronomy. Parsecs and astronomical units (AU) are often preferred for their precision and convenience in specific contexts. Light years, however, provide a more intuitive understanding of distance for the general public.
Are there any other units of measurement used in astronomy?
+
Yes, astronomy employs various units of measurement depending on the scale and context. Some other common units include megaparsecs (Mpc) for measuring distances to galaxies, parsec-kilometers (pc-km) for combining parsecs and kilometers, and even more specialized units like solar radii for measuring the size of stars.