Understanding Trump's Policy on Manufacturing: A Comprehensive Overview
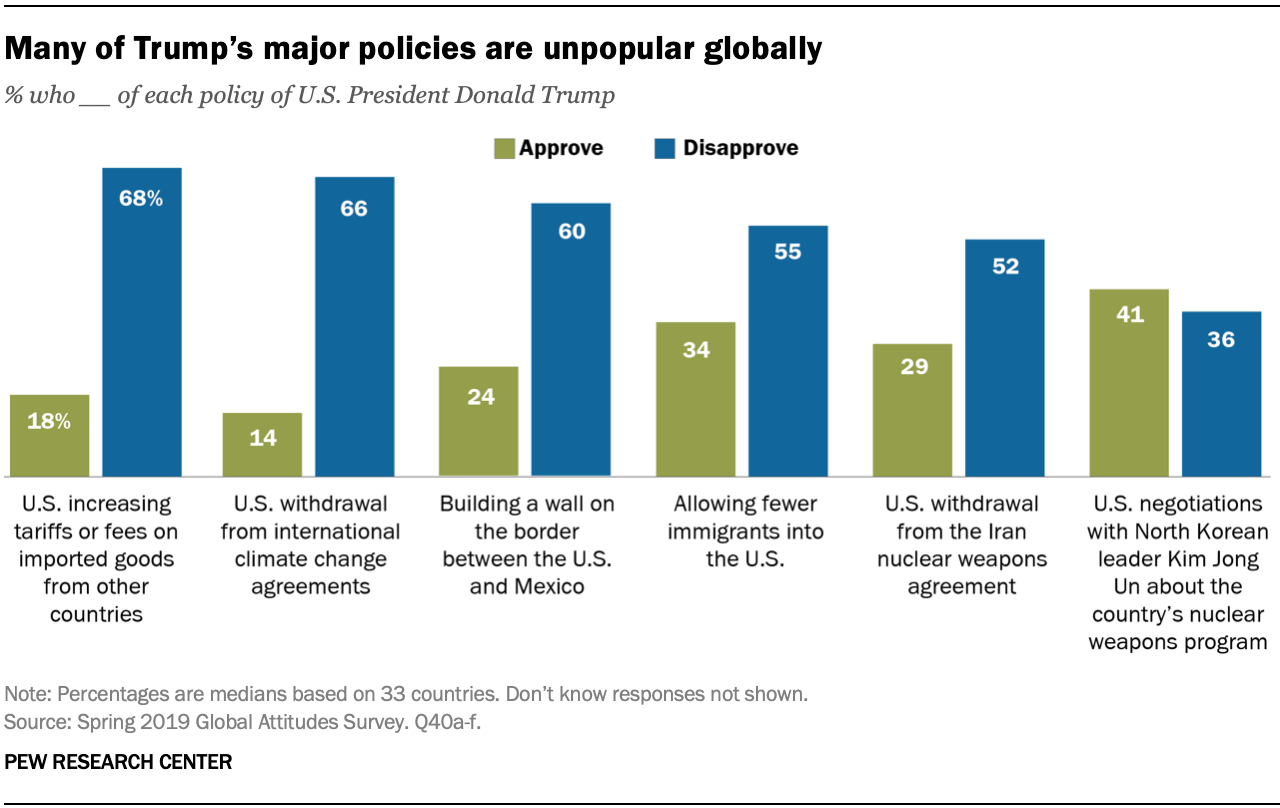
During his presidency, Donald Trump implemented a range of policies aimed at reshaping the American manufacturing landscape. His approach, often described as "America First," sought to bring back jobs, boost domestic production, and reduce the trade deficit. Let's delve into the key aspects of Trump's manufacturing policy and its impact.
Tariffs and Trade Wars

One of the most notable aspects of Trump's manufacturing policy was his aggressive use of tariffs. In an effort to protect American industries, especially steel and aluminum, Trump imposed tariffs on imports from various countries, including China, Mexico, and the European Union. These tariffs were intended to make foreign goods less competitive and encourage domestic production.
However, this move sparked a series of retaliatory tariffs from trading partners, leading to a trade war. While the tariffs initially had a positive impact on certain sectors, such as the steel industry, the long-term effects were mixed. Some industries, particularly those relying on imported components, faced increased costs and supply chain disruptions.
Reshoring and Incentives

Trump's administration actively promoted the reshoring of manufacturing jobs, encouraging companies to bring their production back to the United States. This was achieved through a combination of tax incentives, regulatory reforms, and public-private partnerships. The goal was to create a more favorable business environment, making it more attractive for companies to invest in domestic manufacturing.
The Reshoring Initiative, a non-profit organization, played a significant role in this effort by providing resources and support to companies looking to reshore. Additionally, the Manufacturing Extension Partnership program offered assistance to small and medium-sized manufacturers to improve their competitiveness.
Regulatory Reforms

Trump's administration streamlined regulations to reduce the burden on manufacturers. This included efforts to simplify environmental regulations, ease labor laws, and relax safety standards. While these reforms aimed to lower costs and increase flexibility for businesses, they were met with criticism from environmental and labor rights groups.
One of the most controversial regulatory changes was the rollback of the Clean Power Plan, which aimed to reduce carbon emissions from power plants. This move was seen as a victory for the coal industry but drew criticism from environmentalists and those concerned about climate change.
Investment in Infrastructure
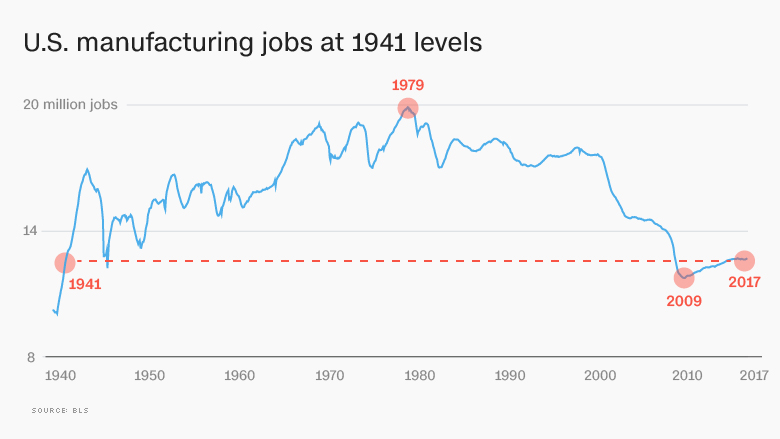
Trump emphasized the importance of infrastructure investment to support manufacturing. His administration proposed a $200 billion infrastructure plan, which aimed to repair and modernize roads, bridges, and other critical infrastructure. This investment was seen as crucial to improving the efficiency of supply chains and reducing transportation costs for manufacturers.
Skills Training and Education

Recognizing the skills gap in the manufacturing sector, Trump's policy included initiatives to improve vocational training and education. The Pledge to America's Workers program, for instance, brought together companies, educational institutions, and training providers to offer free workforce development opportunities.
Additionally, the ApprenticeshipUSA program was expanded to create more apprenticeship opportunities, providing individuals with hands-on training and a pathway to well-paying jobs in manufacturing and other industries.
Impact on Different Sectors

The impact of Trump's manufacturing policy varied across different sectors. While some industries, such as steel and aluminum, benefited from the tariffs and reshoring efforts, others faced challenges.
- Automotive: The industry experienced mixed results. While tariffs on imported vehicles and components provided some protection, the trade wars led to increased costs and supply chain disruptions.
- Electronics: This sector faced challenges due to the reliance on imported components and the impact of tariffs on final products.
- Aerospace: The aerospace industry, particularly defense contractors, benefited from increased military spending and the focus on national security.
- Textiles and Apparel: These industries saw a resurgence, as reshoring efforts and tariffs on imported goods made domestic production more competitive.
The Future of American Manufacturing

Trump's manufacturing policy laid the foundation for a more robust and resilient domestic manufacturing sector. However, the long-term success will depend on various factors, including the resolution of trade disputes, continued investment in infrastructure and skills training, and the ability to adapt to technological advancements.
As the world moves towards a more digital and automated future, American manufacturers will need to embrace innovation and stay competitive on a global scale. The policies implemented during the Trump administration have set the stage for this transformation, but ongoing support and adaptation will be crucial.
Conclusion

Trump's manufacturing policy was a bold attempt to revive the American manufacturing sector and bring back jobs. While the impact was felt across various industries, the long-term success will depend on a delicate balance of trade, investment, and innovation. As the manufacturing landscape continues to evolve, it will be interesting to see how these policies shape the future of American industry.
What was the main goal of Trump’s manufacturing policy?

+
The primary goal was to bring back manufacturing jobs to the United States, reduce the trade deficit, and make American industries more competitive on the global stage.
Did Trump’s tariffs have a positive impact on the steel industry?

+
Yes, the tariffs initially boosted the steel industry by making imported steel less competitive. However, the long-term effects were mixed due to the trade wars and increased costs for other industries.
What was the Reshoring Initiative’s role in Trump’s policy?

+
The Reshoring Initiative provided resources and support to companies looking to bring their production back to the United States, playing a crucial role in the reshoring efforts.
How did Trump’s policy impact the automotive industry?

+
The automotive industry experienced mixed results. While tariffs on imported vehicles and components provided some protection, the trade wars led to increased costs and supply chain disruptions.
What is the future outlook for American manufacturing under Trump’s policy?

+
The future looks promising, but it will require continued investment in infrastructure, skills training, and a focus on innovation to stay competitive in a globalized and digital world.