Introduction to Cowbirdbison Dynamics

In the intricate web of ecological interactions, the relationship between cowbirds and bison serves as a fascinating example of nature’s complexity. This guide aims to delve into the dynamics between these two species, exploring their unique bond and the ecological implications it holds. From the cowbird’s cunning strategies to the bison’s vital role as a host, we will uncover the secrets of this extraordinary partnership.
Understanding Cowbirds and Bison

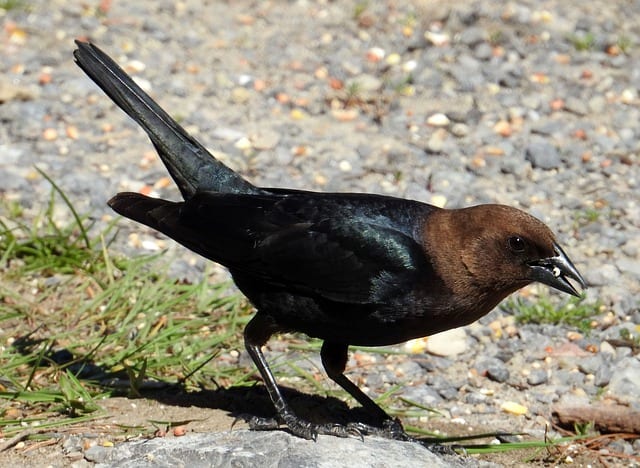
Cowbirds: The Clever Parasitic Birds

Cowbirds, scientifically known as Molothrus, are a group of birds native to the Americas. They are renowned for their parasitic breeding behavior, where they lay their eggs in the nests of other bird species, leaving the host parents to raise their young. This strategy, known as brood parasitism, allows cowbirds to bypass the challenges of raising their own offspring.
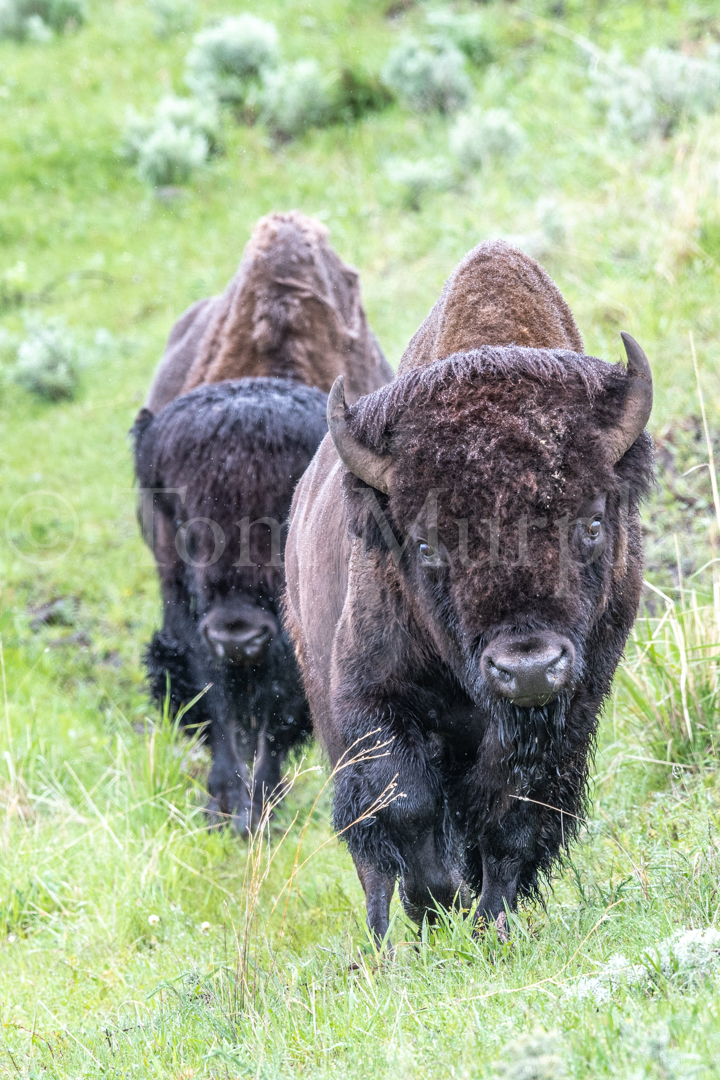
Bison: The Majestic Hosts

Bison, or Bison bison, are iconic North American mammals known for their massive size and strength. They roam the grasslands and prairies, playing a crucial role in shaping their ecosystems. Bison have a unique relationship with cowbirds, as they provide an ideal habitat for these parasitic birds.
The Cowbird-Bison Connection

Cowbirds’ Attraction to Bison

Cowbirds are drawn to bison for several reasons. Firstly, bison create an ideal nesting environment for cowbirds. The large, shaggy coats of bison provide excellent camouflage for cowbird eggs and chicks, making it difficult for predators to spot them. Additionally, bison’s grazing habits create a diverse landscape, offering a variety of food sources for cowbirds and their hosts.
Benefits for Bison

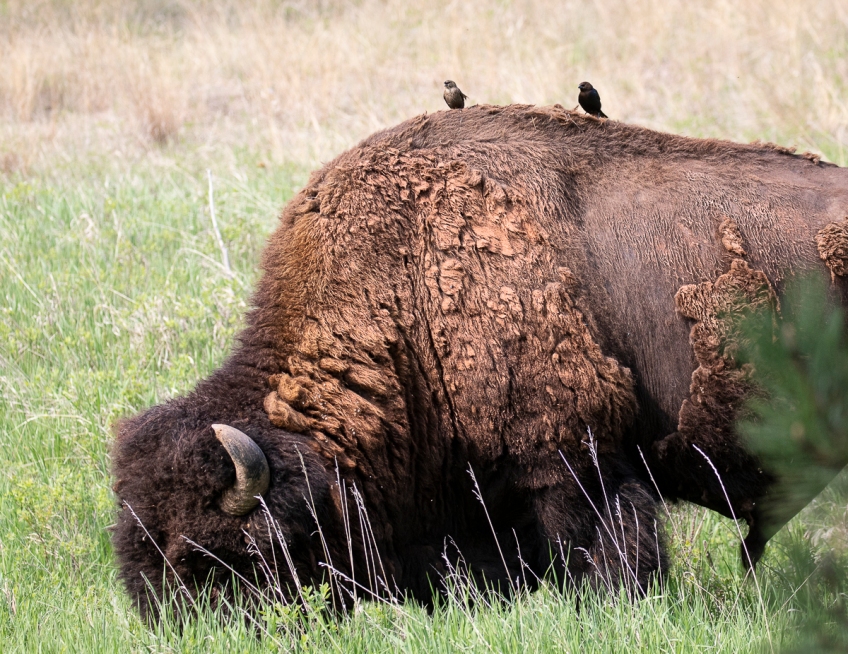
While cowbirds benefit from bison as hosts, the relationship is not one-sided. Bison also gain advantages from this association. Cowbirds, being highly mobile, can act as an early warning system for bison herds. They often perch on bison’s backs, scanning the surroundings for potential threats such as predators or approaching dangers. This alert system allows bison to react quickly and protect their herds.
The Parasitic Breeding Cycle

Cowbird Egg Laying

During the breeding season, female cowbirds seek out suitable host nests to lay their eggs. They carefully select nests that belong to smaller bird species, such as sparrows or warblers. The cowbird eggs are often similar in appearance to the host’s eggs, making it challenging for the host parents to distinguish them.
Host Parents’ Response

When host parents discover a cowbird egg in their nest, they face a challenging decision. Some species, like the brown-headed cowbird, are known to aggressively remove the cowbird egg, while others may accept it and raise the cowbird chick alongside their own offspring. This variation in response adds an interesting dynamic to the cowbird-bison relationship.
Impact on Ecosystem
Cowbirds’ Influence on Biodiversity

The presence of cowbirds in an ecosystem can have both positive and negative effects on biodiversity. On one hand, cowbirds can reduce the population of smaller bird species by exploiting their nests. This can lead to a decline in certain bird species, disrupting the balance of the food chain. However, cowbirds also contribute to the overall diversity of the ecosystem by providing a unique breeding strategy.
Bison’s Role in Shaping the Landscape

Bison are ecological engineers, shaping the landscape through their grazing and wallowing behaviors. Their feeding habits create a mosaic of different vegetation types, providing habitats for a wide range of species. The presence of bison also influences the distribution of other animals, such as wolves and coyotes, which in turn affects the entire ecosystem.
Conservation Efforts

Protecting Cowbirds and Bison

Conservation efforts for cowbirds and bison are crucial to maintain the delicate balance of their ecosystems. Both species face threats from habitat loss, climate change, and human activities. Protecting their habitats, such as grasslands and prairies, is essential for their survival. Additionally, educating the public about the importance of these species can help garner support for conservation initiatives.
Research and Monitoring

Research and monitoring programs play a vital role in understanding the dynamics between cowbirds and bison. By studying their behavior, interactions, and population trends, scientists can develop effective conservation strategies. Long-term studies can provide valuable insights into the impacts of cowbird parasitism on host species and the overall health of the ecosystem.
Cowbirdbison Dynamics in Different Regions

North American Cowbird-Bison Relationship
In North America, the cowbird-bison relationship is well-established, with cowbirds relying on bison as hosts. This dynamic has evolved over time, with cowbirds adapting to the unique characteristics of bison. The vast grasslands and prairies of North America provide an ideal habitat for both species, fostering their interdependence.
European Cowbird-Cattle Relationship
In Europe, a similar relationship exists between cowbirds and cattle. The European cowbird, Molothrus apurleus, exhibits similar parasitic breeding behavior, utilizing cattle as hosts. This relationship highlights the adaptability of cowbirds and their ability to form associations with different large herbivores.
The Future of Cowbirdbison Dynamics

Climate Change and Habitat Loss
Climate change and habitat loss pose significant challenges to the cowbird-bison dynamics. Rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns can affect the availability of suitable nesting sites for cowbirds. Additionally, the loss of grasslands and prairies due to human development threatens the habitats of both cowbirds and bison.
Sustainable Practices for Conservation
To ensure the long-term survival of cowbirds and bison, sustainable practices must be implemented. This includes protecting and restoring their natural habitats, implementing responsible land management practices, and promoting co-existence with human activities. By preserving these species and their ecosystems, we can maintain the delicate balance of nature.
Conclusion
The cowbird-bison dynamics offer a captivating glimpse into the intricate relationships that exist in nature. From the clever strategies of cowbirds to the vital role of bison as hosts, this partnership showcases the interdependence of species within an ecosystem. By understanding and conserving these dynamics, we can contribute to the preservation of biodiversity and the overall health of our planet.
FAQ

How do cowbirds find suitable host nests?
+Cowbirds employ various strategies to locate suitable host nests. They often observe the behavior of other bird species, following them to their nests. Additionally, cowbirds have a keen sense of sight and can detect small nests hidden in vegetation. Some cowbird species also have the ability to mimic the calls of other birds, allowing them to attract potential hosts.
What are the consequences of cowbird parasitism on host species?
+The impact of cowbird parasitism on host species can vary. In some cases, the presence of cowbird chicks in a nest can lead to reduced survival rates for the host’s own offspring. Cowbird chicks often grow faster and demand more food, outcompeting the host’s young. However, certain host species have evolved strategies to mitigate these effects, such as building larger nests or producing more eggs.
How do bison benefit from the presence of cowbirds?
+Bison benefit from cowbirds through their role as an early warning system. Cowbirds are highly vigilant and can detect potential threats, such as predators or human activities, more quickly than bison. By perching on bison’s backs, cowbirds provide an alert system, allowing bison to react promptly and protect their herds. This symbiotic relationship enhances the survival chances of both species.
Are there any conservation efforts specifically focused on cowbirds and bison?
+Yes, there are several conservation initiatives dedicated to protecting cowbirds and bison. These efforts include habitat restoration projects, such as the reintroduction of bison to their natural ranges and the preservation of grasslands. Additionally, research programs aim to study the dynamics between these species and develop effective conservation strategies.