Unlocking the Secrets of Al’s Thermal Conductivity

Aluminum, or Al for short, is a versatile and widely used material known for its excellent thermal conductivity. Its ability to efficiently transfer heat makes it an essential component in various industries, from electronics to aerospace. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of Al’s thermal conductivity, exploring its properties, applications, and how it can be optimized for different purposes. Whether you are an engineer, a researcher, or simply curious about this fascinating material, this ultimate guide will provide you with all the information you need.
Understanding Thermal Conductivity
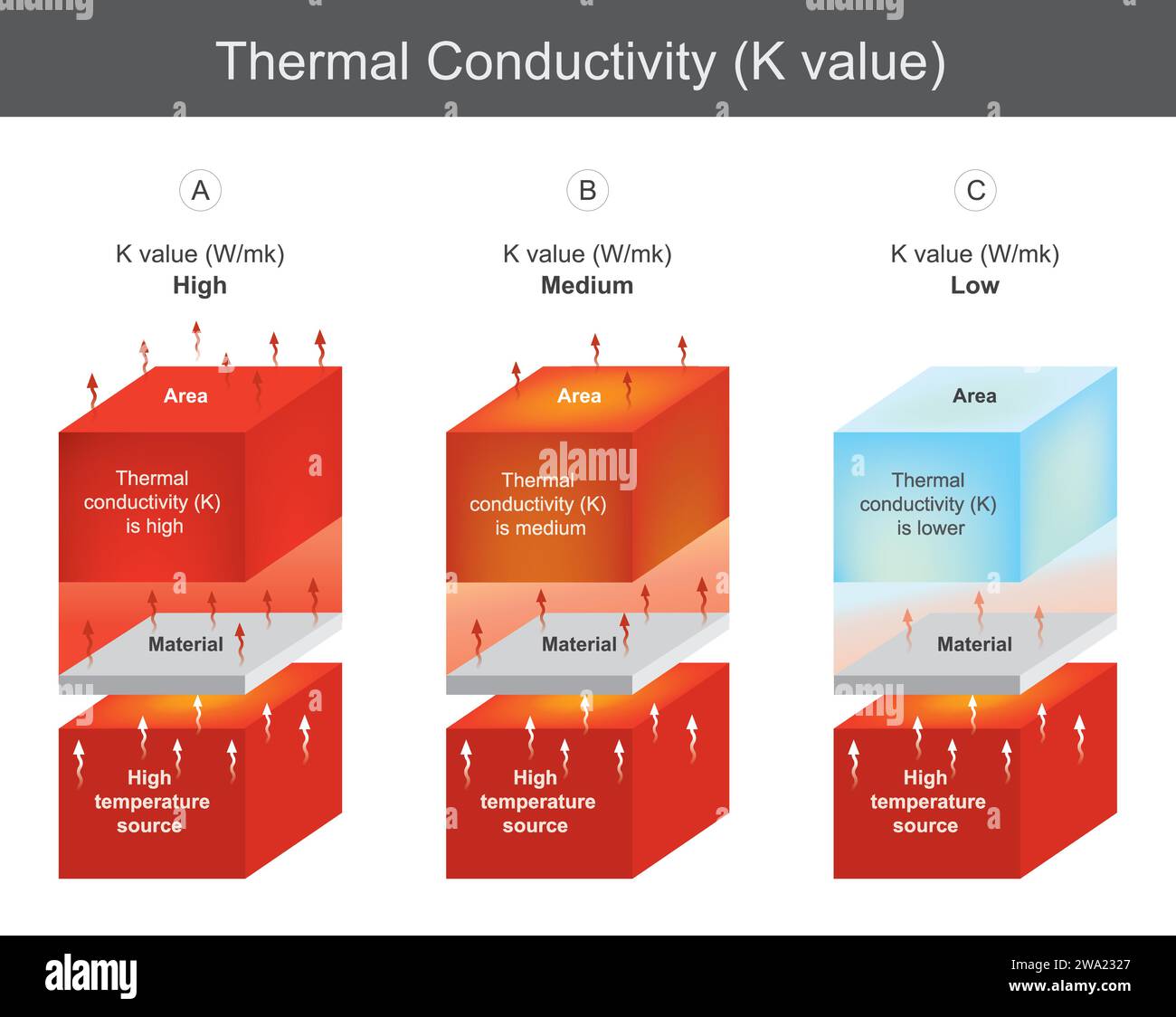
Before we dive into the specifics of Al’s thermal conductivity, let’s briefly understand what thermal conductivity is and why it matters. Thermal conductivity is a material’s ability to conduct heat. It is measured by the rate at which heat flows through a substance, typically represented by the symbol “k” or “λ” (lambda). Materials with high thermal conductivity efficiently transfer heat, while those with low thermal conductivity act as insulators, resisting heat flow.
The Intriguing Properties of Al’s Thermal Conductivity
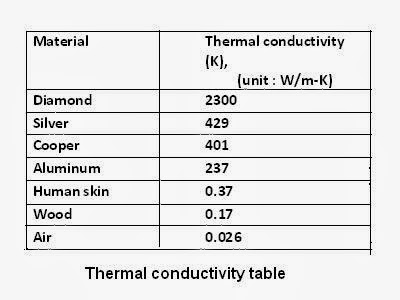
Aluminum boasts an impressive thermal conductivity value, making it an ideal choice for heat transfer applications. Here are some key properties that make Al’s thermal conductivity stand out:
- High Thermal Conductivity: Al has a relatively high thermal conductivity compared to many other metals. Its ability to conduct heat effectively makes it an excellent choice for cooling systems, heat exchangers, and other thermal management applications.
- Lightweight and Durable: Aluminum is known for its lightweight nature, which is a significant advantage in industries where weight reduction is crucial. Despite its light weight, Al maintains excellent mechanical strength, making it durable and suitable for various structural applications.
- Corrosion Resistance: Aluminum naturally forms a protective oxide layer when exposed to air, providing excellent corrosion resistance. This property makes Al suitable for outdoor applications and environments where corrosion is a concern.
- Electrical Conductivity: In addition to its thermal conductivity, Al also exhibits good electrical conductivity. This dual functionality makes it a popular choice for electrical components and wiring.
- Ease of Fabrication: Aluminum is relatively easy to work with and can be shaped, machined, and joined using various methods. Its malleability and formability make it versatile for different manufacturing processes.
Applications of Al’s Thermal Conductivity

The exceptional thermal conductivity of Al finds applications in numerous industries and everyday life. Let’s explore some of the key areas where Al’s thermal properties shine:
Electronics and Semiconductor Industry

- Heat Sinks: Aluminum heat sinks are commonly used in electronic devices to dissipate excess heat generated by components. Their high thermal conductivity ensures efficient heat transfer, preventing overheating and maintaining optimal performance.
- Thermal Interface Materials: Al-based thermal interface materials, such as thermal pads or thermal grease, are applied between heat-generating components and heat sinks to enhance thermal contact and improve heat dissipation.
- LED Lighting: Aluminum is often used in LED lighting fixtures due to its ability to conduct heat away from the LED chips, ensuring longer lifespan and better light output.
Automotive and Transportation

- Engine Cooling: Aluminum radiators and heat exchangers are integral components in automotive cooling systems. Their high thermal conductivity helps regulate engine temperatures, ensuring efficient operation.
- Hybrid and Electric Vehicles: Al’s lightweight and thermal properties make it ideal for electric vehicle components, such as battery packs and thermal management systems, reducing weight and improving overall efficiency.
- Aerospace: Aluminum alloys are widely used in aircraft construction due to their lightweight and thermal management capabilities. They play a crucial role in maintaining optimal temperatures and ensuring the safety and performance of aircraft.
Building and Construction

- Insulation: Aluminum foils and reflective materials are used as insulation in buildings to reflect heat and prevent heat transfer. This helps regulate indoor temperatures and reduce energy consumption.
- Heat-Resistant Structures: Aluminum’s thermal conductivity makes it suitable for constructing heat-resistant structures, such as fire-resistant doors and windows, providing protection against extreme temperatures.
- Solar Panels: Aluminum frames and support structures are commonly used in solar panel installations. Their thermal properties help dissipate heat generated by solar panels, improving their efficiency and longevity.
Consumer Goods

- Cookware: Aluminum cookware, such as pots and pans, is popular due to its excellent heat distribution and retention properties. It ensures even cooking and reduces the risk of hot spots.
- Heat Transfer Applications: Aluminum is used in various consumer products, including hair dryers, heaters, and electronic devices, to efficiently transfer heat and maintain optimal temperatures.
- Packaging: Aluminum foils and containers are widely used for food packaging, as they provide excellent thermal insulation and protect against temperature fluctuations.
Optimizing Al’s Thermal Conductivity

While Al’s natural thermal conductivity is impressive, there are ways to further enhance its performance for specific applications. Here are some techniques and considerations to optimize Al’s thermal conductivity:
Alloying and Treatment
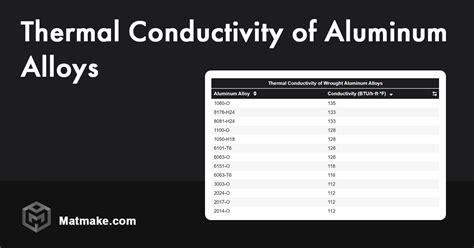
- Alloying: By combining Al with other elements, such as copper or silicon, it is possible to create aluminum alloys with even higher thermal conductivity. These alloys are tailored for specific applications, offering improved heat transfer capabilities.
- Heat Treatment: Heat treating aluminum can alter its microstructure, affecting its thermal conductivity. Certain heat treatment processes can enhance the material’s ability to conduct heat, making it more suitable for high-performance applications.
Surface Treatments

- Anodizing: Anodizing aluminum creates a protective oxide layer on its surface, which can improve its thermal conductivity. This process enhances corrosion resistance and provides a durable finish.
- Coatings: Applying thermal interface coatings or specialized coatings can enhance Al’s thermal conductivity by improving its surface properties and reducing thermal resistance.
Design Considerations

- Heat Sink Design: Optimizing the design of aluminum heat sinks, such as fin density and shape, can significantly impact their thermal performance. Proper design ensures efficient heat dissipation and prevents hotspots.
- Thermal Contact: Ensuring good thermal contact between aluminum components and other materials is crucial. Using thermal interface materials or surface treatments can improve thermal conductivity across interfaces.
Manufacturing Techniques

- Extrusion: Aluminum extrusion allows for the creation of complex shapes with precise dimensions. This manufacturing technique ensures consistent thermal conductivity and is widely used in heat exchangers and heat sink manufacturing.
- Casting: Aluminum casting is ideal for producing complex components with excellent thermal conductivity. It offers design flexibility and is commonly used in the automotive and aerospace industries.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)

What is the thermal conductivity of pure aluminum?

+
The thermal conductivity of pure aluminum can vary depending on factors such as temperature and purity. On average, pure aluminum has a thermal conductivity of around 205-220 W/(m·K) at room temperature.
How does aluminum compare to other metals in terms of thermal conductivity?

+
Aluminum has a relatively high thermal conductivity compared to many other metals. While it is not as conductive as metals like copper or silver, it offers a good balance between thermal conductivity and other desirable properties such as lightweight and corrosion resistance.
Can aluminum's thermal conductivity be improved further?
+Yes, aluminum's thermal conductivity can be enhanced through various techniques. Alloying aluminum with other elements, heat treatment processes, and surface treatments can improve its thermal performance, making it suitable for even more demanding applications.
What are some common challenges when working with aluminum for thermal management?
+One challenge is ensuring good thermal contact between aluminum components and other materials. Surface roughness, oxidation, and contamination can affect thermal conductivity. Proper surface preparation and the use of thermal interface materials are essential to overcome these challenges.
Are there any safety considerations when using aluminum for thermal management applications?
+Yes, it is important to consider the safety aspects of aluminum, especially in high-temperature applications. Aluminum has a relatively low melting point, and excessive heat can lead to deformation or failure. Proper design, temperature control, and the use of suitable alloys can mitigate these risks.
Wrapping Up

In this ultimate guide, we have explored the fascinating world of Al’s thermal conductivity, uncovering its properties, applications, and optimization techniques. Aluminum’s exceptional ability to conduct heat has made it an indispensable material in various industries, from electronics to transportation. By understanding its thermal properties and employing the right strategies, engineers and designers can harness the full potential of Al’s thermal conductivity for innovative and efficient solutions. As technology advances, we can expect further advancements in aluminum-based thermal management, driving progress in numerous fields.