The Bible, a sacred text cherished by billions worldwide, holds immense significance in religious and spiritual practices. Its translation into various languages has played a crucial role in spreading its teachings and messages far and wide. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the art of Bible translation, exploring the challenges, processes, and best practices that translators face when rendering this ancient text into modern languages.
The Importance of Bible Translation

Bible translation is an essential endeavor that ensures the accessibility and understanding of the Bible's message for people from diverse linguistic backgrounds. It allows individuals to connect with the scriptures in their native language, fostering a deeper comprehension and personal connection with its teachings.
Challenges in Bible Translation

Translating the Bible is an intricate task due to the following challenges:
- Ancient Language: The Bible was originally written in ancient languages like Hebrew, Aramaic, and Greek, which have evolved significantly over time. Translators must navigate the complexities of these languages to accurately convey the intended meaning.
- Cultural Context: The Bible reflects the cultural and historical context of its time. Translators must carefully consider the cultural nuances and ensure that the translation remains relevant and understandable to modern readers.
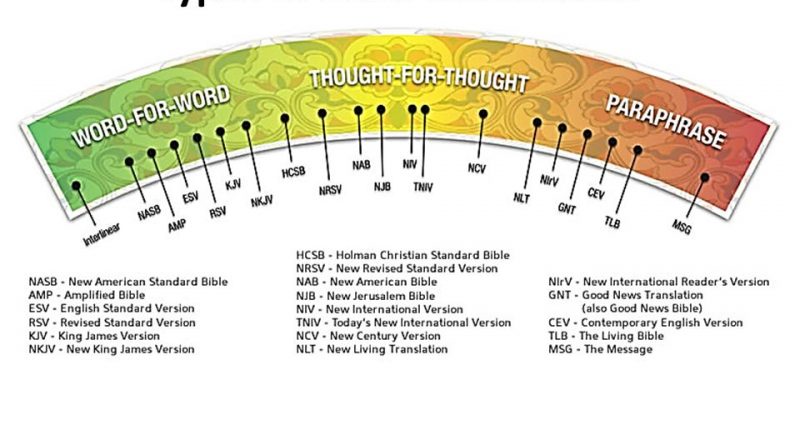
- Literal vs. Dynamic Equivalence: Translators face the dilemma of choosing between a literal word-for-word translation or a more dynamic, thought-for-thought approach. Finding the right balance between accuracy and readability is crucial.
- Poetic and Literary Devices: The Bible contains various literary devices, such as poetry, metaphors, and symbolism. Translators must skillfully interpret and convey these elements to preserve the beauty and impact of the original text.
The Translation Process

The process of Bible translation involves several stages, each requiring meticulous attention to detail and a deep understanding of the source material.
Step 1: Textual Criticism and Source Selection

Translators begin by critically examining the available manuscripts and choosing the most reliable sources for translation. This step involves evaluating the historical accuracy and textual integrity of the manuscripts.
Step 2: Initial Translation

In this stage, translators create a preliminary translation, focusing on accuracy and precision. They carefully analyze the grammatical structure, vocabulary, and context of the source text to ensure a faithful rendering.
Step 3: Review and Revision

The initial translation undergoes rigorous review and revision by a team of experts. This process involves cross-referencing with other translations, consulting linguistic and cultural resources, and making necessary adjustments to enhance clarity and accuracy.
Step 4: Linguistic and Cultural Adaptation

Translators adapt the language and cultural references to suit the target audience. This step requires a deep understanding of the target language's nuances and the cultural context of the readers to ensure the translation resonates with them.
Step 5: Final Review and Editing

Before publication, the translation undergoes a final review to ensure consistency, grammar, and overall quality. This step involves proofreading, fact-checking, and addressing any remaining linguistic or cultural concerns.
Best Practices for Bible Translation

To produce high-quality Bible translations, translators adhere to certain best practices:
- Collaborative Effort: Bible translation is often a collaborative process involving a team of linguists, theologians, and cultural experts. This collective expertise ensures a more accurate and nuanced translation.
- Use of Technological Tools: Translators leverage advanced software and digital tools to aid in their work. These tools assist in textual analysis, vocabulary research, and cross-referencing with other translations.
- Contextual Understanding: Translators delve into the historical, cultural, and literary context of the Bible to grasp the intended meaning and ensure a faithful representation in the target language.
- Reader-Friendly Language: While accuracy is paramount, translators also aim to produce translations that are accessible and engaging for modern readers. They strike a balance between precision and readability.
The Impact of Bible Translation

Bible translation has had a profound impact on the spread of Christianity and the accessibility of religious teachings. It has enabled people from diverse linguistic backgrounds to connect with the scriptures and understand their faith more deeply.
The availability of Bible translations in various languages has fostered interfaith dialogue and promoted religious tolerance. It has also played a significant role in shaping cultural and literary traditions, influencing art, music, and literature worldwide.
The Future of Bible Translation

As technology advances, the field of Bible translation continues to evolve. Digital tools and machine learning algorithms are being utilized to aid in the translation process, enhancing efficiency and accuracy.
Additionally, the rise of digital platforms and online communities has created new opportunities for collaboration and feedback. Translators can now engage directly with readers, incorporating their input and suggestions to improve the translation experience.
The future of Bible translation holds promise, with ongoing efforts to make the scriptures accessible to an even wider audience. As language and cultural landscapes continue to evolve, translators will play a crucial role in bridging the gap between ancient texts and modern readers.
Conclusion

Bible translation is a complex and intricate art that requires dedication, expertise, and a deep respect for the source material. Translators face unique challenges, from navigating ancient languages to capturing the cultural nuances of the Bible's time. Despite these obstacles, their work ensures that the Bible's message remains accessible and relevant to generations of readers.
Through meticulous research, collaborative efforts, and a commitment to accuracy, translators continue to bring the Bible's teachings to life in diverse languages. Their contributions have shaped religious practices, influenced cultures, and inspired countless individuals worldwide. As we embrace the future, the art of Bible translation will undoubtedly continue to evolve, ensuring that the scriptures remain a guiding light for generations to come.
How often are Bible translations updated or revised?

+
Bible translations are periodically updated to ensure accuracy and reflect the evolving language and cultural landscape. The frequency of revisions varies, but major updates are typically made every few decades to incorporate new linguistic research and insights.
Are there any famous Bible translators?

+
Yes, several renowned translators have made significant contributions to Bible translation. One notable example is William Tyndale, whose English translation of the New Testament laid the foundation for future English versions.
Can anyone become a Bible translator?
+
While anyone with a passion for languages and a deep respect for the Bible’s message can contribute to translation efforts, becoming a professional Bible translator requires specialized training and expertise in linguistics, theology, and the target language.