Understanding Linear Approximation Equations: A Comprehensive Guide

Linear approximation is a powerful mathematical tool that allows us to estimate the value of a function at a given point by creating a linear equation that closely resembles the original function. This technique is widely used in various fields, including physics, engineering, and economics, to simplify complex problems and make accurate predictions. In this ultimate guide, we will delve into the world of linear approximation equations, exploring their applications, methods, and benefits.
What is Linear Approximation?

Linear approximation, also known as linearization, is a mathematical process that involves finding a linear equation that best represents the behavior of a function near a specific point. It provides a simplified model of the original function, making it easier to analyze and solve problems. By approximating a function with a linear equation, we can gain valuable insights into its behavior and make predictions with reasonable accuracy.
Applications of Linear Approximation

- Physics: Linear approximation is commonly used in physics to model the behavior of physical systems. For example, it can be applied to calculate the motion of objects under the influence of forces, study the behavior of waves, or approximate the trajectory of a projectile.
- Engineering: Engineers utilize linear approximation to simplify complex mathematical models, making them more manageable for analysis and design. It is particularly useful in areas such as structural analysis, control systems, and signal processing.
- Economics: In economics, linear approximation is employed to study the behavior of economic systems and make predictions about market trends. It helps economists understand the impact of changes in variables such as prices, production levels, and consumer behavior.
- Computer Science: Linear approximation techniques are used in computer graphics and machine learning to optimize algorithms and improve performance. It enables the creation of efficient rendering techniques and helps train machine learning models with reduced computational complexity.
Methods of Linear Approximation

There are several methods to perform linear approximation, each with its own advantages and applications. Here are some commonly used techniques:
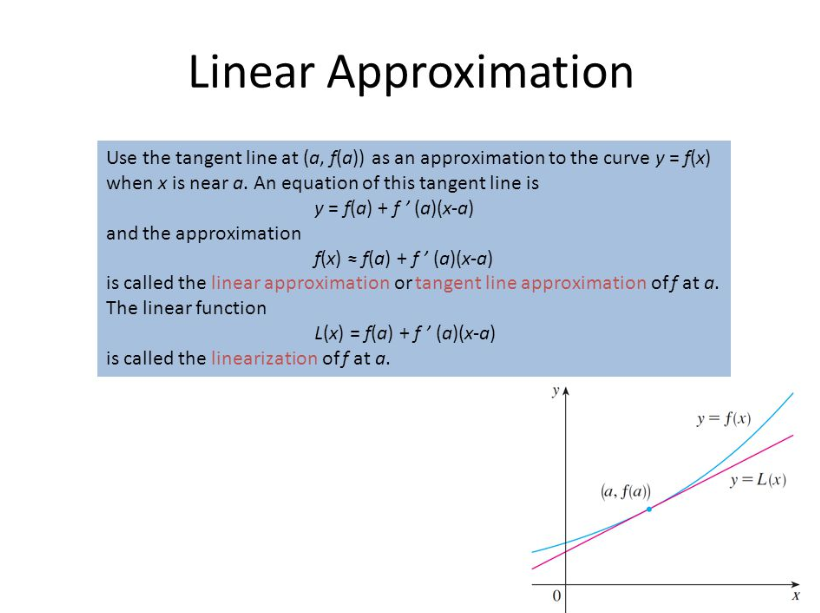
Tangent Line Approximation

Tangent line approximation, also known as differential approximation, involves finding the equation of the tangent line to a function at a specific point. This method is particularly useful when dealing with differentiable functions and provides a linear approximation for small changes in the independent variable.
The equation of the tangent line is given by:
y - f(x0) = f'(x0) * (x - x0)
Where:
- y is the dependent variable.
- f(x0) is the value of the function at the point of approximation.
- f'(x0) is the derivative of the function at the point of approximation.
- x is the independent variable.
- x0 is the point of approximation.
Secant Line Approximation
Secant line approximation, also known as chord approximation, involves finding the equation of the secant line between two points on a function. This method provides a linear approximation for larger changes in the independent variable and is particularly useful when the function is not differentiable at the point of approximation.
The equation of the secant line is given by:
y - f(x1) = (f(x2) - f(x1)) / (x2 - x1) * (x - x1)
Where:
- y is the dependent variable.
- f(x1) and f(x2) are the values of the function at two different points.
- x is the independent variable.
- x1 and x2 are the points of approximation.
Taylor Series Approximation

Taylor series approximation is a more advanced method that involves expanding a function into an infinite series of terms. It provides a highly accurate linear approximation for functions that are infinitely differentiable. The Taylor series of a function f(x) at the point x0 is given by:
f(x) = f(x0) + f'(x0) * (x - x0) + (f''(x0) / 2!) * (x - x0)2 + ...
Where:
- f(x) is the original function.
- f(x0) is the value of the function at the point of approximation.
- f'(x0) is the first derivative of the function at the point of approximation.
- f''(x0) is the second derivative of the function at the point of approximation.
- ... represents higher-order terms.
Benefits of Linear Approximation

- Simplification: Linear approximation simplifies complex functions, making them easier to analyze and solve.
- Accuracy: With careful selection of the point of approximation, linear approximation can provide highly accurate results for small changes in the independent variable.
- Efficiency: Linear approximation techniques are computationally efficient, reducing the computational load when dealing with complex mathematical models.
- Generalization: Linear approximation allows us to make predictions and generalize the behavior of a function beyond the specific point of approximation.
Choosing the Right Method

The choice of linear approximation method depends on the nature of the function and the specific problem at hand. Here are some guidelines to help you select the appropriate method:
- Tangent Line Approximation: Use this method when the function is differentiable at the point of approximation and you are interested in small changes in the independent variable.
- Secant Line Approximation: Opt for this method when the function is not differentiable at the point of approximation or when you need to approximate the function over a larger range of the independent variable.
- Taylor Series Approximation: Consider this method for highly accurate approximations of infinitely differentiable functions. It provides a more precise approximation but requires a deeper understanding of calculus and series expansion.
Examples of Linear Approximation

Example 1: Tangent Line Approximation

Let's approximate the function f(x) = x2 + 3x + 2 at the point x0 = 1 using tangent line approximation. The derivative of the function is f'(x) = 2x + 3. Substituting x0 = 1 into the derivative, we get f'(1) = 2(1) + 3 = 5. Now, we can find the equation of the tangent line:
y - f(1) = 5 * (x - 1)
Simplifying the equation, we get:
y - 6 = 5x - 5
Rearranging the terms, we have:
5x - y + 1 = 0
The linear approximation of the function f(x) = x2 + 3x + 2 at x0 = 1 is 5x - y + 1 = 0.
Example 2: Secant Line Approximation

Let's approximate the function f(x) = sin(x) over the interval [0, π/2] using secant line approximation. We will choose two points within this interval: x1 = 0 and x2 = π/2. The values of the function at these points are f(0) = 0 and f(π/2) = 1. Now, we can find the equation of the secant line:
y - f(0) = (f(π/2) - f(0)) / (π/2 - 0) * (x - 0)
Simplifying the equation, we get:
y = (1 - 0) / (π/2) * x
The linear approximation of the function f(x) = sin(x) over the interval [0, π/2] is y = (2/π) * x.
Best Practices for Linear Approximation

- Choose the point of approximation carefully: Select a point where the function behaves relatively smoothly and represents the typical behavior of the function.
- Consider the range of approximation: Determine the range over which you want the approximation to be valid. This will help you choose the appropriate method and ensure accurate results.
- Evaluate the error: Calculate the error between the original function and the linear approximation to assess the accuracy of your approximation.
- Iterate and refine: If the initial approximation is not accurate enough, consider using a different method or refining the point of approximation to improve the accuracy.
Conclusion

Linear approximation is a valuable tool that enables us to simplify complex functions and make accurate predictions. By understanding the applications, methods, and benefits of linear approximation, we can apply this technique effectively in various fields. Whether it's modeling physical systems, optimizing algorithms, or analyzing economic trends, linear approximation provides a powerful means to gain insights and solve real-world problems.
What is the main purpose of linear approximation?

+
The main purpose of linear approximation is to simplify complex functions and make accurate predictions by creating a linear equation that closely resembles the original function.
When should I use tangent line approximation vs. secant line approximation?

+
Use tangent line approximation when the function is differentiable at the point of approximation and you are interested in small changes in the independent variable. Opt for secant line approximation when the function is not differentiable at the point of approximation or when you need to approximate the function over a larger range of the independent variable.
How accurate is linear approximation?
+
The accuracy of linear approximation depends on the choice of the point of approximation and the method used. With careful selection and refinement, linear approximation can provide highly accurate results for small changes in the independent variable.
What are some common applications of linear approximation in real life?

+
Linear approximation is widely used in physics, engineering, economics, and computer science. It helps in modeling physical systems, optimizing algorithms, analyzing economic trends, and improving the performance of computer graphics and machine learning models.
Can I use linear approximation for non-linear functions?

+
Yes, linear approximation can be applied to non-linear functions by selecting an appropriate point of approximation and using the right method. However, the accuracy of the approximation may vary depending on the nature of the function and the chosen point.