Introduction to Cardiac Muscle Microscopy
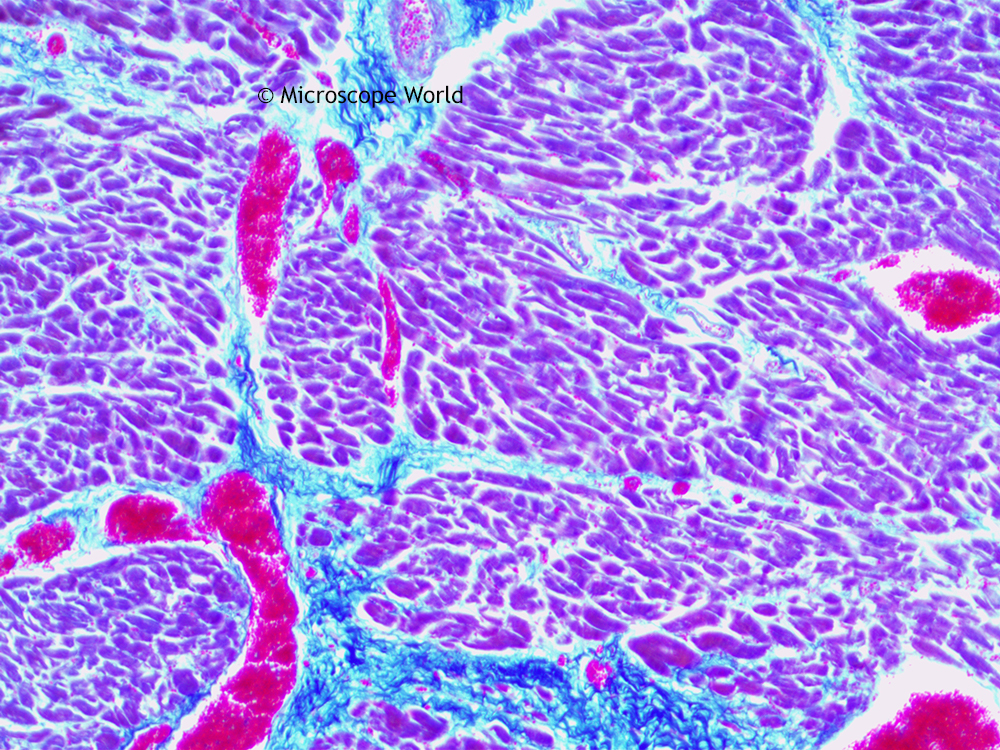
Cardiac muscle, often referred to as the heart muscle, is a specialized type of muscle tissue that plays a vital role in our circulatory system. Studying cardiac muscle under a microscope allows us to delve into its unique structure and understand its remarkable function. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the steps and techniques involved in viewing cardiac muscle, shedding light on its fascinating characteristics.
Understanding Cardiac Muscle
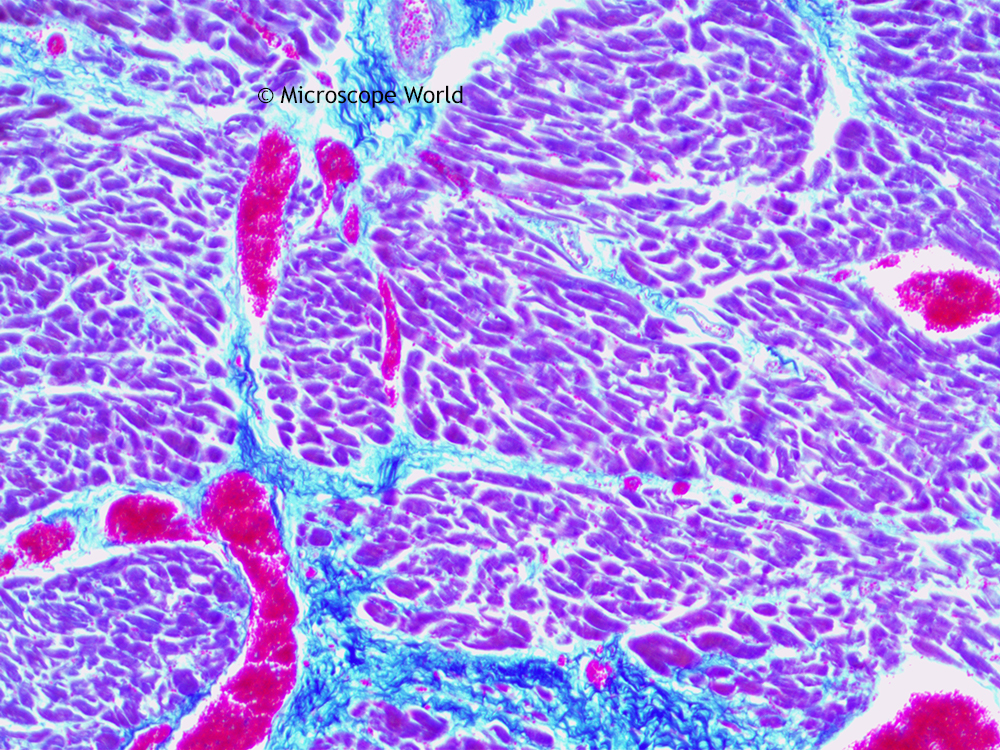
Cardiac muscle is distinct from other muscle types due to its involuntary nature and intricate arrangement. It is composed of highly organized cells called cardiomyocytes, which contract rhythmically to pump blood throughout the body. The unique structure of cardiac muscle enables it to withstand the continuous demands of the circulatory system.
Preparing the Microscope
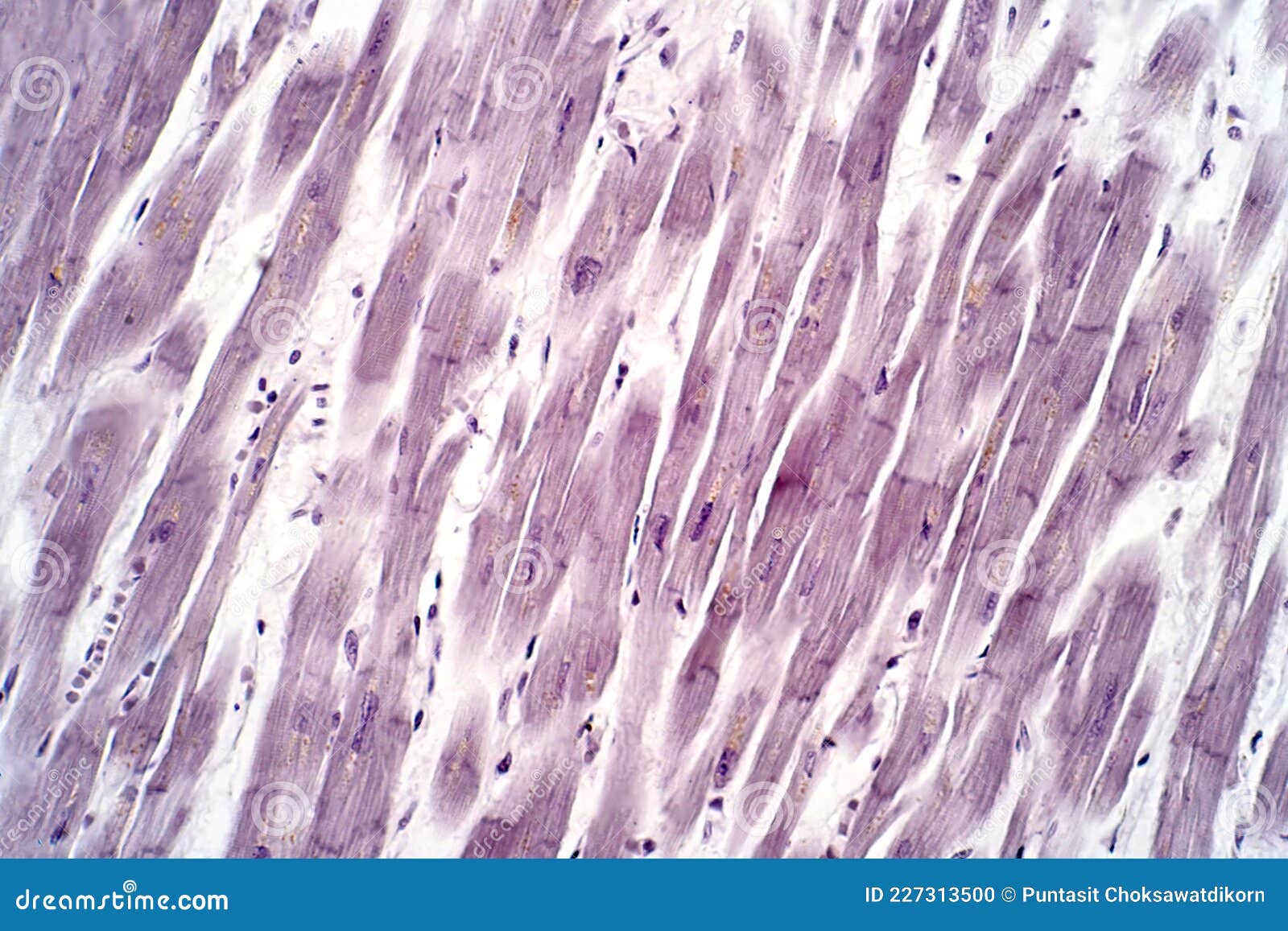
Before examining cardiac muscle, it is essential to ensure your microscope is properly set up. Here’s a step-by-step guide to preparing your microscope:
- Adjust the Lighting: Begin by adjusting the microscope’s light source to achieve optimal illumination. Ensure the light is bright enough to provide clear visibility without causing excessive glare.
- Focus the Objective Lens: Focus the objective lens by turning the coarse adjustment knob until the field of view is in focus. This step ensures that the microscope is ready to capture sharp images.
- Position the Stage: Position the microscope stage so that it is easily accessible and aligned with the objective lens. Make sure the stage is clean and free from any debris or residue.
- Calibrate the Microscope: Calibrate the microscope by adjusting the fine focus knob to obtain a clear and precise image. This step ensures accurate magnification and focus throughout your observations.
Obtaining Cardiac Muscle Samples
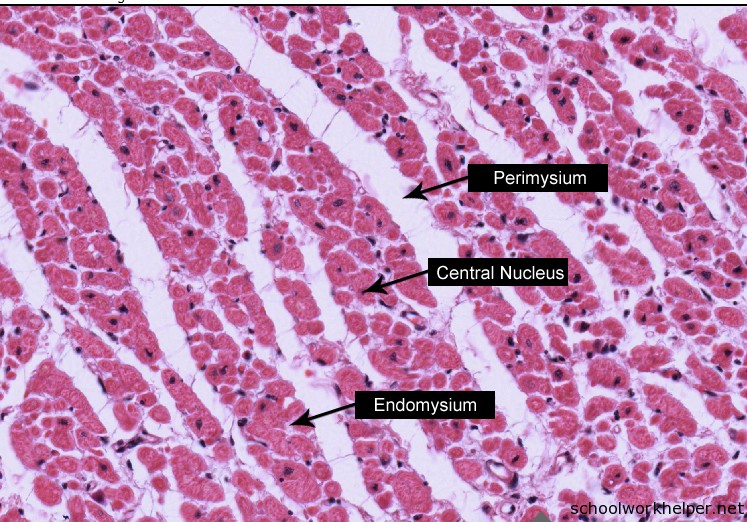
To view cardiac muscle under a microscope, you will need to obtain suitable samples. Here are the steps to collect and prepare cardiac muscle samples:
- Obtain Fresh Samples: Fresh cardiac muscle samples are ideal for microscopy. You can obtain these samples from a local research facility or collaborate with medical professionals to access suitable specimens.
- Fixation Process: Fix the cardiac muscle samples using appropriate fixatives such as formalin or glutaraldehyde. This process preserves the tissue structure and prevents degradation. Follow the recommended fixation protocols to ensure optimal results.
- Sectioning the Samples: After fixation, section the cardiac muscle samples using a microtome or a cryostat. This process creates thin slices of the tissue, allowing for detailed examination under the microscope. Ensure the sections are of an appropriate thickness for your desired magnification.
- Staining Techniques: Apply staining techniques to enhance the visibility of specific structures within the cardiac muscle. Common stains used for cardiac muscle include hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) or trichrome stains. Follow the staining protocols carefully to achieve accurate and consistent results.
Viewing Cardiac Muscle Under the Microscope

Once your microscope is prepared and the cardiac muscle samples are ready, it’s time to view the fascinating world of cardiac muscle. Here’s a guide to help you navigate through the process:
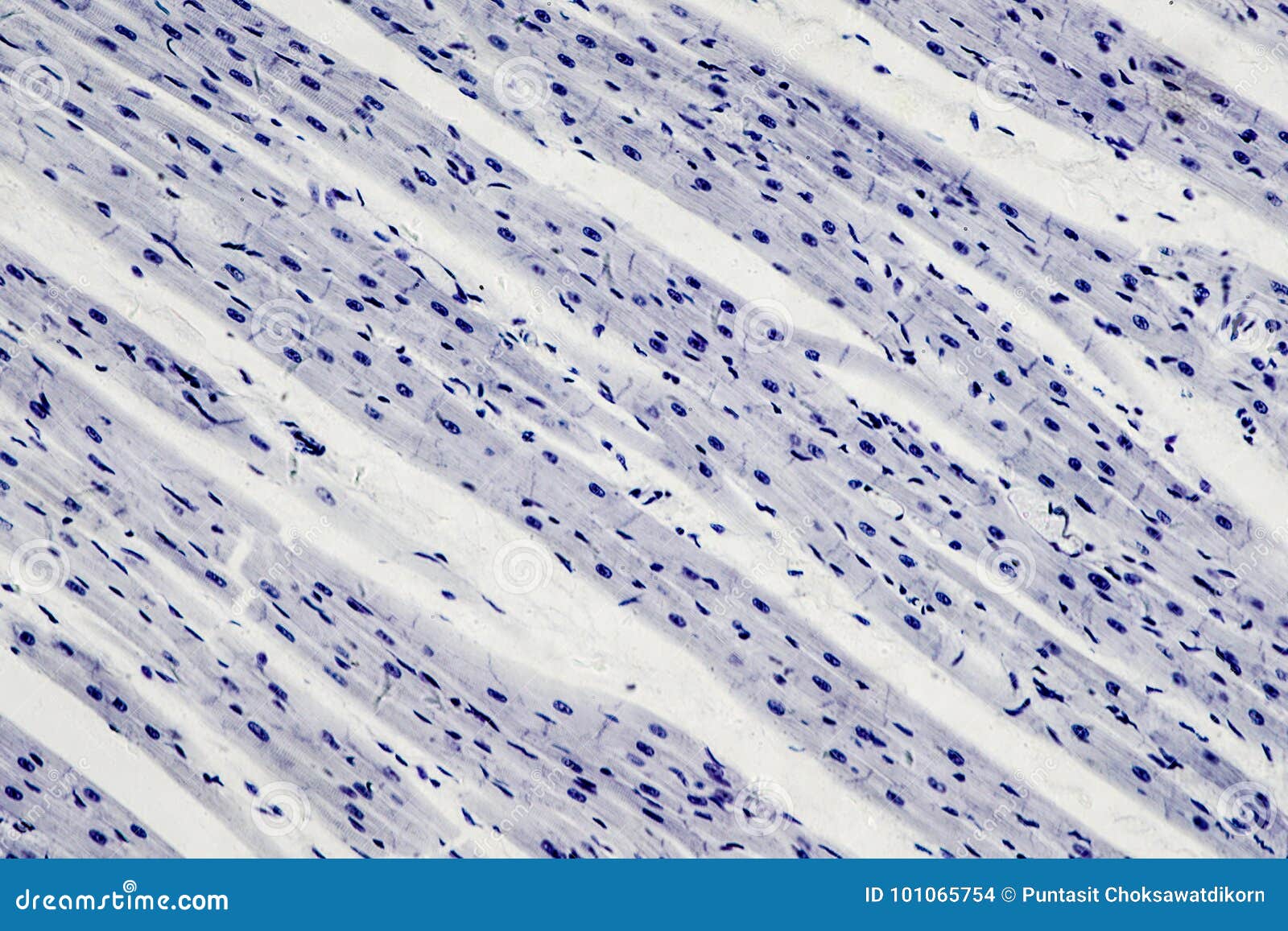
- Low Magnification Observation: Start by observing the cardiac muscle sample at a low magnification, typically around 4x or 10x. This initial observation provides an overview of the tissue’s general structure and arrangement. Look for the characteristic striations and the presence of individual cardiomyocytes.
- Medium Magnification Examination: Increase the magnification to around 40x or 100x to examine the cardiac muscle in more detail. At this level, you can observe the intricate organization of the muscle fibers and the presence of intercalated discs, which connect adjacent cardiomyocytes. Pay attention to the regular arrangement of the muscle fibers and the distinct boundaries between them.
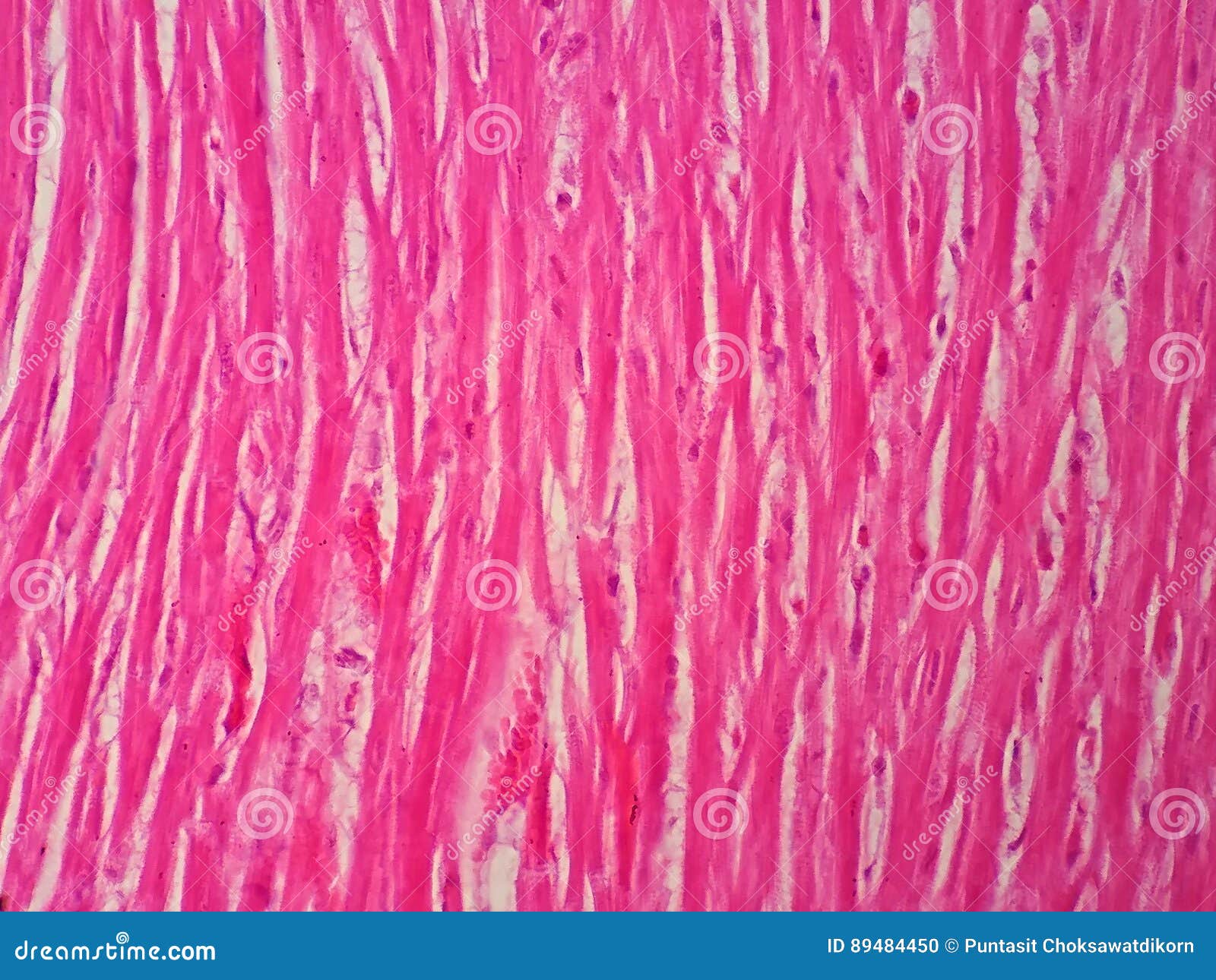
- High Magnification Analysis: For a closer look, increase the magnification to 400x or higher. This level of magnification allows you to visualize the fine details of the cardiac muscle, including the sarcomeres, which are the basic contractile units. Observe the regular pattern of alternating light and dark bands within the sarcomeres, known as the A-bands and I-bands. This pattern reflects the arrangement of myofilaments and provides insights into the contractile properties of the cardiac muscle.
Identifying Key Structures

As you examine the cardiac muscle under the microscope, it is important to identify and understand the key structures present. Here are some of the notable features you should look for:
- Cardiomyocytes: Cardiomyocytes are the individual muscle cells that make up the cardiac muscle. They are characterized by their elongated shape and distinct nuclei. Observe the arrangement and orientation of the cardiomyocytes within the muscle fibers.
- Intercalated Discs: Intercalated discs are specialized cell junctions that connect adjacent cardiomyocytes. They play a crucial role in maintaining the electrical and mechanical coupling between cells, ensuring coordinated contraction of the heart. Look for the presence of intercalated discs as dark lines or regions between the cardiomyocytes.
- Sarcomeres: Sarcomeres are the basic functional units of muscle contraction. They are composed of myofilaments, including actin and myosin, which interact to generate force. Observe the regular pattern of sarcomeres within the cardiomyocytes and note the alternating light and dark bands.
- Connective Tissue: Cardiac muscle is supported and surrounded by connective tissue, which provides structural integrity and anchors the muscle to surrounding structures. Look for the presence of collagen fibers and other connective tissue components surrounding the muscle fibers.
Advanced Techniques for Cardiac Muscle Microscopy
To further enhance your understanding of cardiac muscle, you can explore advanced techniques and imaging methods. Here are a few options to consider:
- Immunohistochemistry: Immunohistochemistry techniques allow for the visualization of specific proteins or antigens within the cardiac muscle. By using antibodies that bind to target proteins, you can identify and localize specific cellular components, such as ion channels or contractile proteins. This technique provides valuable insights into the molecular composition of cardiac muscle.
- Electron Microscopy: Electron microscopy offers an ultra-high magnification view of cardiac muscle, revealing fine details that are not visible under light microscopy. With electron microscopy, you can visualize the ultrastructure of cardiomyocytes, including the intricate arrangement of myofilaments, mitochondria, and other subcellular components. This technique provides a deeper understanding of the cellular organization and function of cardiac muscle.
- Confocal Microscopy: Confocal microscopy is a powerful imaging technique that allows for the creation of high-resolution, three-dimensional images of cardiac muscle. By using laser scanning and a pinhole to eliminate out-of-focus light, confocal microscopy provides exceptional clarity and depth of field. This technique is particularly useful for studying the complex architecture and interactions within cardiac muscle tissue.
Applications of Cardiac Muscle Microscopy

Understanding the structure and function of cardiac muscle through microscopy has numerous applications in various fields. Here are some key areas where cardiac muscle microscopy plays a vital role:
- Medical Research: Microscopic examination of cardiac muscle is essential for understanding the pathophysiology of cardiovascular diseases. Researchers can study the structural changes and cellular abnormalities associated with conditions such as heart failure, cardiomyopathies, and cardiac arrhythmias. This knowledge contributes to the development of new treatments and therapeutic strategies.
- Drug Discovery and Testing: Cardiac muscle microscopy is employed in drug discovery and testing processes. Researchers can evaluate the effects of potential therapeutic compounds on cardiac muscle function and structure. By observing changes at the cellular level, they can assess the safety and efficacy of drugs, leading to the development of more targeted and effective cardiovascular medications.
- Education and Training: Microscopy of cardiac muscle is an invaluable tool for educating and training medical students, researchers, and healthcare professionals. It provides a hands-on approach to learning about cardiac anatomy, physiology, and pathology. By observing cardiac muscle under the microscope, students can gain a deeper understanding of the complex structure and function of the heart.
Conclusion

In this ultimate guide, we have explored the fascinating world of cardiac muscle microscopy. From preparing the microscope to identifying key structures, we have covered the essential steps and techniques for viewing cardiac muscle. By understanding the unique characteristics and organization of cardiac muscle, we gain insights into the remarkable function of the heart. Whether for research, education, or clinical applications, cardiac muscle microscopy continues to play a vital role in advancing our knowledge of cardiovascular health and disease.
FAQ

What are the key differences between cardiac muscle and skeletal muscle?

+
Cardiac muscle and skeletal muscle differ in several ways. Cardiac muscle is involuntary and responsible for the rhythmic contractions of the heart, while skeletal muscle is voluntary and attached to bones for movement. Cardiac muscle has a unique branching and interconnected structure, while skeletal muscle forms parallel bundles. Additionally, cardiac muscle cells have a single nucleus, while skeletal muscle cells have multiple nuclei.
How can I ensure the quality of cardiac muscle samples for microscopy?

+
To ensure high-quality cardiac muscle samples, it is important to obtain fresh tissue and follow proper fixation and staining protocols. Fresh samples should be fixed promptly to preserve the tissue structure. Adhere to recommended fixation times and concentrations to avoid over- or under-fixation. Staining techniques should be chosen based on the specific structures of interest and followed precisely to achieve consistent results.
What are some common challenges in viewing cardiac muscle under the microscope?

+
One common challenge is the small size of cardiomyocytes, which can make it difficult to observe fine details. Proper sample preparation and staining techniques can help enhance visibility. Additionally, the orientation of the muscle fibers and the presence of overlapping structures can make it challenging to identify specific features. Adjusting the focus and magnification, as well as rotating the sample, can aid in obtaining clear and informative images.
Can cardiac muscle microscopy be used to diagnose cardiovascular diseases?
+While cardiac muscle microscopy provides valuable insights into the structure and function of the heart, it is typically not used as a standalone diagnostic tool for cardiovascular diseases. However, it can be a valuable adjunct to other diagnostic methods, such as imaging techniques and blood tests. Microscopic examination can help identify specific cellular abnormalities and provide information on the underlying pathophysiology of cardiovascular conditions.
Are there any safety considerations when working with cardiac muscle samples?
+When handling cardiac muscle samples, it is important to follow proper safety protocols to minimize the risk of exposure to potentially harmful substances. Wear personal protective equipment, such as gloves and lab coats, to protect yourself from contact with fixatives, stains, or any other chemicals used in the preparation process. Ensure proper ventilation in the laboratory to minimize the inhalation of any hazardous fumes. Dispose of waste materials and used reagents according to local regulations and guidelines.