Vertical integration is a powerful business strategy that has been employed by numerous successful companies to gain a competitive edge and optimize their operations. In today's dynamic business landscape, understanding and implementing vertical integration strategies can be a game-changer for businesses looking to thrive and stay ahead of the curve. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of vertical integration, exploring its definition, benefits, challenges, and real-world examples.
Understanding Vertical Integration
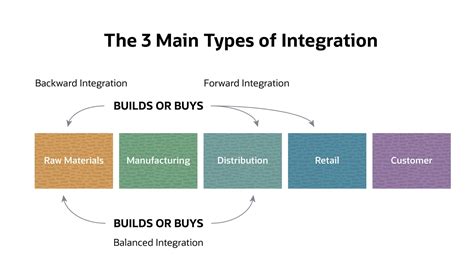
Vertical integration is a business strategy where a company expands its operations by acquiring or establishing control over multiple stages of the supply chain, moving beyond its core competencies. It involves integrating various production stages, from raw material procurement to manufacturing, distribution, and even retail, under a single organizational umbrella. By doing so, companies aim to reduce costs, increase efficiency, and gain greater control over their operations.
This strategy can be categorized into two main types: forward integration and backward integration. Forward integration occurs when a company expands its operations towards the end of the supply chain, such as by acquiring retailers or distributors. On the other hand, backward integration involves expanding operations towards the beginning of the supply chain, such as by acquiring raw material suppliers or manufacturers.
Benefits of Vertical Integration

Cost Reduction
One of the primary advantages of vertical integration is its potential to reduce costs. By owning and controlling multiple stages of the supply chain, companies can eliminate intermediary costs, negotiate better deals with suppliers, and optimize production processes. This cost reduction can lead to increased profitability and a stronger competitive position in the market.
Improved Efficiency

Vertical integration allows companies to streamline their operations and improve overall efficiency. By having direct control over the supply chain, businesses can better coordinate and manage production, inventory, and distribution. This integration enables them to respond quickly to market demands, reduce lead times, and minimize waste, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency.
Enhanced Quality Control

With vertical integration, companies can exert greater control over the quality of their products and services. By overseeing various production stages, they can implement stringent quality standards and ensure consistency throughout the supply chain. This level of control not only enhances the overall quality of the final product but also helps build a strong brand reputation and customer loyalty.
Increased Market Power
Vertical integration can provide companies with increased market power and a stronger negotiating position. By owning multiple stages of the supply chain, businesses can influence the market dynamics, negotiate better terms with suppliers and distributors, and even control the availability of certain products or services. This market power can be a significant advantage when dealing with competitors or entering new markets.
Challenges of Vertical Integration
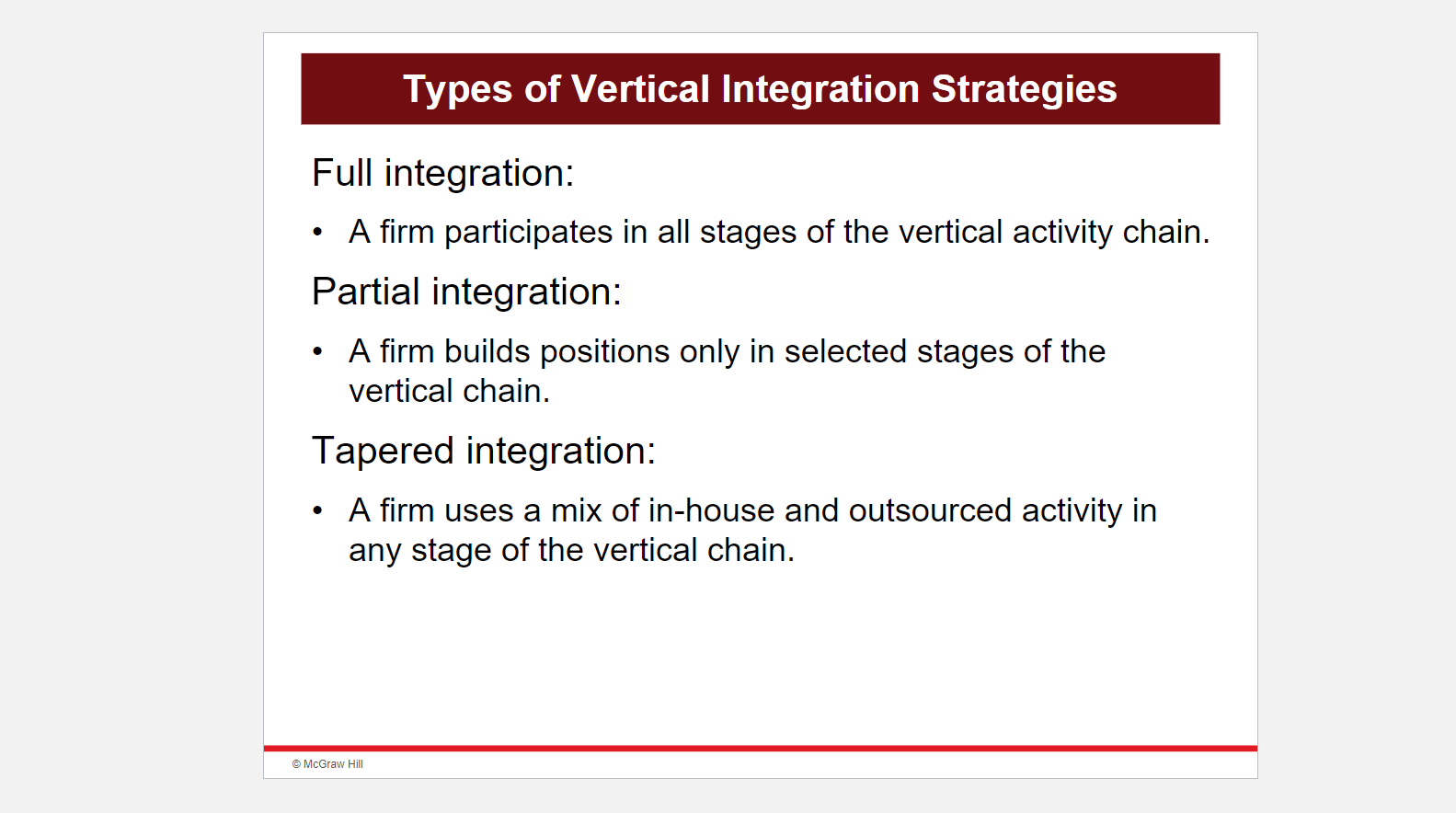
High Initial Investment
Implementing vertical integration often requires a substantial initial investment. Acquiring or establishing control over multiple stages of the supply chain can be costly, and companies must carefully assess their financial capabilities and potential returns before committing to such a strategy. The high upfront costs can be a significant barrier for smaller businesses or those with limited financial resources.
Complex Management
As a company expands its operations through vertical integration, the management and coordination of various stages of the supply chain become more complex. Effective communication, synchronization of processes, and skilled management are essential to ensure the success of the integrated system. Failure to manage the complexity effectively can lead to inefficiencies, delays, and increased costs.
Loss of Flexibility

While vertical integration offers numerous benefits, it can also result in a loss of flexibility. Companies that integrate vertically may become less agile and responsive to market changes. The need to coordinate and manage multiple stages of the supply chain can make it challenging to adapt quickly to shifting consumer trends, technological advancements, or sudden market disruptions.
Real-World Examples of Vertical Integration

Apple Inc.

Apple is a prime example of a company that has successfully employed vertical integration strategies. The tech giant has direct control over various stages of its supply chain, from designing and manufacturing its products to distributing and retailing them. By owning the intellectual property and design process, Apple can ensure the seamless integration of hardware and software, creating a unique and cohesive user experience.
Walmart

Walmart, the world's largest retailer, has also embraced vertical integration. The company has expanded its operations by acquiring or establishing partnerships with suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors. By doing so, Walmart can negotiate better prices, ensure a steady supply of products, and maintain a strong presence in the retail market. This strategy has helped Walmart become a dominant force in the industry and maintain its competitive edge.
Tesla, Inc.

Tesla, a leader in the electric vehicle market, has implemented vertical integration to gain control over its supply chain. The company has established its own manufacturing facilities, including battery production and vehicle assembly plants. By owning the production process, Tesla can optimize its supply chain, reduce costs, and ensure the availability of critical components. This strategy has played a crucial role in Tesla's success and its ability to offer innovative products to the market.
Steps to Implement Vertical Integration
Implementing vertical integration requires careful planning and a strategic approach. Here are some key steps to consider when embarking on a vertical integration strategy:
- Conduct a thorough analysis of your current supply chain and identify areas where integration can bring the most value.
- Assess your financial capabilities and determine the level of investment required for vertical integration.
- Evaluate the potential risks and challenges associated with integrating specific stages of the supply chain.
- Develop a comprehensive plan outlining the steps, timeline, and resources needed for successful integration.
- Communicate your vision and strategy to all stakeholders, ensuring buy-in and alignment.
- Implement effective supply chain management practices to optimize coordination and efficiency.
- Continuously monitor and evaluate the performance of your integrated supply chain to identify areas for improvement.
 Note: Vertical integration is a complex strategy that requires careful consideration and planning. It is essential to conduct a thorough analysis of your business, market dynamics, and financial capabilities before committing to this approach.
Note: Vertical integration is a complex strategy that requires careful consideration and planning. It is essential to conduct a thorough analysis of your business, market dynamics, and financial capabilities before committing to this approach.
Best Practices for Vertical Integration

To maximize the benefits of vertical integration, it is crucial to follow certain best practices. These practices can help ensure a successful and sustainable integration strategy:
- Focus on integrating stages of the supply chain that align with your core competencies and provide the most value.
- Foster collaboration and open communication between different departments and stages of the supply chain.
- Implement robust supply chain management systems and technologies to enhance coordination and efficiency.
- Regularly review and optimize your supply chain processes to identify and address inefficiencies.
- Stay agile and adaptable, especially in response to market changes and customer demands.
- Continuously monitor industry trends and competitor strategies to stay ahead of the curve.
Conclusion

Vertical integration is a powerful strategy that can transform a company's operations and market position. By expanding its control over the supply chain, businesses can unlock numerous benefits, including cost reduction, improved efficiency, and increased market power. However, it is essential to carefully consider the challenges and risks associated with vertical integration and develop a well-thought-out plan. With the right approach and best practices, vertical integration can be a successful strategy for businesses aiming to thrive in today's competitive landscape.
What are the key benefits of vertical integration?
+Vertical integration offers several advantages, including cost reduction, improved efficiency, enhanced quality control, and increased market power. By integrating various stages of the supply chain, companies can optimize their operations, reduce intermediary costs, and gain greater control over their production and distribution processes.
Is vertical integration suitable for all businesses?
+Vertical integration may not be suitable for all businesses, especially those with limited financial resources or a lack of expertise in managing complex supply chains. It requires a significant upfront investment and effective management of multiple stages of the supply chain. Companies should carefully assess their capabilities and market dynamics before committing to vertical integration.
What are some potential challenges of vertical integration?
+Vertical integration can present several challenges, including high initial investment, complex management, and a potential loss of flexibility. Companies must be prepared to manage the increased complexity, coordinate various stages of the supply chain effectively, and maintain agility in response to market changes.
How can companies ensure successful vertical integration?
+To ensure successful vertical integration, companies should conduct a thorough analysis of their supply chain, assess their financial capabilities, and develop a comprehensive plan. Effective communication, collaboration, and the implementation of robust supply chain management practices are also crucial. Regular monitoring and evaluation of the integrated supply chain are essential to identify and address any issues.
Are there any risks associated with vertical integration?
+Yes, vertical integration carries certain risks, such as increased exposure to market fluctuations, potential disruptions in the supply chain, and a higher likelihood of being affected by economic downturns. Companies must carefully consider these risks and develop strategies to mitigate them, such as diversifying their supply sources and maintaining a strong financial position.