In a world where professions vary greatly, some jobs stand out for their inherent risks and challenges. Today, we delve into the realm of the most dangerous occupations, shedding light on the brave individuals who dedicate their lives to these demanding careers. From the heights of construction sites to the depths of the ocean, these workers face unique dangers every day. Join us as we explore the top 5 most dangerous occupations, uncovering the perils and resilience of those who dare to take on these vital roles.
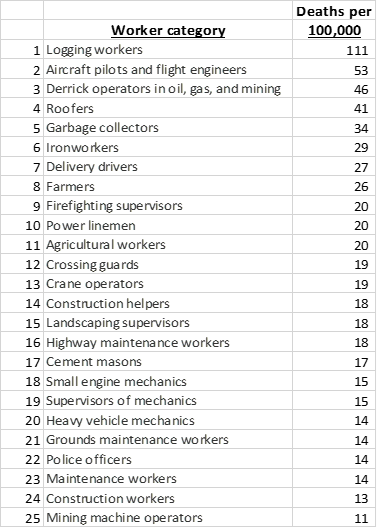
1. Logging Workers

Logging workers, often referred to as lumberjacks or loggers, operate in one of the most hazardous professions. Their job involves felling, trimming, and transporting trees, which requires a high level of skill and physical strength. The nature of their work exposes them to various dangers, making it one of the riskiest occupations globally.
Dangers and Risks

- Tree Felling Accidents: One of the most common and severe risks is the potential for trees to fall unexpectedly or in the wrong direction, leading to serious injuries or fatalities.
- Chain Saw Injuries: Chain saws are essential tools for loggers, but they also pose a significant threat. Accidents with these powerful machines can result in severe cuts, lacerations, and even amputations.
- Weather Conditions: Logging often takes place in remote and rugged terrain, where unpredictable weather can be a major hazard. Heavy rain, strong winds, and lightning storms can make working conditions extremely dangerous.
- Transportation Accidents: Moving logs and equipment requires the use of heavy machinery and vehicles. Accidents during transportation can lead to catastrophic injuries or property damage.
- Insect and Animal Encounters: Loggers work in natural environments, which means they may encounter venomous insects, snakes, or even bears. These encounters can pose serious health risks and require quick thinking and preparedness.
Safety Measures and Training

Given the inherent dangers of the profession, logging workers undergo extensive training and safety protocols. Here are some key safety measures implemented in the logging industry:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Loggers are required to wear appropriate PPE, including hard hats, eye and face protection, hearing protection, and steel-toed boots. This equipment helps minimize the risk of injuries.
- Chain Saw Safety: Proper training in the use and maintenance of chain saws is essential. Loggers learn techniques to minimize the risk of accidents, such as maintaining a firm grip, using the correct cutting techniques, and regularly inspecting and sharpening the saw.
- Weather Monitoring: Logging operations are often closely monitored for weather conditions. When severe weather is predicted, work may be postponed or adjusted to ensure the safety of workers.
- Vehicle and Machinery Safety: Rigorous training is provided for operating heavy machinery and vehicles. Workers learn to inspect equipment regularly, follow safety protocols, and respond appropriately in case of emergencies.
- First Aid and Emergency Response: Loggers are trained in basic first aid and emergency response procedures. This training equips them to handle injuries or accidents until professional medical help arrives.
2. Fishers and Related Fishing Workers

Fishers and related fishing workers brave the unpredictable and often treacherous waters to bring us the seafood we enjoy. Their work involves navigating the open sea, braving harsh weather conditions, and dealing with the challenges of catching and processing fish.
Dangers and Risks

- Weather and Sea Conditions: Fishing is highly dependent on weather conditions. Unexpected storms, high waves, and strong winds can make the sea extremely dangerous, increasing the risk of capsizing or being stranded at sea.
- Equipment Malfunctions: Fishing gear, including nets, lines, and engines, can malfunction or break down. This can lead to accidents, entanglement, or equipment failure, posing significant risks to the crew.
- Falls and Injuries: The deck of a fishing vessel can be slippery and hazardous, especially in rough seas. Slips, trips, and falls are common, leading to injuries or even fatalities.
- Hypothermia and Cold Stress: Working in cold waters or during winter months can expose fishers to extreme cold. Prolonged exposure to cold water or air can result in hypothermia, a potentially life-threatening condition.
- Wildlife Encounters: The open sea is home to various marine life, including sharks, whales, and other large predators. Encounters with these creatures can be dangerous and require quick thinking and evasive maneuvers.
Safety Measures and Training

To mitigate the risks associated with fishing, fishers and related workers undergo specialized training and follow strict safety protocols:
- Safety Equipment: Fishers are required to wear personal flotation devices (PFDs) and other safety gear, such as immersion suits and exposure suits, to protect against cold water and potential immersion.
- Vessel Safety: Fishing vessels must meet specific safety standards, including having emergency equipment, such as lifeboats, life rafts, and distress signals, readily available.
- Weather Monitoring: Fishers closely monitor weather forecasts and sea conditions before heading out. They may postpone trips or adjust their plans based on the predicted weather.
- Safety Drills : Regular safety drills and training sessions are conducted to ensure that the crew is prepared for emergencies, such as man overboard situations, fires, or vessel damage.
- First Aid and Medical Training: Fishers receive training in basic first aid and CPR. They may also have access to advanced medical equipment and training to handle serious injuries or medical emergencies at sea.
3. Aircraft Pilots and Flight Engineers

Aircraft pilots and flight engineers are responsible for the safe operation of airplanes and helicopters. Their job involves navigating through the skies, managing complex machinery, and ensuring the comfort and safety of passengers and crew.
Dangers and Risks

- Weather Conditions: Pilots must contend with various weather conditions, including turbulence, strong winds, and poor visibility. These factors can make flying challenging and increase the risk of accidents.
- Mechanical Failures: Like any complex machinery, aircraft can experience mechanical failures. Engine malfunctions, system failures, or issues with navigation equipment can lead to emergencies during flight.
- Mid-Air Collisions: Although rare, mid-air collisions can occur, especially in busy airspace or during low-visibility conditions. Pilots must be highly vigilant and skilled to avoid such incidents.
- Emergency Landings: In the event of an emergency, pilots must make quick decisions and execute emergency landings. This requires exceptional skill and composure under pressure.
- Fatigue and Stress: Long hours, irregular schedules, and the high-pressure nature of the job can lead to fatigue and stress, which can affect a pilot’s performance and decision-making abilities.
Safety Measures and Training

The aviation industry has rigorous safety standards and training programs to ensure the safety of pilots, crew, and passengers:
- Aircraft Maintenance: Regular and thorough maintenance checks are conducted on aircraft to identify and address any potential issues before they become major problems.
- Flight Training: Pilots undergo extensive training, including flight simulators and practical flying experience, to develop their skills and knowledge. They are trained to handle various emergency scenarios and make quick, accurate decisions.
- Weather Briefings: Before every flight, pilots receive detailed weather briefings to assess the conditions along their route. This information helps them make informed decisions about flight paths and altitudes.
- Crew Resource Management (CRM): CRM training focuses on effective communication, teamwork, and decision-making within the cockpit. It helps pilots and crew members work together seamlessly during normal operations and emergencies.
- Emergency Response Training: Pilots and flight engineers receive specialized training in emergency response procedures, including fire fighting, evacuation protocols, and first aid.
4. Roofers

Roofers play a vital role in the construction industry, working at great heights to install, repair, and maintain roofs on various structures. Their job demands physical strength, balance, and a keen eye for detail.
Dangers and Risks

- Falls: One of the most significant risks roofers face is the potential for falls. Working at heights, often on uneven or slippery surfaces, increases the likelihood of accidents and serious injuries.
- Heat Stress: Roofers often work in hot and humid conditions, especially during the summer months. Prolonged exposure to heat can lead to heat exhaustion, heat stroke, or other heat-related illnesses.
- Electrocution: When working on roofs, roofers may encounter electrical wires or equipment. Accidental contact with live wires can result in severe injuries or fatalities.
- Sharp Tools and Equipment: Roofers use various tools and equipment, such as roofing nails, hammers, and saws. Mishandling or improper use of these tools can lead to cuts, punctures, or other injuries.
- Weather Conditions: Roofing work is often affected by weather conditions. Heavy rain, strong winds, or lightning can make working conditions unsafe and increase the risk of accidents.
Safety Measures and Training

To minimize the risks associated with roofing, roofers undergo specialized training and follow strict safety protocols:
- Fall Protection: Roofers are required to use fall protection systems, such as safety harnesses and guardrails, to prevent falls from heights. Regular inspections and maintenance of these systems are crucial.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Roofers must wear appropriate PPE, including hard hats, eye and face protection, non-slip footwear, and gloves. This equipment helps protect against injuries caused by falls, sharp objects, and extreme weather conditions.
- Electrical Safety: Roofers receive training on electrical safety, including how to identify and avoid electrical hazards. They learn to work safely around power lines and electrical equipment.
- Weather Monitoring: Roofing operations are closely monitored for weather conditions. Work may be postponed or adjusted based on forecasts to ensure the safety of workers.
- First Aid and Emergency Response: Roofers are trained in basic first aid and emergency response procedures. They are equipped to handle injuries or accidents until professional medical help arrives.
5. Refuse and Recyclable Material Collectors

Refuse and recyclable material collectors, often referred to as garbage collectors or sanitation workers, play a crucial role in keeping our communities clean and hygienic. Their job involves collecting and transporting waste materials, which can be physically demanding and expose them to various hazards.
Dangers and Risks

- Traffic Accidents: Refuse collectors often work near moving vehicles, making them vulnerable to traffic accidents. Being struck by a vehicle or getting caught in the path of a moving truck can lead to serious injuries or fatalities.
- Heavy Lifting: The nature of their work requires refuse collectors to lift and carry heavy loads of waste materials. This repetitive physical strain can result in muscle strains, back injuries, or other musculoskeletal disorders.
- Sharp Objects and Hazards: Waste materials can contain sharp objects, broken glass, or other hazardous items. Accidental contact with these objects can cause cuts, punctures, or other injuries.
- Infectious Diseases: Refuse collectors are at risk of exposure to various pathogens and infectious diseases. Handling waste materials can lead to the transmission of bacteria, viruses, or other harmful substances.
- Weather Conditions: Refuse collection work is often performed outdoors, exposing workers to extreme weather conditions. Heat stress, cold stress, and exposure to harsh weather can impact their health and safety.
Safety Measures and Training

To ensure the safety of refuse and recyclable material collectors, comprehensive training and safety protocols are implemented:
- Vehicle Safety: Refuse collection vehicles are equipped with safety features, such as backup cameras and warning systems, to minimize the risk of accidents. Workers are trained to use these features effectively.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Refuse collectors are required to wear appropriate PPE, including gloves, eye protection, and high-visibility clothing. This equipment helps protect against cuts, punctures, and exposure to harmful substances.
- Infectious Disease Control: Workers receive training on proper waste handling and disposal procedures to minimize the risk of exposure to infectious diseases. They are also educated on the importance of personal hygiene and handwashing.
- Weather Monitoring: Refuse collection operations are monitored for weather conditions. Work may be postponed or adjusted based on forecasts to ensure the safety of workers.
- First Aid and Emergency Response: Refuse collectors are trained in basic first aid and emergency response procedures. They are equipped to handle injuries or accidents until professional medical help arrives.
Conclusion
Exploring the most dangerous occupations has given us a glimpse into the bravery and resilience of individuals who dedicate their lives to these demanding professions. From logging workers braving the dangers of the forest to fishers navigating the unpredictable seas, each occupation comes with its unique set of challenges and risks. These workers play vital roles in our society, and their dedication deserves recognition and respect. As we acknowledge their contributions, let us also advocate for continued improvements in safety measures and training to ensure their well-being and protect those who put themselves in harm’s way for our benefit.
Frequently Asked Questions

What are the key safety measures implemented in logging operations?
+Logging operations prioritize safety through various measures, including mandatory personal protective equipment (PPE), comprehensive chain saw safety training, weather monitoring, and strict protocols for vehicle and machinery operation.
How do fishers stay safe in harsh weather conditions at sea?
+Fishers rely on advanced weather monitoring systems, safety equipment such as personal flotation devices and immersion suits, regular safety drills, and comprehensive medical training to handle emergencies at sea.
What training do pilots undergo to ensure safe flights?
+Pilots undergo extensive flight training, including simulator sessions and practical flying experience. They receive weather briefings, crew resource management (CRM) training, and emergency response training to handle various in-flight scenarios.
How do roofers prevent falls from heights?
+Roofers use fall protection systems, such as safety harnesses and guardrails, to prevent falls. Regular inspections and maintenance of these systems are crucial, along with the use of appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) to protect against other hazards.
What safety protocols are in place for refuse collectors to handle hazardous waste materials?
+Refuse collectors are trained in proper waste handling and disposal procedures. They wear personal protective equipment (PPE) to protect against sharp objects and infectious diseases. Additionally, vehicles are equipped with safety features, and workers receive first aid and emergency response training.