Unveiling the Secrets of Image Orientation in Radiography
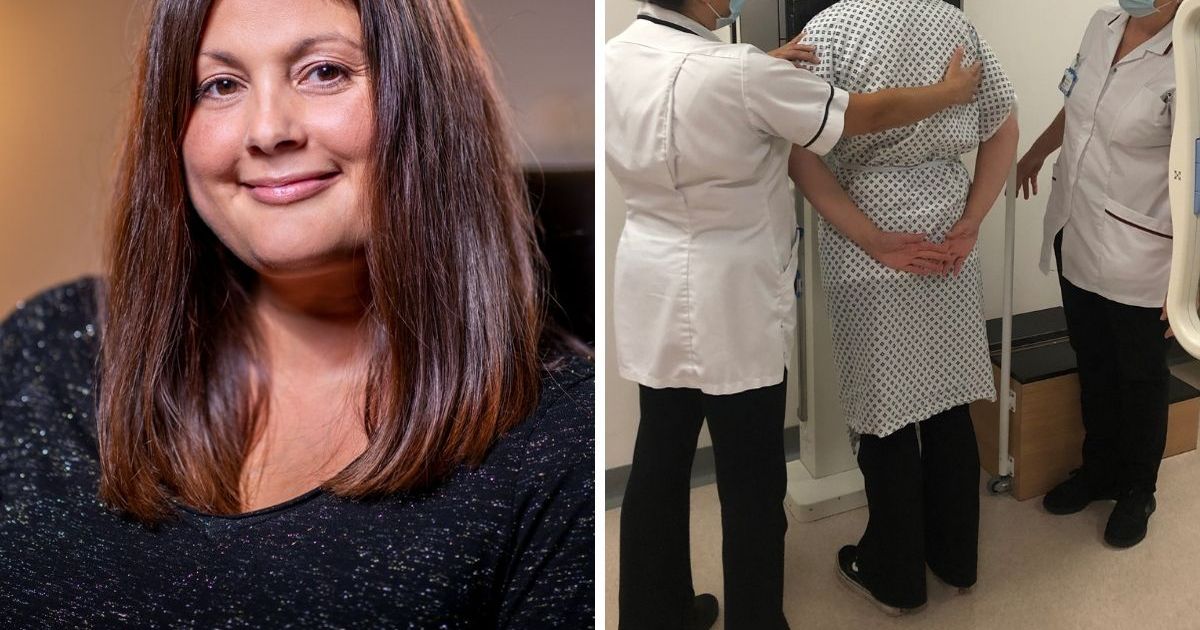

Radiography, a vital tool in modern medicine, relies heavily on precise image orientation to ensure accurate diagnoses and effective treatment planning. The correct positioning of patients and the alignment of radiographic equipment are crucial steps in this process. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of image orientation in radiography, exploring its importance, techniques, and best practices. By the end, you’ll have a deeper understanding of this critical aspect of medical imaging.
Understanding Image Orientation

Image orientation refers to the proper positioning of a patient’s body and the alignment of the radiographic equipment to capture clear and diagnostic-quality images. It involves aligning the body part of interest with the central ray of the X-ray beam, ensuring that the image produced provides the necessary information for diagnosis and treatment.
Why is Image Orientation Important?
Accurate image orientation is fundamental in radiography for several reasons:
- Diagnostic Accuracy: Proper orientation ensures that the radiologist can obtain clear and detailed images, leading to accurate diagnoses.
- Patient Safety: Incorrect orientation can result in overexposure to radiation, increasing the risk of adverse effects.
- Treatment Planning: Precise images are crucial for planning effective treatment strategies, especially in procedures like radiation therapy.
- Research and Education: Well-oriented images contribute to medical research and are essential for teaching purposes.
Techniques for Achieving Optimal Image Orientation

Achieving optimal image orientation requires a combination of technical skills and an understanding of human anatomy. Here are some key techniques and considerations:
1. Patient Positioning
- Supine Position: Patients lie on their back, with the body part of interest in a neutral position. This is a common position for many radiographic examinations.
- Prone Position: Lying face down, often used for spine and abdominal imaging.
- Lateral Position: Lying on the side, useful for imaging the chest, abdomen, and some skeletal structures.
- Oblique Position: A diagonal position, beneficial for certain skeletal and soft tissue examinations.
2. Alignment with the Central Ray
- Central Ray Path: Ensure the central ray of the X-ray beam passes through the body part of interest. This can be achieved by adjusting the patient’s position and the angle of the X-ray tube.
- Collimation: Use collimation to narrow the X-ray beam, focusing it on the specific area of interest and reducing scatter radiation.
3. Radiographic Equipment Setup
- X-ray Tube Angle: Adjust the angle of the X-ray tube to align with the body part being imaged.
- Image Receptor: Position the image receptor (film or digital detector) correctly to capture the image.
- Grids: Use grids to reduce scatter radiation and improve image quality, especially for thick body parts.
4. Communication and Collaboration
- Radiographer-Patient Communication: Clear communication with the patient is essential to ensure comfort and accurate positioning.
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Radiographers often work with physicians, nurses, and other healthcare professionals to ensure the best possible image orientation.
Best Practices for Image Orientation

To achieve consistent and high-quality image orientation, consider the following best practices:
- Standardized Protocols: Develop and follow standardized protocols for different types of radiographic examinations.
- Training and Education: Ensure that radiographers receive comprehensive training on image orientation techniques.
- Quality Assurance: Regularly review and assess the quality of images to identify areas for improvement.
- Patient Comfort: Prioritize patient comfort and safety during the imaging process.
- Documentation: Maintain detailed records of image orientation and patient positioning for future reference.
Advanced Techniques and Considerations
In addition to the fundamental techniques, there are advanced methods and considerations to enhance image orientation:
- 3D Imaging: Three-dimensional imaging techniques, such as computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), offer advanced visualization and orientation capabilities.
- Digital Imaging: Digital radiography provides flexibility in image manipulation and allows for post-processing to enhance image quality.
- Contrast Media: The use of contrast media can enhance the visibility of certain structures, aiding in accurate image orientation.
- Specialized Techniques: Certain procedures, like angiography and fluoroscopy, require specialized image orientation techniques.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications
Let’s explore some real-world scenarios where image orientation plays a crucial role:
Case Study 1: Chest Radiography
Scenario: A patient presents with symptoms of pneumonia.
Image Orientation: - Patient is positioned supine with the chest exposed. - The central ray is directed through the chest, capturing both lungs and the heart. - Collimation is used to reduce scatter radiation and focus on the chest area.
Case Study 2: Orthopedic Imaging
Scenario: A patient sustains a suspected fracture in their arm.
Image Orientation: - The patient is positioned with the affected arm in a neutral position. - The central ray is aligned with the suspected fracture site. - Grids are used to reduce scatter radiation and enhance image quality.
Notes:

🧠 Note: Image orientation is a critical skill for radiographers and requires a deep understanding of human anatomy and radiographic techniques.
💡 Tip: Practice and experience are key to mastering image orientation. Stay updated with the latest advancements in medical imaging technology.
Conclusion:

Image orientation is a cornerstone of radiography, playing a vital role in ensuring accurate diagnoses and effective treatment planning. By mastering the techniques and best practices outlined in this guide, radiographers can consistently produce high-quality images, contributing to better patient care and outcomes. Remember, precise image orientation is a skill that requires dedication and continuous learning.
FAQ

What is the central ray in radiography, and why is it important for image orientation?

+
The central ray is the primary beam of X-rays emitted from the X-ray tube. Aligning the central ray with the body part of interest is crucial for obtaining clear and diagnostic-quality images. It ensures that the X-rays pass through the area of interest, producing an accurate representation of the internal structures.
How can digital radiography enhance image orientation?

+
Digital radiography offers several advantages for image orientation. It allows for real-time adjustments, providing immediate feedback on image quality. Radiographers can manipulate images, adjust contrast, and enhance specific areas, ensuring optimal visualization of the body part being examined.
What are some common challenges in achieving optimal image orientation?
+Challenges in image orientation can arise due to patient factors (e.g., obesity, injuries), equipment limitations, and complex anatomical structures. Additionally, ensuring patient comfort and cooperation can be a challenge, especially in pediatric or geriatric patients.
How can radiographers ensure patient comfort during image orientation?
+Radiographers can prioritize patient comfort by providing clear instructions, ensuring proper padding and support, and offering reassurance throughout the procedure. Maintaining open communication and addressing any concerns can help create a positive imaging experience.
What role does collimation play in image orientation?
+Collimation is a crucial technique in image orientation. It involves narrowing the X-ray beam to focus on the specific area of interest. By reducing scatter radiation and limiting the beam to the necessary field of view, collimation enhances image quality and reduces the patient’s radiation exposure.