A Census Designated Place (CDP) is a statistical entity defined by the United States Census Bureau for the purpose of compiling and presenting statistical data. It refers to a concentrated population area that lacks a separate municipal government but is recognized for its distinct characteristics and boundaries.
CDPs are designated by the Census Bureau in cooperation with state and local officials, ensuring that they represent meaningful entities within a county or equivalent entity. These places can include small towns, suburbs, neighborhoods, or even resort areas, as long as they meet the criteria for being a distinct community.
Criteria for a Census Designated Place

To be classified as a CDP, an area must meet the following criteria:
- A minimum population of 2,500 people, although some areas with populations as low as 1,000 may be considered if they meet other criteria.
- A discernible concentration of population, typically in the form of a community with its own name.
- A degree of social and economic integration, such as shared services or a common interest.
- Clearly defined boundaries, which may be natural features, roads, or other landmarks.
- Recognition by local residents as a distinct community.
It's important to note that CDPs are not legally incorporated municipalities and do not have their own local government. They are designated solely for the purpose of collecting and presenting statistical data, providing a more detailed representation of the population and its characteristics.
Advantages of Census Designated Places

CDPs offer several advantages for data analysis and community understanding:
- They provide a more detailed and accurate picture of population distribution and characteristics, especially in areas with dispersed populations.
- CDPs allow for the collection of data on areas that may not have their own municipal government, ensuring that these communities are not overlooked in statistical analyses.
- The designation of CDPs helps in identifying and addressing the needs of specific communities, especially those that may be underserved or have unique characteristics.
- CDPs can also serve as a basis for the creation of new municipalities or the expansion of existing ones, as they provide a clear definition of a community's boundaries and population.
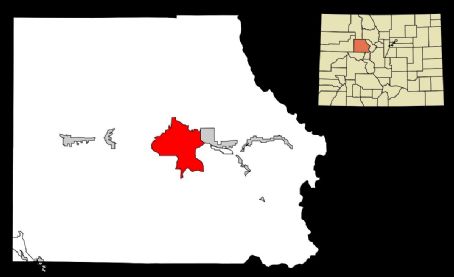
For example, a CDP might encompass a small town that, while not legally incorporated, has its own post office, school district, and community organizations. By recognizing this area as a CDP, the Census Bureau can provide data on the population, housing, and economic characteristics of this distinct community.
Comparison with Other Statistical Entities
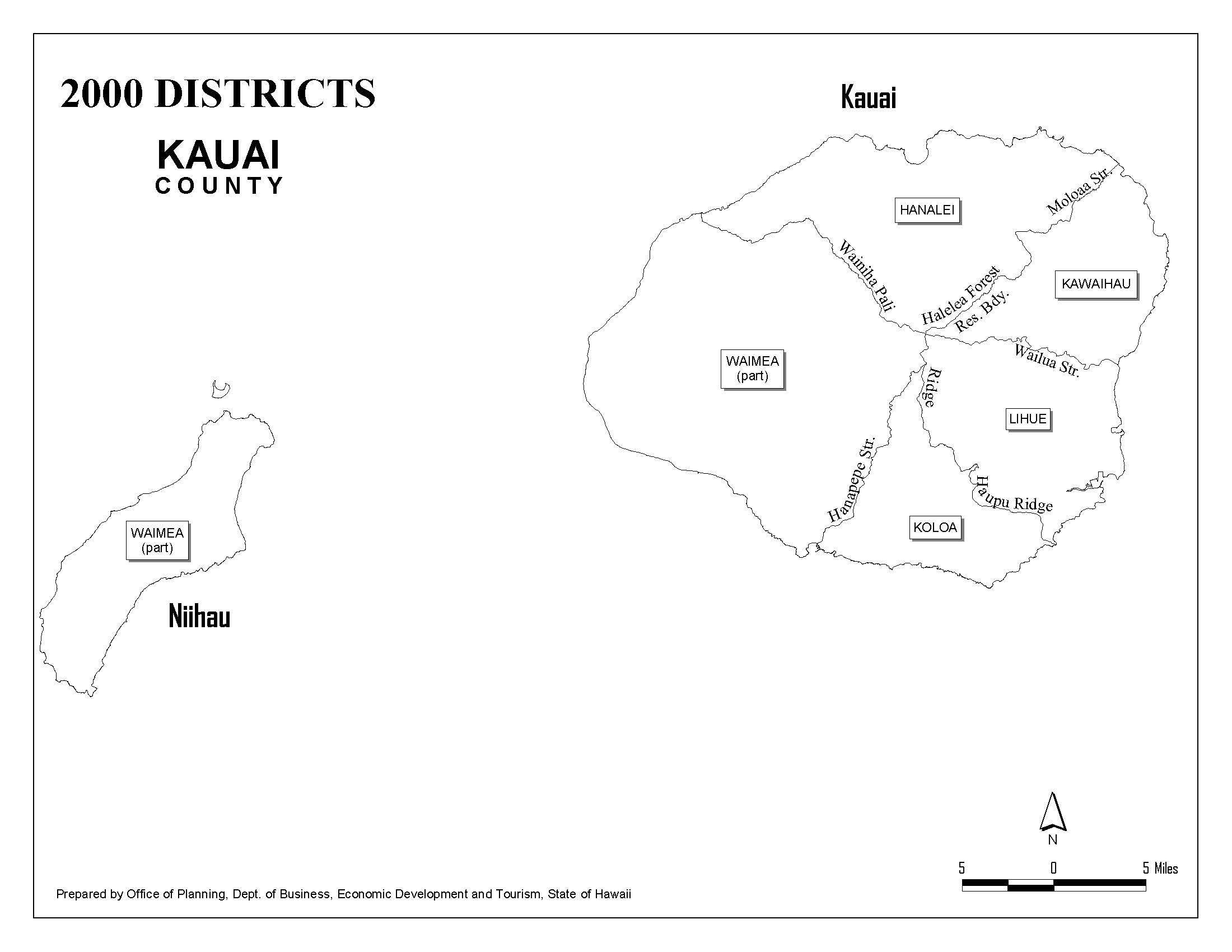
CDPs are distinct from other statistical entities defined by the Census Bureau, such as Incorporated Places and Minor Civil Divisions (MCDs). Incorporated Places are legally incorporated municipalities, while MCDs are the primary divisions of a county, such as townships or villages.
CDPs, on the other hand, are designated to represent communities that may not have their own municipal government but still have distinct characteristics and boundaries. They are especially useful in areas with dispersed populations or where the boundaries of legal municipalities do not align with the actual settlement patterns.
For instance, a CDP might be designated for a suburban neighborhood that, while not legally incorporated, has its own shopping center, schools, and community associations. This CDP would provide valuable data on the population and characteristics of this specific neighborhood, which might not be captured by the data for the larger municipality it is technically a part of.
Data Collection and Presentation
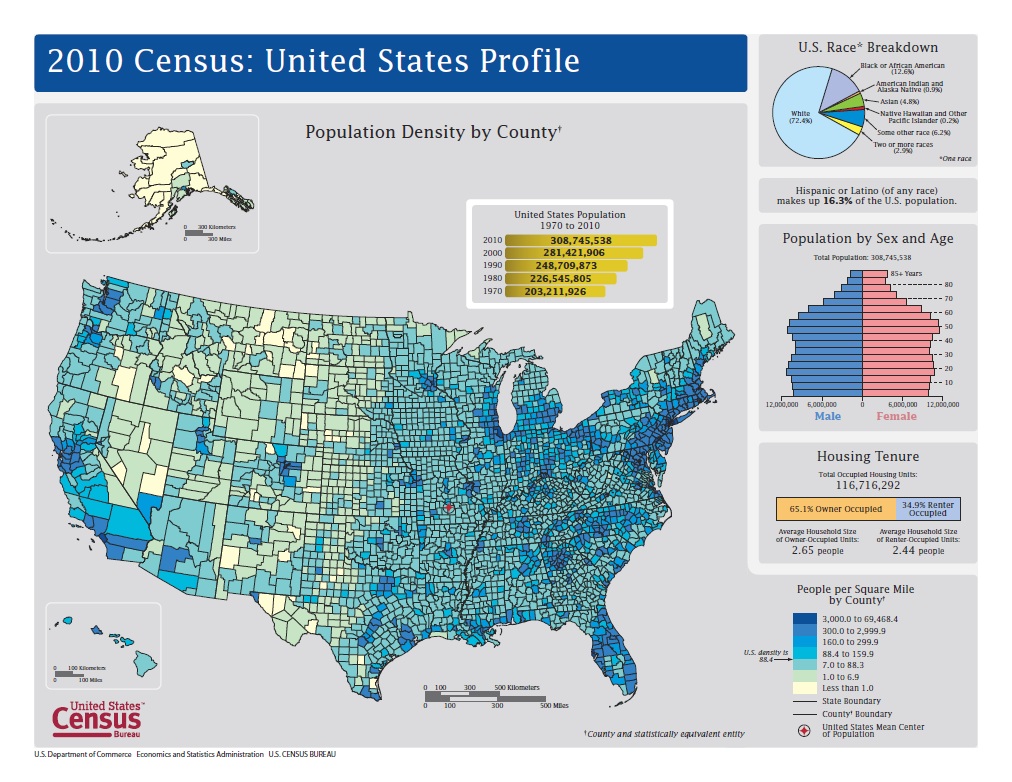
The Census Bureau collects data on CDPs through the decennial census and other surveys. This data includes information on population, housing, demographics, and economic characteristics. The bureau then presents this data in a way that allows for easy comparison and analysis, often using tables, maps, and other visual representations.
For example, the Census Bureau might create a table comparing the population and housing characteristics of different CDPs within a county. This table would provide a snapshot of the diversity and uniqueness of these communities, allowing for a better understanding of the county's overall population and its various components.
📍 Note: It's important to note that the specific criteria and procedures for designating CDPs may vary from state to state, as the Census Bureau works with local officials to define these areas.
Conclusion and Further Reading
Census Designated Places (CDPs) are an essential tool for understanding the diverse population and settlement patterns within the United States. By recognizing and defining these distinct communities, the Census Bureau provides valuable data that can inform policy decisions, community development, and a deeper understanding of our nation's demographics.
For further reading on CDPs and related topics, you can explore the official U.S. Census Bureau website, which offers a wealth of information, data, and resources on various statistical entities and their designations.
What is the purpose of Census Designated Places (CDPs)?

+
CDPs are designated to provide a more detailed representation of population and its characteristics, especially in areas without a separate municipal government. They help in understanding the unique communities within a county or equivalent entity.
How are CDPs different from Incorporated Places and Minor Civil Divisions (MCDs)?

+
Incorporated Places are legally incorporated municipalities, while MCDs are the primary divisions of a county. CDPs, on the other hand, represent communities that may not have their own municipal government but still have distinct characteristics and boundaries.
What are the criteria for a CDP designation?

+
CDPs must have a minimum population of 2,500 people (although some with populations as low as 1,000 may be considered), a discernible concentration of population, a degree of social and economic integration, clearly defined boundaries, and recognition by local residents as a distinct community.
How does the Census Bureau collect and present data on CDPs?
+
The Census Bureau collects data on CDPs through the decennial census and other surveys, including information on population, housing, demographics, and economic characteristics. This data is then presented in tables, maps, and other visual representations for easy analysis and comparison.