Understanding the Relationship between Metformin and GLP-1

Metformin and GLP-1 are two key players in the management of diabetes and metabolic disorders, and their connection is an intriguing aspect of modern medicine. This comprehensive guide aims to unravel the complex relationship between these two entities, providing an in-depth understanding of their individual roles and their potential synergy.
Metformin: A Widely-Prescribed Diabetes Medication
Metformin, a biguanide class drug, has been a cornerstone in diabetes treatment for decades. It is primarily used to manage type 2 diabetes, helping to control blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. This medication works by reducing glucose production in the liver and enhancing the body’s response to insulin. Its effectiveness and relatively low risk of side effects have made it a go-to treatment for many healthcare professionals.
GLP-1: A Powerful Hormone in Glucose Regulation

GLP-1, or Glucagon-Like Peptide-1, is a hormone produced by the intestine in response to food intake. It plays a crucial role in glucose homeostasis by stimulating insulin secretion and inhibiting glucagon release. GLP-1 also slows down the rate at which food leaves the stomach, leading to a feeling of fullness and potentially aiding in weight loss. This hormone’s impact on glucose regulation has made it a target for diabetes medication development.
The Metformin-GLP-1 Connection
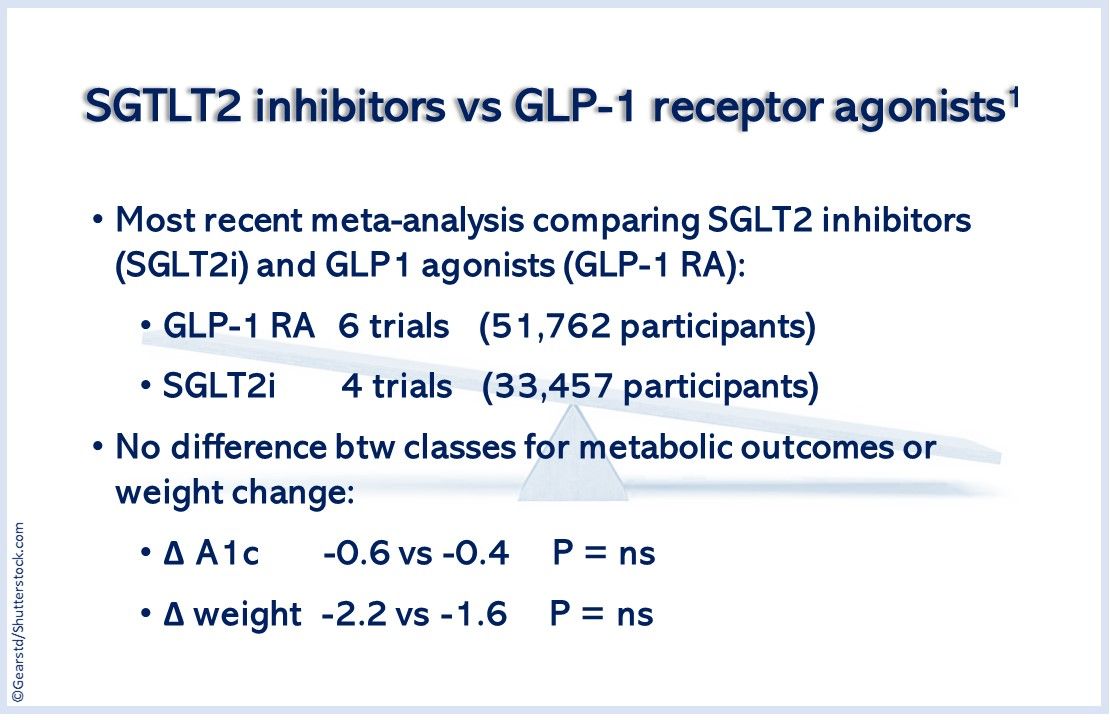
The relationship between Metformin and GLP-1 is an area of active research, as understanding their interaction could lead to more effective diabetes management strategies. Here’s a deeper look:
Metformin’s Impact on GLP-1
Studies suggest that Metformin may enhance the effects of GLP-1. It appears to increase GLP-1 secretion and improve its action on insulin-producing cells, potentially leading to better glucose control. This synergy could be particularly beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes, as it may offer a dual approach to managing the disease.
GLP-1’s Influence on Metformin
Conversely, GLP-1 may also impact Metformin’s effectiveness. Some research indicates that GLP-1 can enhance the insulin-sensitizing effects of Metformin, further improving glucose control. This interplay highlights the potential for a combined treatment approach, utilizing the strengths of both Metformin and GLP-1-based therapies.
Clinical Applications

The Metformin-GLP-1 connection has led to the development of combination therapies, offering a more comprehensive approach to diabetes management. These therapies aim to leverage the benefits of both medications, providing better glucose control and potentially reducing the risk of diabetes-related complications.
Potential Benefits of Combined Therapy
- Improved Glucose Control: By combining Metformin and GLP-1-based therapies, individuals may experience better control over their blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of hyperglycemia.
- Weight Management: GLP-1’s ability to promote a feeling of fullness, combined with Metformin’s potential impact on weight, could lead to effective weight management strategies.
- Reduced Risk of Complications: Better glucose control and weight management can potentially lower the risk of diabetes-related complications, such as heart disease and kidney damage.
Important Notes:

- Consult Your Healthcare Provider: Before starting any new medication or combination therapy, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional. They can provide personalized advice based on your medical history and current health status.
- Potential Side Effects: While Metformin and GLP-1-based therapies are generally well-tolerated, they can have side effects. It’s important to be aware of these and discuss them with your doctor.
- Individual Variability: The response to these medications can vary from person to person. What works for one individual may not have the same effect on another, so personalized treatment plans are essential.
Conclusion

The relationship between Metformin and GLP-1 is a fascinating aspect of diabetes management, offering a potential dual approach to controlling blood sugar levels. While more research is needed to fully understand their synergy, the current evidence suggests a promising future for combined therapy. As always, it is crucial to approach these treatments with guidance from healthcare professionals to ensure the best possible outcomes.
FAQ

Can Metformin and GLP-1 be used together for diabetes management?

+
Yes, the potential synergy between Metformin and GLP-1 has led to the development of combination therapies. These therapies aim to leverage the benefits of both medications, offering improved glucose control and potential weight management benefits.
What are the potential side effects of Metformin and GLP-1-based therapies?

+
While generally well-tolerated, Metformin and GLP-1-based therapies can have side effects. Common side effects of Metformin include gastrointestinal issues like nausea and diarrhea. GLP-1-based therapies may cause nausea, vomiting, and headaches. It’s important to discuss potential side effects with your healthcare provider.
How effective is the combination of Metformin and GLP-1 in diabetes management?

+
The combination of Metformin and GLP-1-based therapies has shown promising results in improving glucose control and managing weight in individuals with type 2 diabetes. However, the effectiveness can vary depending on individual factors, so personalized treatment plans are crucial.
Are there any precautions to consider when taking Metformin and GLP-1-based therapies together?

+
Yes, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new medication or combination therapy. They can provide guidance based on your medical history and current health status. Additionally, regular monitoring of blood sugar levels and kidney function is recommended when taking these medications together.
Can Metformin and GLP-1-based therapies be used as a first-line treatment for diabetes?
+The decision to use Metformin and GLP-1-based therapies as a first-line treatment for diabetes depends on various factors, including the severity of the disease, individual health status, and potential side effects. It’s important to discuss these options with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.