Soil compaction is a critical aspect of urbanization and construction, often overlooked but crucial for the stability and longevity of structures. This process, when done correctly, ensures the soil can support the weight of buildings, roads, and other infrastructure. In this blog post, we will delve into the intricacies of soil compaction, its impact on urbanization, and the best practices to ensure optimal results.
Understanding Soil Compaction

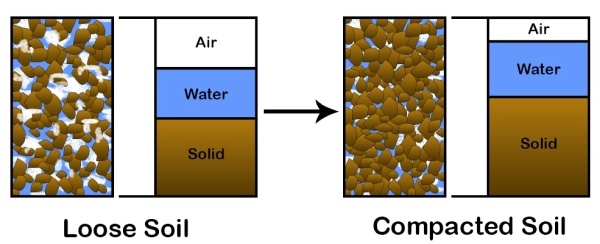
Soil compaction is the method of mechanically increasing the density of soil. This is achieved by reducing the air voids between soil particles, leading to an increase in soil strength and a decrease in its volume. The process involves the application of mechanical force, typically through the use of specialized equipment like rollers or compactors, to compress the soil.
The goal of soil compaction is to improve the engineering properties of the soil, making it more suitable for construction purposes. Compacted soil is less likely to settle or shift, which is crucial for the stability of buildings and infrastructure. It also helps to prevent issues like soil erosion and waterlogging, which can lead to significant structural damage over time.
The Impact of Soil Compaction on Urbanization

Urbanization relies heavily on the stability and integrity of the soil on which cities are built. Soil compaction plays a pivotal role in ensuring that the soil can support the weight of high-rise buildings, extensive road networks, and other urban infrastructure. Without proper compaction, the soil may not be able to bear the load, leading to structural issues and potential disasters.
In urban areas, soil compaction is particularly important due to the high density of construction and the need for strong, stable foundations. It helps to distribute the weight of structures evenly across the soil, reducing the risk of settlement and ensuring the safety and longevity of the buildings.
Best Practices for Soil Compaction

Achieving optimal soil compaction requires careful planning and execution. Here are some best practices to ensure successful compaction:
- Soil Testing: Before beginning any compaction work, it is essential to conduct thorough soil tests. These tests help determine the soil type, moisture content, and other factors that influence compaction. By understanding the soil characteristics, you can choose the appropriate compaction method and equipment.
- Moisture Control: The moisture content of the soil plays a crucial role in compaction. Dry soil is more difficult to compact, while overly wet soil can lead to uneven compaction and potential issues like soil liquefaction. Maintaining the optimal moisture content is key to achieving effective compaction.
- Gradual Compaction: Soil compaction should be a gradual process. Applying excessive force or compaction in a single pass can lead to over-compaction, which can weaken the soil structure. Instead, multiple passes with varying force and equipment types are recommended to achieve uniform compaction.
- Equipment Selection: Choosing the right compaction equipment is essential. Different types of soil and construction projects may require different equipment. For example, for cohesive soils, vibratory rollers may be more effective, while for granular soils, vibratory plates or pneumatic tire rollers might be better suited.
- Quality Control: Regular quality control checks during the compaction process are vital. This includes visual inspections, density tests, and, if necessary, laboratory testing. These checks ensure that the soil is being compacted to the desired density and that any issues are identified and addressed promptly.
Soil Compaction Techniques

There are several techniques used for soil compaction, each suited to different soil types and construction projects. Here are some of the most common methods:
- Static Compaction: This technique involves applying static pressure to the soil using heavy equipment like vibratory rollers or smooth-wheeled rollers. The equipment is moved slowly over the soil, compressing it uniformly.
- Vibratory Compaction: Vibratory compaction uses equipment with a vibrating base to create rapid oscillations in the soil. This technique is particularly effective for cohesive soils and can help improve the density and stability of the compacted layer.
- Pneumatic Compaction: Pneumatic compaction, also known as air-filled compaction, uses equipment with pneumatic tires. The tires, filled with air, apply pressure to the soil as the equipment moves over it. This method is commonly used for granular soils like sand and gravel.
- Dynamic Compaction: Dynamic compaction is a technique that involves dropping a heavy weight from a certain height onto the soil surface. The impact of the weight creates a shock wave that propagates through the soil, causing it to compact. This method is often used for large-scale projects and deep soil layers.
Case Studies: Successful Soil Compaction Projects

To further illustrate the importance and effectiveness of soil compaction, let's explore a few case studies of successful projects:
The New York City Subway System

The construction of the New York City Subway system in the early 20th century required extensive soil compaction to ensure the stability of the tunnels and stations. The project involved the use of vibratory rollers and other heavy equipment to compact the soil along the subway routes. This meticulous compaction process contributed to the long-term stability and safety of the subway system, which continues to serve millions of passengers daily.
The Great Wall of China

The construction of the Great Wall of China, which began over 2,000 years ago, is another example of the importance of soil compaction. The wall, stretching over 13,000 miles, was built using a combination of rammed earth and stone. The rammed earth sections were created by compacting layers of soil and gravel, providing a strong and durable foundation for the wall. This ancient construction technique, which utilized soil compaction, has withstood the test of time and remains a symbol of China's rich history.
Challenges and Solutions in Soil Compaction

While soil compaction is a critical process, it does come with its own set of challenges. Here are some common issues and potential solutions:
- Soil Type Variability: Different soil types, such as clay, silt, sand, and gravel, have varying compaction characteristics. It is essential to understand the soil type and its specific compaction requirements to ensure effective compaction. Soil testing and proper equipment selection can help overcome this challenge.
- Moisture Management: Maintaining the optimal moisture content in the soil can be challenging, especially in areas with variable weather conditions. Proper moisture control techniques, such as irrigation or the use of moisture-retaining agents, can help ensure that the soil is at the ideal moisture level for compaction.
- Over-Compaction: Applying excessive force or compaction can lead to over-compaction, which can weaken the soil structure and reduce its load-bearing capacity. To prevent over-compaction, it is crucial to follow best practices, conduct regular quality control checks, and adjust the compaction process as needed.
Conclusion

Soil compaction is a critical aspect of urbanization and construction, ensuring the stability and longevity of structures. By understanding the principles of soil compaction, implementing best practices, and utilizing appropriate techniques and equipment, we can create a solid foundation for our urban environments. With careful planning and execution, soil compaction can contribute to the development of safe, durable, and resilient cities.
What is the ideal moisture content for soil compaction?

+
The ideal moisture content for soil compaction depends on the soil type and the specific compaction method being used. In general, a moisture content of around 5-10% above the optimal moisture content (OMC) is considered ideal. However, this can vary, and it is essential to conduct soil tests to determine the specific moisture requirements for your project.
How can I prevent soil liquefaction during compaction?

+
Soil liquefaction can occur when loose, saturated soils are subjected to shaking or other external forces. To prevent liquefaction, it is crucial to compact the soil to a high density, reducing its void ratio and increasing its shear strength. Proper moisture control and the use of suitable compaction equipment can help mitigate the risk of liquefaction.
What are the signs of successful soil compaction?

+
Successful soil compaction is indicated by several factors, including a smooth and level surface, the absence of visible air pockets or soft spots, and consistent density throughout the compacted layer. Regular density tests and visual inspections can help confirm the effectiveness of the compaction process.
Can soil compaction be done in all weather conditions?
+
Soil compaction can be challenging in extreme weather conditions. Excessive heat can lead to rapid moisture loss, while heavy rainfall can make the soil too wet for effective compaction. It is best to avoid compaction during extreme weather and ensure that the soil is at the optimal moisture content for the chosen compaction method.
How can I ensure the long-term stability of compacted soil?

+
To ensure the long-term stability of compacted soil, it is crucial to maintain proper moisture content and avoid overloading the soil. Regular maintenance and monitoring, including visual inspections and density tests, can help identify and address any potential issues before they become major problems.